Chapter: Embedded Systems
Case Study of an Embedded System for Smart Card
Design Examples and Case Studies
off Program Modeling and Programming withith RTOS
CASE STUDY OF AN EMBEDDED SYSTEM
FOR SMART CARD
1. Smart Card System
Requirementsnts
Enabling
authentication and verification of card and card holder by a host
Enabling
GUI at host machine to interact with the card holder/user for the required
transactions, for example, financial transactions with a bank or credit card
transactions.
Inputs
Received
header and messages at IO port Port_IO from host through the antenna
Internal Signals, Events and
Notifications
On
power up, radiation-powered charge-pump supply of the card activated and a
signal to start the system boot program at resetTask
Card
start requestHeader message to task_ReadPort from resetTask
Host
authentication request requestStart message to task_ReadPort from resetTask to
enable requests for Port_IO
UserPW
verification message (notification) through Port_IO from host
Card
application close request requestApplClose message to Port_IO
Outputs
Transmitted
headers and messages at Port_IO through antenna
Control panel
No
control panel is at the card. The control panel and GUIs activate at the host
machine (for example, at ATM or credit card reader)
Functions of the system
The
card inserts at a host machine.
The
radiations from the host activate a charge pump at the card.
The
charge pump powers the SoC circuit consisting of card processor, memory, timer,
interrupt handler and IO port, Port_IO.
On
power up, system reset signals resetTask to start.
The
resetTask sends the messages requestHeader and requestStart for waiting
task
task_ReadPort.
task_ReadPort
sends requests for host identification and reads through the Port_IO the
host-identification message and request for card identification.
task_PW
sends through Port_IO the requested card identification after system receives
the host identity through Port_IO.
task_Appl
then runs required API. The requestApplClose message closes the application.
The
card can now be withdrawn
All
transactions between card-holder/user now takes place through GUIs using at the
host control panel (screen or touch screen or LCD display panel).
Design metrics
Power
Source and Dissipation: Radiation powered contact less
Code
size: optimum. card system memory needs should not exceed 64 kB memory.
Limited
use of data types; multidimensional arrays, long 64-bit integer and floating
points and very limited use of the error handlers, exceptions, signals,
serialization, debugging and profiling.
File
system(s): Three-layered file system for data.
File
management: There is either a fixed length file management or a variable file
length management with each file with a predefined offset.
Microcontroller
hardware: Generates distinct coded physical addresses for the program and data
logical addresses. Protected once writable memory space
Validity:
System is embedded with expiry date, after which the card authorization through
the hosts disables.
Extendibility:
The system expiry date is extendable by transactions and authorization of
master control unit (for example, bank servee).
Performance:
Less than 1s for transferring control from the card to host machine.
Process
Deadlines: None.
User
Interfaces: At host machine, graphic at LCD or touch screen display on LCD and
commands for card holder (card user) transactions.
Engineering
Cost: US$ 50000 (assumed)
Manufacturing
Cost: US$ 1 (assumed)
Test and validation conditionss
Tested
on different host machine versions for fail proof card-host communication
2. Classes and class diagram
Class diagram
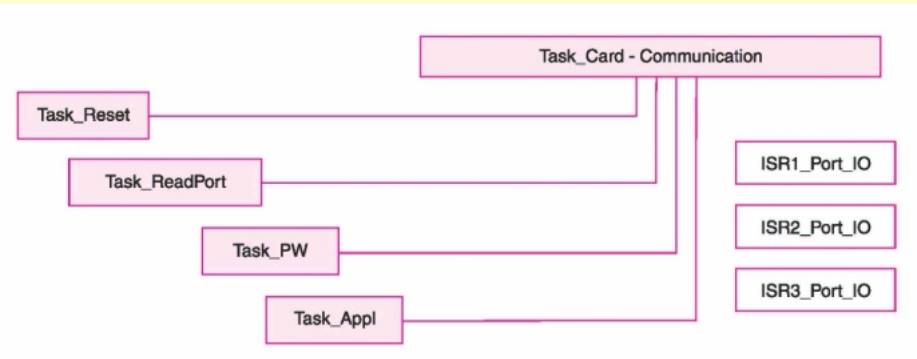
Classes
Task_CardCommunication
is an abstract class from which extended to class (es) derive to read port and
authenticate.
The
tasks (objects) are the instances of the classes Task_Appl, Task_Reset,
Task_ReadPort and Task_PW.
ISR1_Port_IO,
ISR2_Port_IO and ISR3_Port_IO are interfaces to the tasks
Other Classes
• Classes for the network, sockets,
connections, datagrams, character-input output and streams, security
management, digital-certification, symmetric and asymmetric keys-based
cryptography and digital signatures
3. Hardware Architecture
Smart card hardware
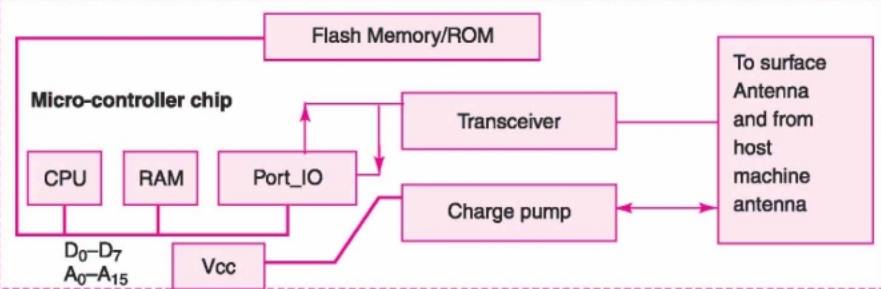
Smart Card Hardware
• A plastic card in ISO standard
dimensions, 85.60 mm x 53.98 x 0.80 mm. It is an embedded SoC (System-On-Chip).
[ISO standards - ISO7816 (1 to 4) for host-machine contact based card and
ISO14443 (Part A or B) for the contact-less cards.]
• Microcontroller MC68HC11D0 or PIC16C84
or a smart card processor Philips Smart XA or an ASIP Processor. Needs 8 kB+
internal RAM and 32 kB EPROM and 2/3 wire protected memory.
• CPU special features, for example, a
security lock
• CPU locks certain section of memory -
protect 1 kB or more data from modification and access by any external source
or instruction outside that memory
• Other way of protecting - CPU access
through the physical addresses, which are different from logical address used
in the program.
• Standard ROM 8 kB for usual or 64 kB
when using advanced cryptographic features
• Full or part of ROM bus activates take
place after a security check only.
ROM
Contains:
i. Fabrication key and Personalisation key
(after insertion of this key, RTOS and application use only the logical
addresses)
ii. RTOS codes
iii. Application codes
iv. Utilisation lock
• EEPROM or Flash scalable – only needed
part unlocks when storing P.I.N., unlocking P.I.N., access condition, card-user
data, post activation application run generated non-volatile data, invalidation
lock to invalidate card after the expiry date or server instruction
• RAM – run time temporary variables
• Chip-supply system using charge pump
• I/O system
4. Software Architecture
Smart Card Software
• Needs cryptographic software, needs
special features in its operating system over and above the MS DOS or UNIX
system features.
• Protected environment -OS stored in the
protected part of ROM.
• A restricted run-time environment.
• OS, every method, class and run time
library should be scalable.
• Optimum Code-size
• Limited use of data types;
multidimensional arrays, long 64-bit integer and floating points and very
limited use of the error handlers, exceptions, signals, serialisation,
debugging and profiling
• Three-layered file system for the data
• master file to store all file headers
(file status, access conditions and the file lock)
• A header means file status, access
conditions and the file lock.
• Dedicated file─ second file to hold a
file grouping and headers of the immediate successor
• Elementary file ─ third file to hold the
file header and its file data.
• Either a fixed length file management or
a variable file length management with each file with a predefined offset.
• Java CardTM, EmbeddedJava or J2ME (Java
2 Micro Edition) JVM has thread scheduler built in.
• Java provides the features to support
(i) security using class java.lang.SecurityManager), (ii) cryptographic needs
(package java.security*).
5. SmartOS RTOS used as alternative
to MUCOS
Smart Card OS
• SmartOS─ assumed hypothetical OS in this
example, as RTOS in the card.
• Use for understanding purposes identical
to MUCOS but actual SmartOS has to be different from MUCOS.
• Its file structure is different, though
it has MUCOS like IPCs and ECBs.
• function unsigned char [ ]
SmartOSEncrypt (unsigned char *applStr, EnType type) encrypts as per encryption
method, EnType = "RSA" or "DES" algorithm chosen and
returns the encrypted string
• function unsigned char [ ]
SmartOSDecrypt (unsigned char *Str, DeType type) encrypts as per deciphering
method, DeType = "RSA" or "DES" algorithm chosen and
returns the deciphered string.
SmartOSEncrypt and SmartOSDecrypt
execute after verifying the access conditions from the data files that store
the keys, PIN (Personal Identification Number) and password.
6. Tasks and their priority, action
and IPCs
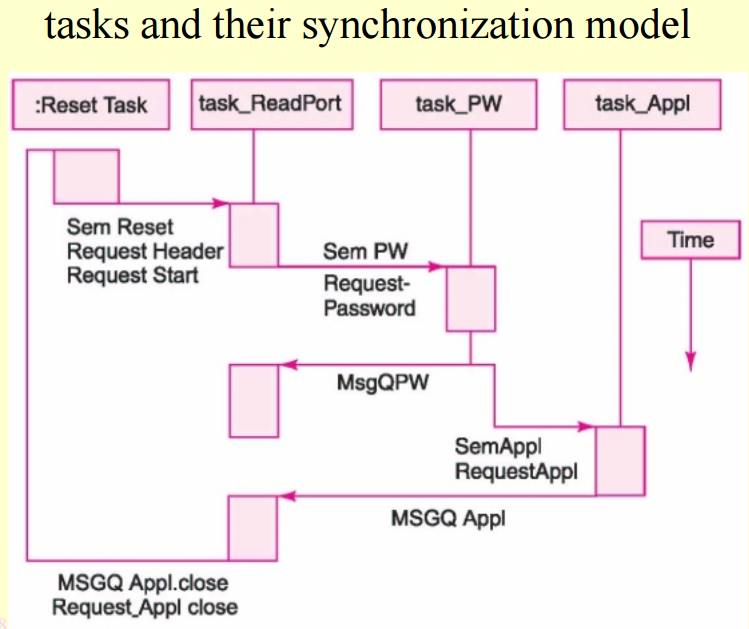
resetTask
Priority
─ 1
Action─
Initiates system timer ticks, creates tasks, sends initial messages and
suspends itself.
IPC
pending:
IPC
posted: SigReset, MsgQStart
String
Output: request-Header; request-Start
task_ReadPort
Priority
─ 2
Action─
Wait for resetTask suspension,
sends
the queue messages and receives the messages. Starts the application and seeks
closure permission for closing the application
IPC
pending: SigReset, MsgQStart, MsgQPW, MsgQAppl, MsgQAppl-Close
IPC
posted: SemPW
Output:
request-password, request-Appl, request-ApplClose
task_PW
Priority
─ 3
Action─
Sends request for password on verification of host when SemPW = 1
IPC
pending: SemPW IPC posted: MsgQPW Input: request-Password
task_Appl
Priority
─ 8
Action─
when SemPW = 1, runs the application program
IPC
pending: SemAppl IPC posted: MsgQAppl
7. Multiple tasks and their
synchronization model
tasks
and their synchronization model
8. Coding using SmartOS
Coding using VxWorks Adapted toto
OSEK-OS Features
•Refer
Example 12.4 in Section 12.4.5 Note: At each step, explanation for the set of
statements given there.
Summary
We learnt
• Smart Card hardware and software
• Code design given using the a
hypothetical RTOS, SmartOS, which has MUCOS features plus the embedded system
required cryptographic features and file security, access conditions and
restricted access permissions during code run.
Related Topics