Preparation, Properties, Structure, Uses, Test - Sulphuric acid | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Sulphuric acid
Sulphuric
acid: (H2SO4)
Preparation:
Sulphuric acid can be
manufactured by lead chamber process, cascade process or contact process. Here
we discuss the contact process.
Manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process:
The contact process
involves the following steps.
i. Initially sulphur
dioxide is produced by burning sulphur or iron pyrites in oxygen/air.
S + O2 → SO2
4FeS2 + 11O2
→ 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2
ii. Sulphur dioxide
formed is oxidised to sulphur trioxide by air in the presence of a catalyst
such as V2O5 or platinised asbestos.
iii. The sulphur trioxide is absorbed in concentrated sulphuric
acid and produces oleum (H2S2O7). The oleum is
converted into sulphuric acid by diluting it with water.
SO3 + H2SO4
→ H2S2O7 →H2O→ 2H2SO4
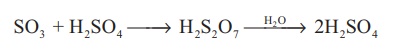
To maximise the yield
the plant is operated at 2 bar pressure and 720 K. The sulphuric acid obtained
in this process is over 96 % pure.
Physical properties:
Pure sulphuric acid is a
colourless, viscous liquid (Density: 1.84 g/mL at 298 K). High boiling point
and viscosity of sulphuric acid is due to the association of molecules together
through hydrogen bonding.
The acid freezes at
283.4 K and boils at 590 K. It is highly soluble in water and has strong
affinity towards water and hence it can be used as a dehydrating agent. When
dissolved in water, it forms mono (H2SO4.H2O)
and dihydrates (H2SO4.2H2O) and the reaction
is exothermic.
The dehydrating property
can also be illustrated by its reaction with organic compounds such as sugar,
oxalic acid and formic acid.
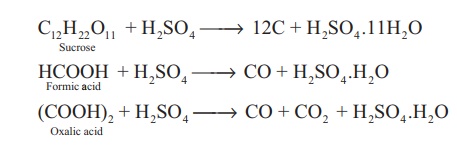
C12H22O11
+ H2SO4 → 12C + H2SO4 .11H2O
HCOOH + H2SO4
→ CO + H2SO4 .H2O
(COOH)2 + H2SO4
→ CO + CO2 + H2SO4 .H2O
Chemical Properties:
Sulphuric acid is highly
reactive. It can act as strong acid and an oxidising agent. Decomposition: Sulphuric
acid is stable, however, it decomposes at high temperatures to sulphur
trioxide.
H2SO4
→ H2O + SO3
Acidic nature: It is a strong dibasic
acid. Hence it forms two types of salts namely sulphates and
bisulphates.
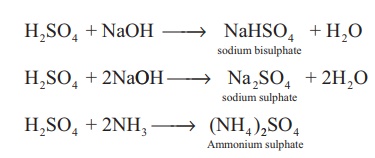
H2SO4
+ NaOH → NaHSO4 + H2O
H2SO4
+ 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
H2SO4
+ 2NH3 → (NH4 )2SO4
Oxidising property: Sulphuric acid is an
oxidising agent as it produces nascent oxygen as shown below.
H 2 SO4
→ H2O + SO2 + (O) nascent oxygen
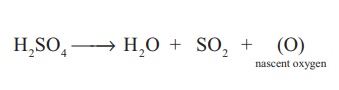
Sulphuric acid oxidises
elements such as carbon, sulphur and phosphorus. It also oxides bromide and
iodide to bromine and iodine respectively.
C + 2H2SO4
→ 2SO2 + 2H2O + CO2
S + 2H2SO4
→ 3SO2 + 2H2O
P4 + 10H2SO4
→ 4H3PO4 + 10SO2 + 4H2O
H2S + H2SO4
→ SO2 + 2H2O + S
H2SO4
+ 2HI → 2SO2 + 2H2O + I2
H2SO4
+ 2HBr → 2SO2 + 2H2O + Br2
Reaction with metals: Sulphuric acid reacts
with metals and gives different product depending on the reactants and
reacting condition.
Dilute sulphuric acid
reacts with metals like tin, aluminium, zinc to give corresponding sulphates.
Zn + H2SO4
→ ZnSO4 + H2
↑
2Al + 3H2SO4
→ Al2 (SO4
)3 + 3H2 ↑
Hot concentrated
sulphuric acid reacts with copper and lead to give the respective sulphates as
shown below.
Cu + 2H2SO4
→ CuSO4 + 2H2O
+ SO2 ↑
Pb + 2H2SO4
→ PbSO4 + 2H2O
+ SO2 ↑
Sulphuric acid doesn’t
react with noble metals like gold, silver and platinum.
Reaction with salts: It reacts with different
metal salts to give metal sulphates and bisulphates.
KCl + H2SO4
→ KHSO4 + HCl
KNO3 + H2SO4
→ KHSO4 + HNO3
Na2CO3
+ H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O +
CO2
2NaBr + 3H2SO4
→ 2NaHSO4 + 2H2O + Br2 + SO2
Reaction with organic
compounds: It reacts organic compounds such as benzene to give sulphonic
acids.
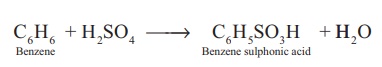
C6H6
+ H2SO4 → C6H5SO3H + H2O
Uses of sulphuric acid:
·
Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilisers, ammonium
sulphate and super phosphates and other chemicals such as hydrochloric acid,
nitric acid etc...
·
It is used as a drying agent and also used in the preparation of
pigments, explosives etc..
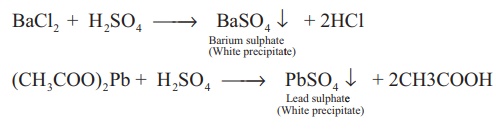
Test for sulphate/sulphuric acid:
Dilute solution of sulphuric acid/aqueous solution of sulphates gives white precipitate (barium sulphate) with barium chloride solution. It can also be detected using lead acetate solution. Here a white precipitate of lead sulphate is obtained.
BaCl2 + H2SO4
→ BaSO4 ↓ + 2HCl
(CH3COO)2Pb
+ H2SO4 → PbSO4 ↓
+ 2CH3COOH
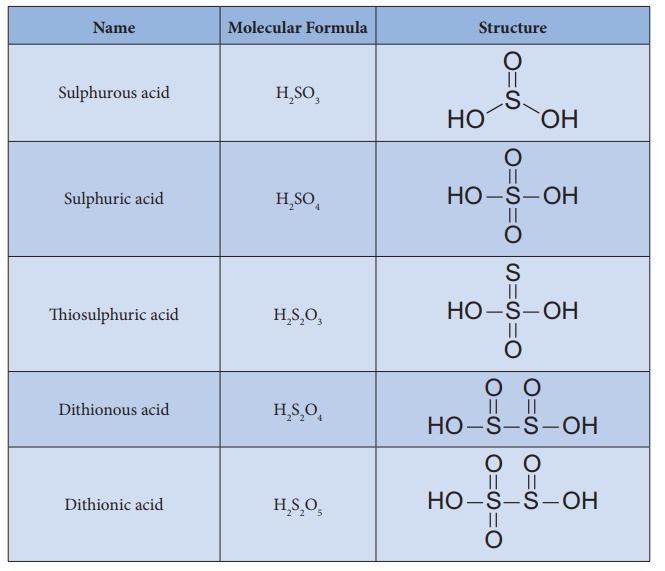
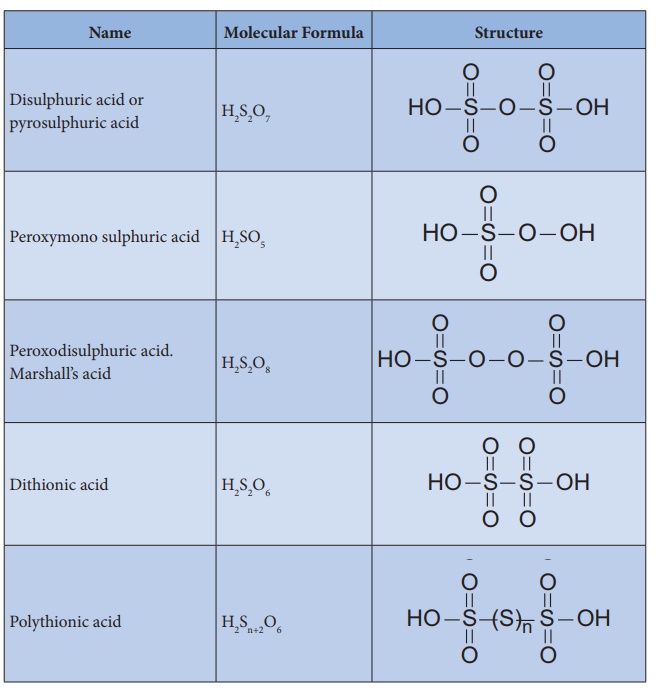
Structure of oxoacids of sulphur:
Sulphur forms many
oxoacids. The most important one is sulphuric acid. Some acids like sulphurous
and dithionic acids are known in the form of their salts only since the free
acids are unstable and cannot be isolated.
Various oxo acids of
sulphur with their structures are given below
Related Topics