Preparation, Properties, Uses - Oxygen | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Oxygen
Oxygen:
Preparation:
The atmosphere and water
contain 23% and 83% by mass of oxygen respectively. Most of the world’s rock
contain combined oxygen. Industrially oxygen is obtained by fractional
distillation of liquefied air. In the laboratory, oxygen is prepared by one of
the following methods.
The decomposition of
hydrogen peroxide in the presence of catalyst (MnO2) or by oxidation
with potassium permanganate.
2H2 O2
↔ 2H2O + O2
5H2O2
+ 2MnO4− + 6H+ → 5O2 + 8H2O + 2Mn2+
The thermal
decomposition of certain metallic oxides or oxoanions gives oxygen.
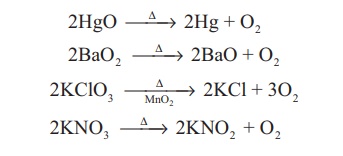
Properties
Under ordinary condition
oxygen exists as a diatomic gas. Oxygen is paramagnetic. Like nitrogen and
fluorine, oxygen form strong hydrogen bonds. Oxygen exists in two allotropic
forms namely dioxygen (O2) and ozone or trioxygen (O3).
Although negligible amounts of ozone occurs at sea level it is formed in the
upper atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet light. In the laboratory ozone is
prepared by passing electrical discharge through oxygen. At a potential of
20,000 V about 10% of oxygen is converted into ozone it gives a mixture known
as ozonised oxygen. Pure ozone is obtained as a pale blue gas by the fractional
distillation of liquefied ozonised oxygen.
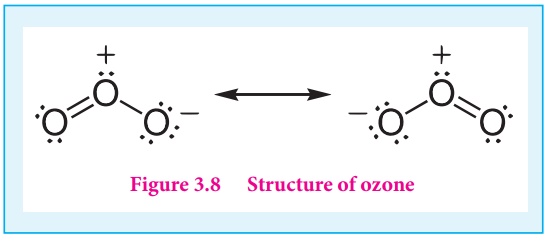
The ozone molecule have a bent shape and symmetrical with delocalised bonding between the oxygen atoms.
Chemical properties:
The chemical properties
of oxygen and ozone differ vastly. Oxygen combines with many metals and
non-metals to form oxides. With some elements such as s-block elements
combination of oxygen occurs at room temperature. Some of less reactive metals
react when powdered finely and made to react exothermically with oxygen at room
temperature but a lump of metal is unaffected under same condition. These
finely divided metals are known as pyrophoric and when set the powder on fire,
heat is liberated during a reaction.
On the other hand ozone
is a powerful oxidising agent and it reacts with many substances under
conditions where oxygen will not react. For example, it oxidises potassium
iodide to iodine. This reaction is quantitative and can be used for estimation
of ozone.
O3 + 2KI + H2O
→ 2KOH + O2 +
I2
Ozone is commonly used
for oxidation of organic compounds. In acidic solution ozone exceeds the
oxidising power of fluorine and atomic oxygen. The rate of decomposition of
ozone drops sharply in alkaline solution.
Uses:
·
Oxygen is one of the essential component for the survival of
living organisms.
·
It is used in welding (oxyacetylene welding)
·
Liquid oxygen is used as fuel in rockets etc...
Related Topics