Preparation, Properties, Uses - Nitrogen | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Nitrogen
Nitrogen:
Preparation:
Nitrogen, the principle
gas of atmosphere (78 % by volume) is separated industrially from liquid air by
fractional distillation
Pure nitrogen gas can be
obtained by the thermal decomposition of sodium azide about 575 K
2NaN3 2→ Na +
3N2
It can also be obtained
by oxidising ammonia using bromine water
8NH3 + 3Br2
→ 6NH4Br + N2
Properties
Nitrogen gas is rather
inert. Terrestrial nitrogen contains 14.5% and 0.4% of nitrogen-14 and
nitrogen-15 respectively. The later is used for isotopic labelling. The
chemically inert character of nitrogen is largely due to high bonding energy of
the molecules 225 cal mol-1 (946 kJ mol-1). Interestingly the triply bonded
species is notable for its less reactivity in comparison with other
iso-electronic triply bonded systems such as -C≡C-, C≡O,
X-C≡N, X-N≡C, -C≡C-, and -C≡N. These groups can act
as donor where as dinitrogen cannot. However, it can form complexes with metal
(M→ N≡N) like CO to a less
extent.
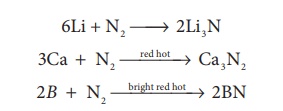
The only reaction of
nitrogen at room temperature is with lithium forming Li3N. With
other elements, nitrogen combines only at elevated temperatures. Group 2 metals
and Th forms ionic nitrides.
6Li + N2 → 2Li3N
3Ca + N2→red
hot → Ca3N2
2B + N2→bright
red hot→ 2BN
Direct reaction with
hydrogen gives ammonia. This reaction is favoured by high pressures and at
optimum temperature in presence of iron catalyst. This reaction is the basis of
Haber’s process for the synthesis of ammonia.
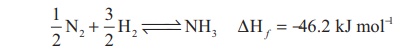
With oxygen, nitrogen
produces nitrous oxide at high temperatures. Even at 3473 K nitrous oxide yield
is only 4.4%.
2N2 + O2 → 2N2O
Uses of nitrogen
·
Nitrogen is used for the manufacture of ammonia, nitric acid and
calcium cyanamide etc.
·
Liquid nitrogen is used for producing low temperature required in
cryosurgery, and so in biological preservation .
Related Topics