Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Solutions
Reverse osmosis (RO)
Reverse
osmosis (RO):
Let
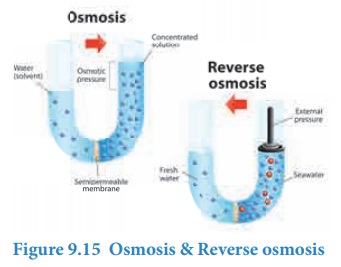
us consider the experimental setup (Figure 9.15) discussed in the osmosis. The
pure water moves through the semipermeable membrane to the NaCl solution due to
osmosis. This process can be reversed by applying pressure greater than the
osmotic pressure to the solution side. Now the pure water moves from the
solution side to the solvent side and this process is called reverse osmosis.
It can be defined as a process in which a solvent passes through a
semipermeable membrane in the opposite direction of osmosis, when subjected to
a hydrostatic pressure greater than the osmotic pressure.
Application of Reverse osmosis in
water purification:
Reverse
osmosis is used in the desalination of sea water and also in the purification
of drinking water. A simple set up used in both the process is shown in the
figure 9.15. When a pressure higher than the osmotic pressure is applied on the
solution sided (sea water) the water molecules moves from solution side to the
solvent side through semipermeable membrane (Opposite to the Osmotic flow). The
pure water can be collected. There are different types of semipermeable
membranes used in this process. The membrane used for reverse osmosis has to
withstand high pressures. Generally, cellulose acetate or polyamide membranes
are commonly used in commercial systems. The selection of membrane used for
reverse osmosis will be decided based on the nature of the input water.
Example Problem-6 :
At
400K 1.5 g of an unknown substance is dissolved in solvent and the solution is
made to 1.5 L. Its osmotic pressure is found to be 0.3 bar. Calculate the molar
mass of the unknown substance.

Related Topics