Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipids
Phospholipids
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are compound lipids containing
phosphoric acid in addition to fatty acid, alcohol and a nitrogenous base.
1. Classification
Phospholipids are classified into two types.
1.
Glycerophospholipids
(or) Phosphoglycerides that contain glycerol as alcohol.
2.
Sphingophospholipids
that contain sphingosine as alcohol.
Glycerophospholipids
These are the major lipids that occur in
biological membranes. They present in all plant and animal cells. They are
abundantly present in heart, brain, kidney, egg yolk and soyabean. The
important glycerophospholipids are lecithin, cephalin, phosphotidyl inositol,
cardiolipin and plasmalogen.
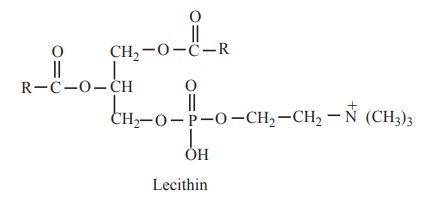
The lecithins contain glycerol, fatty acids,
phosphoric acid and choline (nitrogenous base). Lecithins generally contain a
saturated fatty acid at a1 position and an unsaturated fatty acid at β postition.
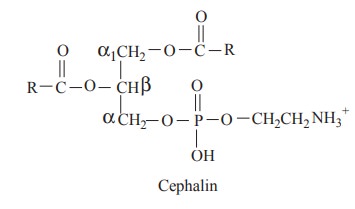
The cephalin contains glycerol, fatty acids,
phosphoric acids and ethanol amine as nitrogenous base.
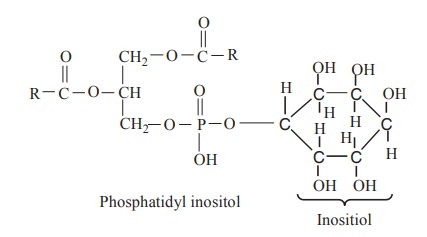
Phosphatidyl inositol contains a hexahydric
alcohol called as inositol.
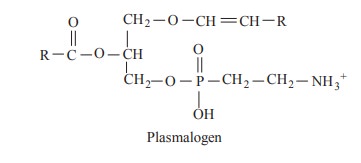
Plasmalogens posses an ether link in a1
position instead of ester link. The alkyl radical is an unsaturated alcohol and
they are found in brain and nervous tissue
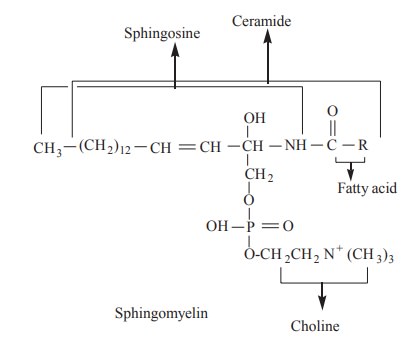
Spingophospholipids
These are present in plasma membrane and myelin
sheath. They are amphipathic lipids having polar head and non-polar tail. They
contain an amino alcohol called shingosine. It is attached to a fatty acid by
an amide linkage to form ceramide. Ceramide is linked to phosphoryl choline to
form sphingomyelin, which is an important member of sphingophospholipids.
2. Properties of glycero phospholipids
·
Glycerophospholipids
are white waxy substances, which become dark when exposed to air and light,
owing to autoxidation and decomposition. This is due to the presence of
unsaturated fatty acids in the molecules.
·
They are
soluble in alcohol and other fat solvents except in acetone.
·
They are
hygroscopic and mix well with water to form cloudy, colloidal and slimy
solutions.
·
They
donot have definite melting point and decompose when heated.
·
They are
readily hydrolysed by boiling with acids and alkalies to their constituents.
·
They are
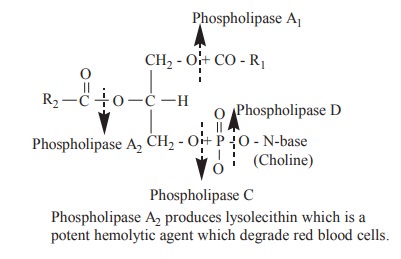
hydrolysed by enzyme phospholipase to various components.
3. Properties of sphingophospholipids
·
They are
white crystalline substances
·
They
form opelescent suspension in water.
·
They are
insoluble in fat solvents like ether and acetone.
·
They are
stable in air and light.
4. Importance of phospholipids
·
They
form the structural components of membrane and regulate membrane permeability.
·
They
play an important role in cellular respiration.
·
They
participate in the absorption of fat from the intestine.
·
They act
as surface tension lowering agent.
·
They are
essential components of bile where they act as detergents and help in the
solubilisation of cholesterol.
·
They
also participate in blood clotting.
·
They
protect and insulate the neuronal fibres of myelin sheath.
·
They are
involved in the interaction of hormones with receptors.
·
They can
act as lipotropic agents and prevent fatty liver formation.
·
They
help in the reverse transport of cholesterol.
Related Topics