Chapter: Embedded Systems
Embedded Development Life Cycle
EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE
Chapter
Structure
Objectives
1 Introduction
2 EDLC
2.1 Need
For ELDC
2.2 Objectives
3 Different Phases of EDLC
4 ELDC Approaches
OBJECTIVES
After Reading this chapter you will understand
The Embedded Development Life Cycle
Phases Involved in the EDLC
1 INTRODUCTION
Just like the SDLC used in Software Development,
there is EDLC used in Embedded product development. This chapter explains what
is the EDLC, its objectives, the phases that are involved in the EDLC.
2 EMBEDDED
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE (EDLC)
EDLC is Embedded Product Development Life Cycle
It is an Analysis – Design – Implementation
based problem solving approach for embedded systems development.
There are three phases to Product development:
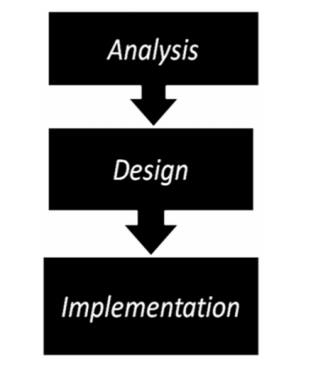
Analysis involves understanding what product
needs to be developed
Design involves what approach to be used to
build the product
Implementation is developing the product by
realizing the design.
2.1
Need for EDLC
EDLC is essential for understanding the scope andcomplexity of the work involved in embedded systems development
It can be used in any developing any embedded product
EDLC defines the interaction and activities among variousgroups of a product development phase.
Example:-project management, system design
2.2
Objectives of EDLC
The ultimate aim of any embedded product in a
commercial production setup is to produce Marginal benefit
Marginal is usually expressed in terms of Return
On Investment
The investment for product development includes
initial investment, manpower, infrastructure investment etc.
EDLC has three primary objectives are:
Ensure
that high quality products are delivered to user
Quality in
any product development is Return On Investment achieved by the product
The
expenses incurred for developing the product the product are:-
Initial
investment
Developer
recruiting
Training
Infrastructure
requirement related
Risk
minimization defect prevention in product development through project
management
In which
required for product development ‘loose’ or ‘tight’ project management
‘project
management is essential for ’ predictability co-ordination and risk
minimization
Resource
allocation is critical and it is having a direct impact on investment
Example:- Microsoft @ Project Tool
Maximize
the productivity
Productivity
is a measure of efficiency as well as Return On Investment
This
productivity measurement is based on total manpower efficiency
Productivity
in which when product is increased then investment is fall down
Saving
manpower
3 DIFFERENT
PHASES OF EDLC
The following figure depicts the different
phases in EDLC:
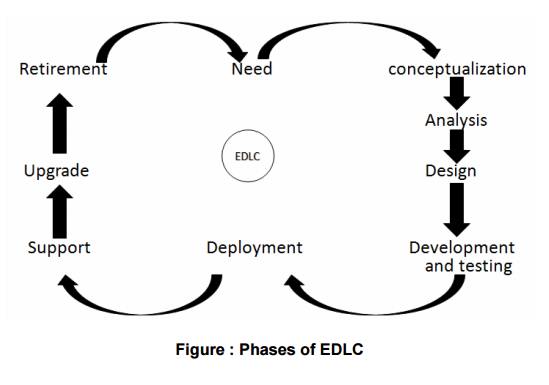
Need
The need may come from an individual or from the
public or from a company.
‘Need’ should be articulated to initiate the
Development Life Cycle; a ‘Concept Proposal’ is prepared which is reviewed by
the senior management for approval.
Need
can be visualized in any one of the following three needs:
New or
Custom Product Development.
Product
Re-engineering.
Product
Maintenance.
Conceptualization
Defines the scope of concept, performs cost
benefit analysis and feasibility study and prepare project management and risk
management plans.
The
following activities performed during this phase:
Feasibility
Study : Examine the need and
suggest possible solutions.
Cost
Benefit Analysis (CBA): Revealing
and assessing the total development
cost and profit expected from the product.
Product
Scope: Deals with the
activities involved in the product
to be made.
Planning
Activities: Requires
various plans to be developed first
before development like Resource Planning & Risk management Plans.
Analysis
The product is defined in detail with respect to
the inputs, processes, outputs, and interfaces at a functional level.
The
various activities performed during this phase..
• Analysis
and Documentations: This activity consolidates the business needs of the
product under development.
• Requirements that need to be addressed..
Functional Capabilities like performance
Operational and non-operational quality
attribute
Product external interface requirements
Data requirementsUser manuals
Operational requirements
Maintenance requirements
General assumptions
Unit
testing – Testing Individual
modules
Integration
testing – Testing a group of
modules for required functionality
System
testing- Testing functional
aspects or functional requirements
of the product after integration
User
acceptance testing- Testing
the product to meet the end user
requirements.
Design
The design phase identifies application
environment and creates an overall architecture for the product.
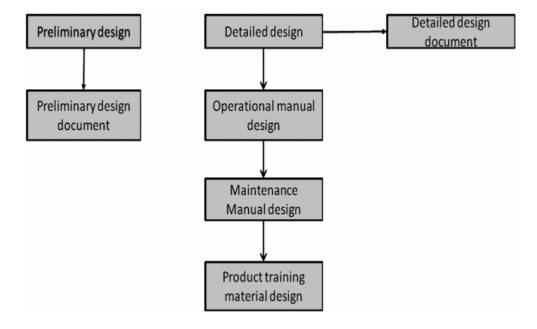
It starts with the Preliminary Design. It
establishes the top level architecture for the product. On completion it
resembles a ‘black box’ that defines only the inputs and outputs. The final
product is called Preliminary Design Document (PDD).
Once the PDD is accepted by the End User the
next task is to create the ‘Detailed Design’.
It encompasses the Operations manual design,
Maintenance Manual Design and Product Training material Design and is together
called the ‘Detailed Design Document’.
Development
and Testing
Development phase transforms the design into a
realizable product.
The detailed specification generated during the
design phase is translated into hardware and firmware.
The Testing phase can be divided into
independent testing of firmware and hardware that is:
Unit testing
Integration testing
System testing
User acceptance testing
Deployment
Deployment is the process of launching the first
fully functional model of the product in the market.
It is also known as First Customer Shipping
(FCS).
Tasks
performed during this phase are:
Notification
of Product Deployment: Tasks
performed here include:
Deployment schedule
Brief description about the product
Targeted end user
Extra features supported
Product support information
Execution
of training plan
Proper training should be given to the end user
top get them acquainted with the new product.
Product
installation
Install the product as per the installation
document to ensure that it is fully functional.
Product
post Implementation Review
After the product launch, a post implementation
review is done to test the success of the product.
Support
The support phase deals with the operational and
maintenance of the product in the production environment.
Bugs in the product may be observed and
reported.
The support phase ensures that the product meets
the user needs and it continues functioning in the production environment.
Activities involved under support are
Setting
up of a dedicated support wing: Involves providing 24 x 7 supports
for the product after it is launched.
Identify
Bugs and Areas of Improvement: Identify bugs and take
measures to eliminate them.
Upgrades
Deals with the development of upgrades (new
versions) for the product which is already present in the market.
Product upgrade results as an output of major
bug fixes.
During the upgrade phase the system is subject
to design modification to fix the major bugs reported.
Retirement/Disposal
The retirement/disposal of the product is a
gradual process.
This phase is the final phase in a product
development life cycle where the product is declared as discontinued from the
market.
The disposal of a product is essential due to
the following reasons
Rapid technology advancement
Increased user needs
4
ELDC APPROACHES
Following are some of the different types of
approaches that can be used to model embedded products.
Waterfall or Linear Model
Iterative/ Incremental or Fountain Model
Prototyping Model
Spiral Model
Related Topics