Preparation, Properties, Structure - Ammonia | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 3 : p-Block Elements-II
Ammonia
Ammonia
(NH3)
Preparation:
Ammonia is formed by the
hydrolysis of urea.
NH2CONH2
+H2O → 2NH3 +CO2
Ammonia is prepared in
the laboratory by heating an ammonium salt with a base.
2 NH4 +
+ OH− → 2NH3 + H2O
2NH4Cl + CaO → CaCl2 + 2NH3
+ H2O
It can also be prepared
by heating a metal nitrides such as magnesium nitride with water.
Mg3 N2
+ 6H2O → 3Mg(OH)2 +
2NH3
It is industrially
manufactured by passing nitrogen and hydrogen over iron catalyst (a small
amount of K2O and Al2O3 is also used to
increase the rate of attainment of equilibrium) at 750 K at 200 atm pressure.
In the actual process the hydrogen required is obtained from water gas and
nitrogen from fractional distillation of liquid air.
Properties
Ammonia is a pungent
smelling gas and is lighter than air. It can readily liquefied by at about 9
atmospheric pressure. The liquid boils at -38.4°C and freezes at -77° C. Liquid
ammonia resembles water in its physical properties. i.e. it is highly
associated through strong hydrogen bonding. Ammonia is extremely soluble in water
(702 Volume in 1 Volume of water) at 20°C and 760mm pressure.
At low temperatures two
soluble hydrate NH3.H2O and 2NH3.H2O
are isolated. In these molecules ammonia and water are linked by hydrogen
bonds. In aqueous solutions also ammonia may be hydrated in a similar manner
and we call the same as (NH3.H2O)
NH3 + H2ON ↔ H4+
OH
The dielectric constant
of ammonia is considerably high to make it a fairly good ionising solvent like
water.
2NH3 ↔ NH4+ + NH2-
K−50C = [NH4+ ][NH2− ] = 10−30
2H2O ↔ H3O+
+ OH−
K23 C
= [H3O+
][OH− ] = 10−14
Chemical Properties
Action of heat: Above 500°C ammonia
decomposes into its elements. The decomposition may be accelerated by
metallic catalysts like Nickel, Iron. Almost complete dissociation occurs on
continuous sparking.
2NH3 → > 5000 C →N2 + 3H2
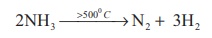
Reaction with
air/oxygen: Ammonia does not burn in air but burns freely in free oxygen with
a yellowish flame to give nitrogen steam.
4NH3 + 3O2 ↔ N2
+ 6H2O
In presence of catalyst
like platinum, it burns to produce nitric oxide. This process is used for the
manufacture of nitric acid and is known as ostwalds process.
4NH3 + 5O2 ↔ 4NO + 6H2O
Reducing property: Ammonia acts as a
reducing agent. It reduces the metal oxides to metal when passed over
heated metallic oxide.
3PbO + 2NH3 → 3Pb + N2 + 3H2O
Reaction with acids: When treated with acids
it forms ammonium salts. This reaction shows that the affinity of
ammonia for proton is greater than that of water.
Reaction with chlorine
and chlorides: Ammonia reacts with chlorine and chlorides to give ammonium
chloride as a final product. The reactions are different under different
conditions as given below.
With excess ammonia
2 NH3 + 3 Cl2
→N2 + 6 HCl
6 HCl + 6 NH3
→ 6 NH4Cl
With excess of chlorine
ammonia reacts to give nitrogen
trichloride, an explosive substance.
2NH3 + 6Cl2
→ 2NCl3 + 6 HCl
2NH3 (g) +
HCl(g) →NH4Cl (s)
Formation of amides and nitrides: With strong electro positive
metals such as sodium, ammonia forms amides while
it forms nitrides with metals like magnesium.
2Na + 2NH3 →
2NaNH2 + H2
3Mg + 2NH3 → Mg3N2 + 3H2
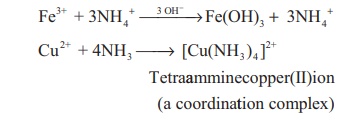
With metallic salts: Ammonia reacts with
metallic salts to give metal hydroxides (in case of Fe) or forming
complexes (in case Cu)
Fe3+ + 3NH4+ →3 OH− →Fe(OH)3 + 3NH4+
Cu2+ + 4NH3
→ [Cu(NH3 )4 ]2+ etraamminecopper(II)ion (a
coordinattion complex)
Formation of amines: Ammonia forms ammonated
compounds by ion dipole attraction. Eg. [CaCl2.8NH3]. In
this, the negative ends of ammonia dipole is attracted to Ca2+ ion.
It can also act as a ligand and form coordination compounds such as [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Ag(NH3)2]+.
For example when excess
ammonia is added to aqueous solution copper sulphate a deep blue colour
compound [Cu(NH3)4 ]2+ is formed.
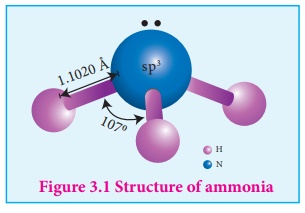
Structure of ammonia
Ammonia molecule is pyramidal in shape N-H bond distance is 1.016 Å and H-H bond distance is 1.645 Å with a bond angle 107 °. The structure of ammonia may be regarded as a tetrahedral with one lone pair of electrons in one tetrahedral position hence it has a pyramidal shape as shown in the figure.
Related Topics