Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 9 : Kinetic Theory of Gases
Multiple Choice Questions - Physics: Kinetic Theory of Gases
Physics : Kinetic Theory of Gases
Multiple choice questions
1. A particle of mass m is moving with speed u in a direction which makes 60° with respect to x axis. It undergoes elastic collision with the wall. What is the change in momentum in x and y direction?
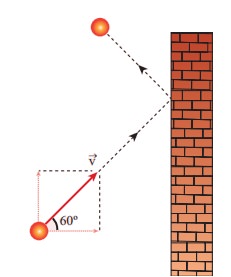
(a) ∆px = −mu, ∆py = 0
(b) ∆px = −2mu, ∆py = 0
(c) ∆px = 0, ∆py = mu
(d) ∆px = mu, ∆py = 0
Answer : (a) Δpx = −mu, Δpy = 0
Solution :
Δpx = 2mucos60
= − 2mu × ½ = (−2 mu ) / 2 = −mu
ΔPy = 0
2. A sample of ideal gas is at equilibrium. Which of the following quantity is zero?
(a) rms speed
(b) average speed
(c) average velocity
(d) most probable speed
Answer : (c) average velocity
3. An ideal gas is maintained at constant pressure. If the temperature of an ideal gas increases from 100K to 1000K then the rms speed of the gas molecules
(a) increases by 5 times
(b) increases by 10 times
(c) remains same
(d) increases by 7 times
Answer : (b) increases by 10 times
Solutions :
Vrms = √[3RT / m]
Vrms ∝√T
Vrms ∝√100
V´rms ∝√1000
V´rms / Vrms = √(1000 / 100)
V'rms = √10 Vrms
4. Two identically sized rooms A and B are connected by an open door. If the room A is air conditioned such that its temperature is 4° lesser than room B, which room has more air in it?
(a) Room A
(b) Room B
(c) Both room has same air
(d) Cannot be determined
Answer : (a) Room A
5. The average translational kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on
(a) number of moles and T
(b) only on T
(c) P and T
(d) P only
Answer: (a) number of moles and T
Solution :
(K = μR)
K.E = 3/2 KT
= 3/2 μRT
6. If the internal energy of an ideal gas U and volume V are doubled then the pressure
(a) doubles
(b) remains same
(c) halves
(d) quadruples C
Solution : P = (2/3) (u/v)
P' = (2/3) × (2u / 2v )
P' = P
7. The ratio γ = Cp/Cv for a gas mixture consisting of 8 g of helium and 16 g of oxygen is
(a) 23/15
(b) 15/23
(c) 27/11
(d) 17/27
Answer : (c) 27/17
Solution:
γ = CP / CV = ( 5μ1 + 7μ2 ) / ( 3μ1 + 5μ2)
= [ 5 × 2 + (7 × 1/2 ) ] / [ 3 × 2 + (5 × 1/2) ]
= [ 10 + 7/2 ] / [ 6 + 5/2 ] = [27/2] / [17/2]
γ = 27 / 17
8. A container has one mole of monoatomic ideal gas. Each molecule has f degrees of freedom. What is the ratio of γ = Cp/Cv
(a) f
(b) f/2
(c) f / [ f +2]
(d) [f +2] / f
Answer: (d) (f + 2) / f
Solution:
γ = CP / CV
CV = 3/2 R = f /2 R
CP = 5/2 R = [ (f + 2) / 2 ] R
γ = { R [ (f + 2) / 2 ] } / { R (f / 2) }
γ = ( f + 2) / f
9. If the temperature and pressure of a gas is doubled the mean free path of the gas molecules
(a) remains same
(b) doubled
(c) tripled
(d) quadrapoled
Answer : (a) remains same
Solution:
λ = kT / [√2 πd2P]
λ´ = [ k (2T) ] / [√2 πd2 (2P) ]
λ = λ´
10. Which of the following shows the correct relationship between the pressure and density of an ideal gas at constant temperature?
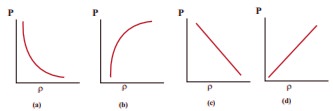
Answer: (d)
Solution:
P = 1/3 ρV2,
ρ ∝P
11. A sample of gas consists of μ1 moles of monoatomic molecules, μ2 moles of diatomic molecules and μ3 moles of linear triatomic molecules. The gas is kept at high temperature. What is the total number of degrees of freedom?
(a) [3μ1 + 7( μ2 + μ3)] NA
(b) [3μ1 + 7 μ2 + 6μ3] NA
(c) [7μ1 + 3( μ2 + μ3)] NA
(d) [3μ1 + 6( μ2 + μ3)] NA
Answer : (a) [3μ1 + 7( μ2 + μ3)] NA
Solution:
For a monoatomic molecule, f = 3
For a diatomic molecule, f = 7 (H.T)
For a triatomic molecule, f = 7 (L.T)
Total degrees of freedom, f = [3μ1 + 7( μ2 + μ3)] NA
12. If sP and sV denote the specific heats of nitrogen gas per unit mass at constant pressure and constant volume respectively, then
(a) sP - sV = 28R
(b) sP - sV = R/28
(c) sP - sV = R/14
(d) sP - sV = R
Answer: (b) sP − sv = R/28
Solution:
V = μCV ΔT;
V= μCP ΔT
mSV = μCV
(m/μ) SV = CV
mSV = CV
For N2 → M = 28
28 SV = CV
28SP = CP
CP – CV = R
28 (SP − SV) = R
SP − SV = R / 28
13. Which of the following gases will have least rms speed at a given temperature?
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Oxygen
(d) Carbon dioxide
Answer : (d) Carbon dioxide
Solution:
Vrms = √[3RT / M]
Vrms ∝ 1 / √M
14. For a given gas molecule at a fixed temperature, the area under the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve is equal to
(a) PV/kT
(b) kT/PV
(c) P/NkT
(d) PV
Answer: (a) PV / kT
Solution:
PV = NkT
N = PV / kT
15. The following graph represents the pressure versus number density for ideal gas at two different temperatures T1 and T2. The graph implies
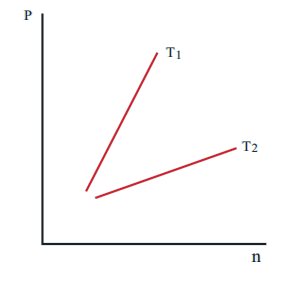
(a) T1 = T2
(b) T1 > T2
(c) T1 < T2
d) Cannot be determined
Answer : (b) T1 > T2
Solution:
P = 2/3 U,
U∝T,
P∝T
Answers:
1) a 2) c 3) b 4) a
5) a 6) b 7) c 8) d
9) a 10) d 11) a 12) b
13) d 14) a 15) b
Related Topics