Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Solutions
Isotonic solutions
Isotonic solutions
Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions. When such solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane, solvent flow between one to the other on either direction is same, i.e. the net solvent flow between the two isotonic solutions is zero.
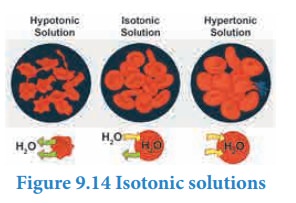
The osmotic pressure of the blood cells is approximately equal to 7 atm at 37ňöC. The intravenous injections should have same osmotic pressure as that of the blood (isotonic with blood). If the Intravenous solutions are too dilute that is hypotonic, the solvent from outside of the cells will flow into the cell to normalise the osmotic pressure and this process which is called hemolysis, causes the cells to burst. On the other hand, if the solution is too concentrated, that is hypertonic, the solvent molecules will flow out of the cells, which causes the cells to shrink and die. For this reason, the Intravenous fluids are prepared such they are isotonic to blood (0.9 % mass/ volume sodium chloride solution).
Related Topics