Chapter: Embedded Systems
EDLC Models
EDLC
MODELS
Chapter
Structure
Objectives
1 Introduction
2 Waterfall or Linear Model
3 Iterative/ Incremental or Fountain Model
4 Prototyping Model
5 Spiral Model
OBJECTIVES
After reading this chapter you will understand:
Some EDLC
Models like:
Waterfall
or Linear Model
Iterative/
Incremental or Fountain Model
Prototyping
Model
Spiral
Model
1 INTRODUCTION
The previous chapters introduced the readers to
what is meant by EDLC. This chapter is meant to explain the various models
available under the EDLC.
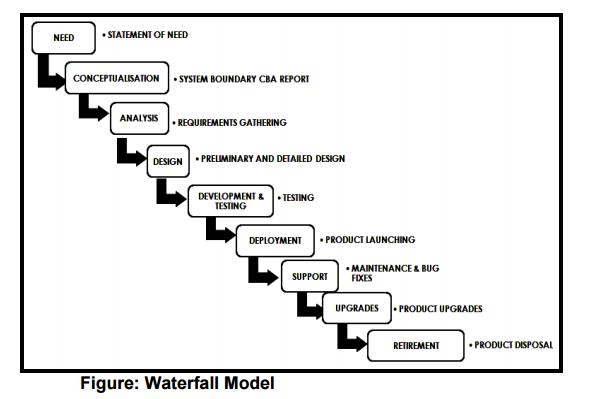
2 WATERFALL
MODEL
Linear or waterfall model is the one adopted in
most of the olden systems.
In this approach each phase of EDLC (Embedded
Development Product Lifecycle) is executed in sequence.
It establishes analysis and design with highly
structured development phases.
The execution flow is unidirectional.
The output of one phase serves as the input of
the next phase
All activities involved in each phase are well
planned so that what should be done in the next phase and how it can be done.
The feedback of each phase is available only
after they are executed.
It implements extensive review systems To ensure
the process flow is going in the right direction.
One significant feature of this model is that
even if you identify bugs in the current design the development process
proceeds with the design.
The fixes for the bug are postponed till the
support phase.
Advantages
Product development is rich in terms of:
Documentation
Easy
project management
Good
control over cost & Schedule
Drawbacks
It assumes all the analysis can be done without
doing any design or implementation
The risk
analysis is performed only once.
The
working product is available only at the end of the development phase
Bug fixes and correction are performed only at
the maintenance/support phase of the life cycle.
3 ITERATIVE/ INCREMENTAL
OR FOUNTAIN MODEL
Iterative and Incremental development is at the
heart of a cyclic software development process developed in response to the
weaknesses of the waterfall model.
The iterative model is the repetitive process in
which the Waterfall model is repeated over and over to correct the ambiguities
observed in each iteration.
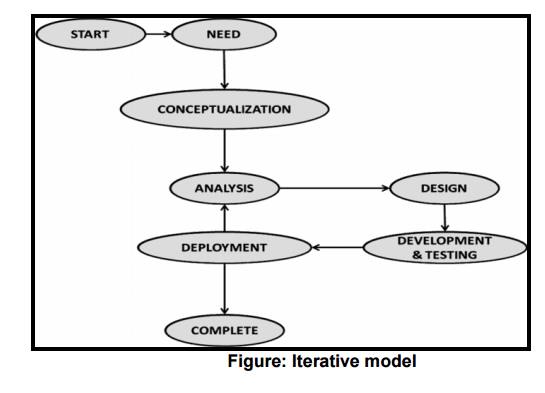
The above figure illustrates the repetitive
nature of the Iterative model.
The core set of functions for each group is
identified in the first cycle, it is then built, deployed and release. This
release is called as the first release.
Bug fixes and modification for first cycle
carried out in second cycle.
Process is repeated until all functionalities
are implemented meeting the requirements.
Advantages
Good development cycle feedback at each
function/feature implementation
Data can be used as reference for similar
product development in future.
More responsive to changing user needs.
Provides working product model with at least
minimum features at the first cycle.
Minimized Risk
Project management and testing is much simpler
compared to linear model.
Product development can be stopped at any stage
with a bare minimum working product.
Disadvantages
Extensive review requirement each cycle.
Impact on operations due to new releases.
Training requirement for each new deployment at
the end of each development cycle.
Structured and well documented interface
definition across modules to accommodate changes
4
PROTOTYPING MODEL
It is similar to iterative model and the product
is developed in multiple cycles.
The only difference is that, Prototyping model
produces a refined prototype of the product at the end of each cycle instead of
functionality/feature addition in each cycle as performed by the iterative
model.
There won’t be any commercial deployment of the
prototype of the product at each cycle’s end.
The shortcomings of the proto-model after each
cycle are evaluated and it is fixed in the next cycle.
After the initial requirement analysis, the
design for the first prototype is made, the development process is started.
On finishing the prototype, it is sent to the
customer for evaluation.
The customer evaluates the product for the set
of requirements and gives his/her feedback to the developer in terms of
shortcomings and improvements needed.
The developer refines the product according to
the customer’s exact expectation and repeats the proto development process.
After a finite number of iterations, the final
product is delivered to the customer and launches in the market/operational
environment
In this approach the product undergoes
significant evolution as a result of periodic shuttling of product information
between the customer and developer
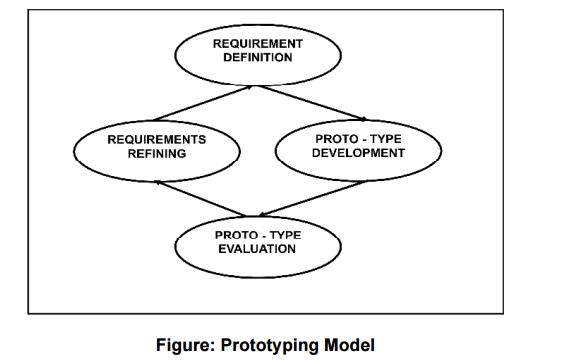
The prototyping model follows the approach-
Requirement
definition
Proto-type
development
Proto-type
evaluation
Requirements refining
5
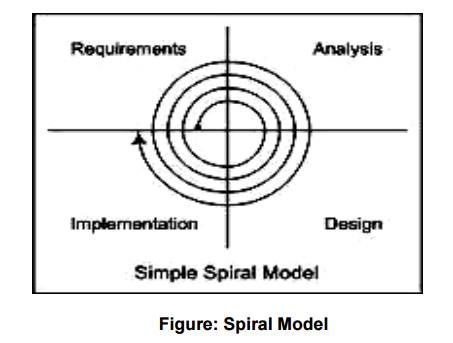
SPIRAL MODEL
Spiral model is developed by Barry Boehm in
1988.
The Product development starts with project
definition and traverse through all phases of EDLC(Embedded Product Development
Life Cycle).
The activities involved are:
Determine
objectives, alternatives, constraints
Evaluate
alternatives, identify and resolve risks III. Develop and test
IV. Plan
It is a combines the concept of Linear Model and
iterative nature of Prototyping Model.
Prototyping
Model
In prototyping after the requirement analysis
the design for the prototype is made and development process is started.
On finishing the prototype it is send to the
customer for evaluation ie. Judgment.
After customer evaluation for the product the
feedback is taken from the customer in term of what improvement is needed.
Then developer refines the product according to
the customer expectation.
Linear
Model
Spiral Model contains the concept of linear
model, having following type.
Requirement
Analysis
Design
Implementation
Requirement:
This process is focused specifically on embedded
software, to understand the nature of the software to be build and what are the
requirement for the software.
And the requirement for both the system &
the software is documented & viewed to customer.
Analysis:
Analysis is performed to develop a detailed
functional module under consideration.
The product is defined in detailed with respect
to the input, processing & output.
This phase emphasis on determining ‘what
function must be performed by the product’ & how to perform those function.
Design:
Product design deals with the entire design of
the product taking the requirement into consideration.
The design phase translates requirement into
representation.
Implementation:
In this process the launching of first fully
functional model of the product in the market is done or handing over the model
to an end user/client
In this product modifications are implemented
& product is made operational in production environment.
Related Topics