Chapter: Embedded Systems
Important Short Questions and Answers: Embedded Software
EMBEDDED SOFTWARE
1. State some advantages of Assembly language?
It gives
a precise control of the processor internal devices and full use of processor
specific features in its instruction set and its addressing modes.
The
machine codes are compact.
With the
help of assembly language the basic concepts could be easily studied. Memory
required for the system is less.
Minimum
assembly languages instruction only needed for device drivers.
2. Write the advantages of high level language?
Standard
library functions
Modular
programming approach Bottom up design
Top down
design Data types
Type
checking
Control
structures Portability
3. Give the details of TCON SFR.
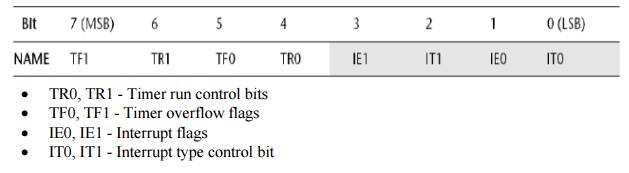
TR0, TR1 - Timer run control bits
TF0, TF1 - Timer overflow flags
IE0, IE1 - Interrupt
flags
4. Give the details of TMOD SFR?

Mode 1 (M1 = 1; M2 = 0)-16-bit timer/counter (with manual reload)
GATE -Gating control
C / T- Counter or timer select bit
5. What is the advantage of a hardware generated delay
over a software generated delay?
Software
generated delay is unreliable; it may change during compiler optimizations or
depending
on the machine on which it is run. Hardware generated delays are precise and is
reliable.
6. What is the advantage of a portable hardware
delay?
In a
portable hardware delay the operating frequencies can be changed dynamically
and it is easy for the maintenance of the system.
7. Give the need for timeout mechanism.
When a
system has to be created as reliable then it should assure that the system will
not get into an indefinite loop. To do this assurance, we need the timeout
mechanism. They are loop timeout which is software based and hardware timeout
which is based on hardware.
8. Give the uses of timer 2?
It is used to produce the delay. It is
employed in
1. Creation
of an operating system 2. Real time
applications.
9. Give the
types of Multi State Systems?
1. Multi-state (timed)
2. Multi state (input/timed)
3. Multi state (input)
10.
Give the
characteristics of Multi state systems.
They
involve a series of system states.
In each
state, one or more functions may be called.
There
will be rules defining the transitions between states.
As the
system moves between states, one or more functions may be called.
11.
What are
multi-state timed systems? Give example.
In a
multi-state (timed) system, the transition between states will depend only on
the passage of time.
A basic traffic-light control system is an example.
12. What are multi-state timed input systems? Give
example.
In a
multi-state timed input system the transition between states (and behaviors in
each state) will depend both on the passage of time and on system inputs.
The autopilot system, a washing machine, or
intruder alarm systems are the examples.
13. What do you mean by a host and target machine?
A typical
embedded computing system has a relatively small amount of everything,
including CPU horsepower, memory, I/O devices, and so forth. As a result, it is
common to do at least part of the software development on a PC or workstation
known as a host. The hardware on which the code will finally run is known as
the target.
14. What is a cross compiler?
A
cross-compiler is a compiler that runs on one type of machine but generates
code for another. After compilation, the executable code is downloaded to the
embedded system by a serial link or perhaps burned in a PROM and plugged in.
15. What is test-bench program?
The test-bench
program generates inputs to simulate the actions of the input devices; it may
also take the output values and compare them against expected values, providing
valuable early debugging help.
16. What is a breakpoint?
A
breakpoint is a debugging tool for the user to specify an address at which the
program’s execution is to break. When the PC reaches that address, control is
returned to the monitor program. From the monitor program, the user can examine
and/or modify CPU registers, after which execution can be continued.
17. What is an in-circuit-emulator?
The
microprocessor in-circuit emulator (ICE) is a specialized hardware tool that
can help debug software in a working embedded system. At the heart of an
in-circuit emulator is a special version of the microprocessor that allows its
internal registers to be read out when it is stopped.
The
in-circuit emulator surrounds this specialized microprocessor with additional
logic that allows the user to specify breakpoints and examine and modify the
CPU state.
18. What is a logic analyzer?
A logic
analyzer is an array of inexpensive oscilloscopes—the analyzer can sample many
different signals simultaneously (tens to hundreds) but can display only 0, 1,
or changing values for each. All these logic analysis channels can be connected
to the system to record the activity on many signals simultaneously.
19. What are the two modes in which logic analyzer
can acquire data?
A logic
analyzer can acquire data in either of two modes that are typically called state
and timing modes.
20. What is a simulator?
A
simulator is a software tool that runs on your host and simulates the behavior
of the microprocessor and memory in your target system.
21. What is a Monitor?
Monitors
are debugging tools which are used to run the software on the actual target
microprocessor while still giving a debugging interface similar to that of an
in-circuit emulator.
22. Why debugging is a challenge in real time
systems?
Real-time
programs are required to finish their work within a certain amount of time; if
they run too long, they can create much unexpected behavior. The exact results
of missing real-time deadlines depend on the detailed characteristics of the
I/O devices and the nature of the timing violation. This makes debugging
real-time problems especially difficult.
Related Topics