Chapter: Embedded Systems Design : Embedded processors
INTEL 80286
INTEL 80286
The Intel 80286 was the successor to the 8086 and 8088 processors and
offered a larger addressing space while still pre-serving compatibility with
its predecessors. Its initial success was in the PC market where it was the
processor engine behind the IBM PC AT and all the derivative clones.
Architecture
The 80286 has two modes of operation known as real mode and protected
mode: real mode describes its emulation of the 8086/8088 processor including
limiting its external address bus to 20 bits to mimic the 8086/8088 1 Mbyte
address space. In its real mode, the 80286 adds some additional registers to
allow access to its larger 16 Mbyte external address space, while still
preserving its compatibility with the 8086 and 8088 processors.
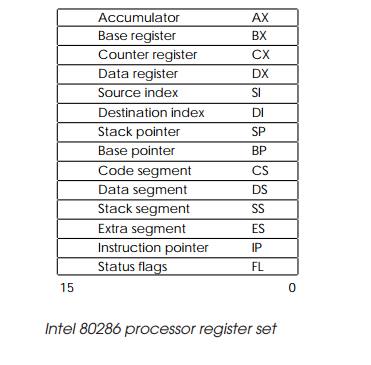
The register set comprises four general-purpose 16 bit registers (AX,
BX, CX and DX) and four segment address registers (CS, DS, SS and ES) and a 16
bit program counter. The general-purpose registers — AX, BX, CX, and DX — can
be accessed as two 8 bit registers by changing the X suffix to either H or L.
In this way, each half of register AX can be accessed as AH or AL and so on for
the other three registers.
These registers form a set that is the same as that of an 8086. However,
when the processor is switched into its protected mode, the register set is
expanded and includes two index registers (DI and SI) and a base pointer
register. These additions allow the 80286 to support a simple virtual memory
scheme.
Within the IBM PC environment, the 8086 and 8088 proces-sors can access
beyond the 1 Mbyte address space by using paging and special hardware to
simulate the missing address lines. This additional memory is known as expanded
memory. This non-linear memory mapping can pose problems when used in an
embedded space where a large linear memory structure is needed, but these
restrictions can be overcome as will be shown in later design examples.
Interrupt facilities
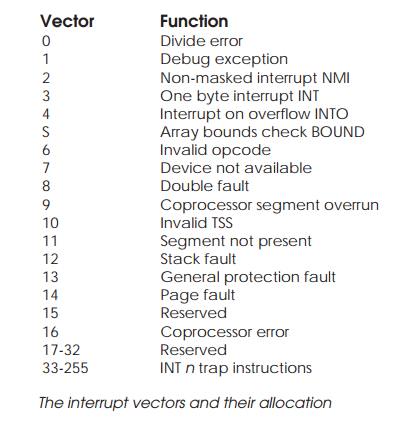
The 80286 can handle 256 different exceptions and the vectors for these
are held in a vector table. The vector table’s construction is different
depending on the processor’s operating mode. In the real mode, each vector
consists of two 16 bit words that contain the interrupt pointer and code
segment address so that the associated interrupt routine can be located and
executed. In the protected mode of operation each entry is 8 bytes long.
Instruction set
The instruction set for the 80286 follows the same pattern as that for
the Intel 8086 and programs written for the 8086 are compatible with the 80286
processor.
80287 floating point support
The 80286 can also be used with the 80287 floating point coprocessor to
provide acceleration for floating point calculations. If the device is not
present, it is possible to emulate the floating point operations in software,
but at a far lower performance.
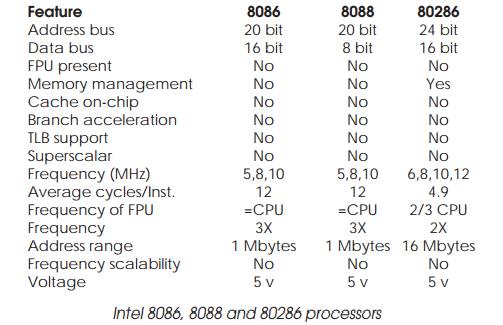
Feature comparison
Related Topics