Solutions | Chemistry - Vapour pressure of liquid | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Solutions
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Solutions
Vapour pressure of liquid
Vapour
pressure of liquid
Generally,
liquids have a tendency to evaporate. If the kinetic energy of molecules in the
liquid state overcomes the intermolecular force of attraction between them,
then the molecules will escape from the liquid state. This process is called
'evaporation' and it happens on the surface of the liquid.
If
evaporation is carried out in a closed container then the vapour remains in
contact with the surface of the liquid. These vapour molecules are in
continuous random motion during which they collide with each other and also
with the walls of the container. As the collision is inelastic, they lose their
energy and as result the vapour returns back to liquid state. This process is
called as 'condensation'.
Evaporation
and condensation are continuous processes. If the process is carried out in a
closed system, a stage is reached when the rate of evaporation becomes equal to
the rate of condensation. Thus, an equilibrium is established between liquid
and its vapour. The pressure of the vapour in equilibrium with its liquid is
called vapour pressure of the liquid at the given temperature. The vapour
pressure of a liquid depends on its nature, temperature and the surface area.
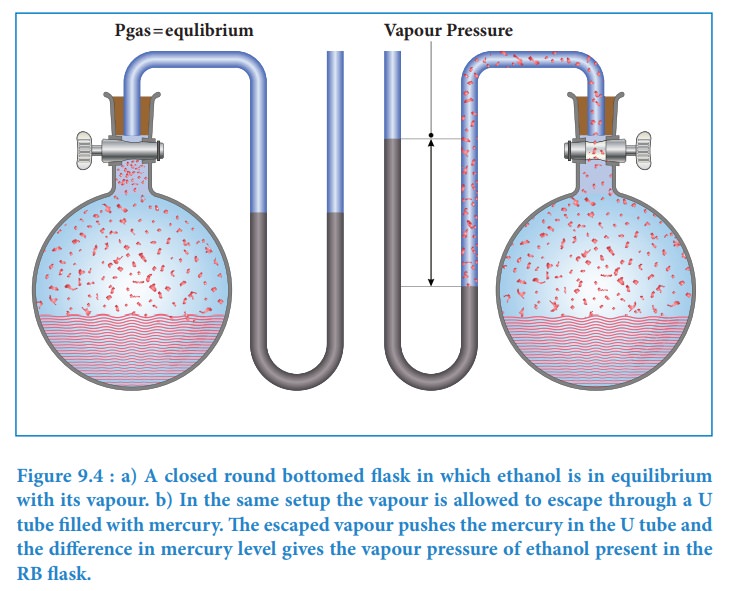
The following simple apparatus demonstrates the measurement of vapour pressure
of a liquid.
Related Topics