Chapter: Embedded Systems
Trends in Embedded Systems
TRENDS
IN EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Chapter
Structure
Objectives
1 Introduction
2 Processor Trends
3 Operating System Trends
4 Development Language Trends
5 Open Standards, Frameworks and alliances
6 Bottlenecks faced by Embedded Industry
OBJECTIVES
After reading this chapter you will understand:
Different trends in
the embedded industry related to:
Processor
Trends
Operating
System Trends
Development
Language Trends
Open
Standards, Frameworks and alliances
Bottlenecks
faced by Embedded Industry
1 INTRODUCTION
This concluding chapter describes the trends in
the embedded systems industry.
2
PROCESSOR TRENDS
There have been tremendous advancements in the
area of processor design.
Following are some of the points of difference
between the first generation of processor/controller and today’s processor/
controller.
Number
of ICs per chip: Early
processors had a few number of
IC/gates per chip. Today’s processors with Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
technology can pack together ten of thousands of IC/gates per processor.
Need
for individual components: Early
processors need different components
like brown out circuit, timers, DAC/ADC separately interfaced if required to be
used in the circuit. Today’s processors have all these components on the same
chip as the processor.
Speed
of Execution: Early
processors were slow in terms of
number of instructions executed per second. Today’s processor with advanced
architecture support features like instruction pipeline improving the execution
speed.
Clock
frequency: Early
processors could execute at a frequency
of a few MHz only. Today’s processors are capable of achieving execution
frequency in rage of GHz.
O Application specific processor: Early systems were designed using the processors available at that time. Today it is
possible to custom create a processor according to a product requirement.
Following
are the major trends in processor architecture in embedded development.
System
on Chip (SoC)
This concept makes it possible to integrate
almost all functional systems required to build an embedded product into a
single chip.
SoC are now available for a wide variety of
diverse applications like Set Top boxes, Media Players, PDA, etc.
SoC integrate multiple functional components on
the same chip thereby saving board space which helps to miniaturize the overall
design.
Multicore
Processors/ Chiplevel Multi Processor
This concept employs multiple cores on the same
processor chip operating at the same clock frequency and battery.
Based on the number of cores, these processors
are known as:
o Dual Core – 2 cores
o Tri Core – 3 cores
Quad Core
– 4 cores
These processors implement multiprocessing
concept where each core implements pipelining and multithreading.
Reconfigurable
Processors
It is a
processor with reconfigurable hardware features.
Depending
on the requirement, reconfigurable processors can change their functionality to
adapt to the new requirement. Example: A reconfigurable processor chip can be
configured as the heart of a camera or that of media player.
These
processors contain an Array of Programming Elements (PE) along with a
microprocessor. The PE can be used as a computational engine like ALU or a
memory element.
3 OPERATING
SYSTEM TRENDS
The advancements in processor technology have
caused a major change in the Embedded Operating System Industry.
There are lots of options for embedded operating
system to select from which can be both commercial and proprietary or Open
Source.
Virtualization concept is brought in picture in
the embedded OS industry which replaces the monolithic architecture with the
microkernel architecture.
This enables only essential services to be
contained in the kernel and the rest are installed as services in the user
space as is done in Mobile phones.
Off the shelf OS customized for specific device
requirements are now becoming a major trend.
4
DEVELOPMENT LANGUAGE TRENDS
There are two aspects to Development Languages
with respect to Embedded Systems Development
Embedded
Firmware
It is the application that is responsible for
execution of embedded system.
It is the software that performs low level
hardware interaction, memory management etc on the embedded system.
Embedded
Software
It is the software that runs on the host
computer and is responsible for interfacing with the embedded system.
It is the user application that executes on top
of the embedded system on a host computer.
Early languages available for embedded systems
development were limited to C & C++ only. Now languages like Microsoft C$,
ASP.NET, VB, Java, etc are available.
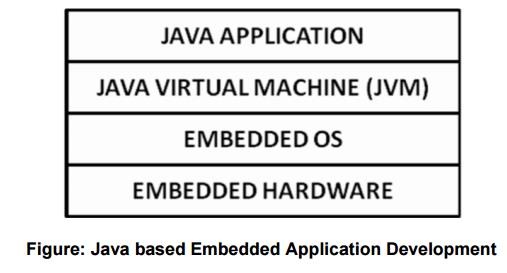
Java
Java is not a popular language for embedded
systems development due to its nature of execution.
Java programs are compiled by a compiler into
bytecode. This bytecode is then converted by the JVM into processor specific
object code.
During runtime, this interpretation of the bytecode by the JVM makes
java applications slower that other cross compiled applications.
This disadvantage is overcome by providing in
built hardware support for java bytecode execution.
Another technique used to speed up execution of
java bytecode is using Just In Time (JIT) compiler. It speeds up the program
execution by caching all previously executed instruction.
Following are some of the disadvantage of Java
in Embedded Systems development:
o For real time applications java is slow
Garbage collector of Java is non-deterministic in behavior which makes it not suitable for hard real time systems.
o Processors need to have a built in version of JVM
Those processors that don’t have JVM require it
to be ported for the specific processor architecture.
Java is limited in terms of low level hardware
handling compared to C and C++
Runtime memory requirement of JAVA is high which
is not affordable by embedded systems.
B.
.NET CF
It stands for .NET
Compact Framework.
.NET CF is a
replacement of the original .NET framework to be used on embedded systems.
The CF version is
customized to contain all the necessary components for application development.
The Original version
of .NET Framework is very large and hence not a good choice for embedded
development.
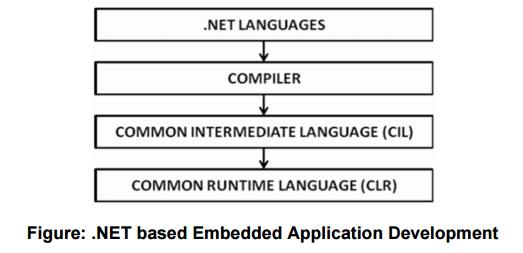
The .NET Framework is
a collection of precompiled libraries.
Common Language
Runtime (CLR) is the runtime environment of .NET. It provides functions like
memory management, exception handling, etc.
Applications written
in .NET are compiled to a platform neutral language called Common Intermediate
Language (CIL).
For execution, the CIL
is converted to target specific machine instructions by CLR.
5 OPEN STANDARDS,
FRAMEWORKS AND ALLIANCES
Following are some of the popular strategic
alliances, open source standards and frameworks specific to the mobile handset
industry.
Open
Mobile Alliance (OMA)
It is a standard body
for creating open standards for mobile industry.
OMA is the Leading
Industry Forum for Developing Market Driven – Interoperable Mobile Service
Enablers
OMA was formed in June
2002 by the world’s leading mobile operators, device and network suppliers,
information technology companies and content and service providers.
OMA delivers open
specifications for creating interoperable services that work across all
geographical boundaries, on any bearer network. OMA’s specifications support
the billions of new and existing fixed and mobile terminals across a variety of
mobile networks, including traditional cellular operator networks and emerging
networks supporting machine-to-machine device communication.
OMA is the focal point
for the development of mobile service enabler specifications, which support the
creation of interoperable end-to-end mobile services.
Goals
of OMA
Deliver high quality, open technical specifications
based upon market requirements that drive modularity, extensibility, and
consistency amongst enablers to reduce industry implementation efforts.
Ensure OMA service enabler specifications
provide interoperability across different devices, geographies, service
providers, operators, and networks; facilitate interoperability of the
resulting product implementations.
Provide value and benefits to members in OMA
from all parts of the value chain including content and service
providers, information technology providers,
mobile operators and wireless vendors such that they elect to actively
participate in the organization.
Open
Handset Alliance (OHA)
The Open Handset Alliance is a group of 84
technology and mobile companies who have come together to accelerate innovation
in mobile and offer consumers a richer, less expensive, and better mobile
experience. Together they have developed Android™, the first complete, open,
and free mobile platform and are committed to commercially deploy handsets and
services using the Android Platform.
Members of OHA include mobile operators, handset
manufacturers, semiconductor companies, software companies, and
commercialization companies.
Android
Android is an operating system based on the
Linux kernel, and designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as
smartphones and tablet computers.
Initially developed by Android, Inc., which
Google supported financially and later bought in 2005, Android was unveiled in
2007 along with the founding of the Open Handset Alliance: a consortium of
hardware, software, and telecommunication companies devoted to advancing open
standards for mobile devices.
Openmoko
Openmoko is a project to create a family of open
source mobile phones, including the hardware specification and the operating
system.
The first sub-project is Openmoko Linux, a
Linux-based operating system designed for mobile phones, built using free
software.
The second sub-project is developing hardware
devices on which Openmoko Linux runs.
6 Bottlenecks
faced by Embedded Industry
Following are some of the problems faced by the
embedded devices industry:
Memory
Performance
The rate at which processors can process may
have increased considerably but rate at which memory speed is increasing is
slower.
Lack
of Standards/ Conformance to standards
Standards in the embedded industry are followed
only in certain handful areas like Mobile handsets.
There is growing trend of proprietary
architecture and design in other areas.
Lack
of Skilled Resource
Most important aspect in the development of
embedded system is availability of skilled labor. There may be thousands of
developers who know how to code in C, C++, Java or .NET but very few in
embedded software.
Related Topics