Thermodynamics of cell reactions | Electro Chemistry - FaradayŌĆÖs Laws of electrolysis | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Electro Chemistry
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Electro Chemistry
FaradayŌĆÖs Laws of electrolysis
FaradayŌĆÖs Laws of electrolysis
First Law
The mass of the substance (m) liberated at an electrode during
electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of charge (Q) passed
through the cell.
i.e m ╬▒ Q
We know that the charge is related to the current by the equation I =
Q/t ŌćÆ Q = It
Ōł┤ m ╬▒ It
(or)
m = Z It ..... (9.33)
Where is Z is known as the electro chemical equivalent of the substance
produced of the electrode.
When, I = 1A and t = 1sec, Q = 1C , in such case the equation (9.32)
becomes, (9.33)
ŌćÆ m = Z .....(9.34)
Thus, the electrochemical equivalent is defined as the amount of
substance deposited or liberated at the electrode by a charge of 1 coulomb.
Electro chemical equivalent and molar mass
Consider the following general electrochemical redox reaction
M n+ (aq) + ne- ŌåÆ M(s)
We can infer from the above equation that ŌĆśnŌĆÖ moles of electrons are
required to precipitate 1 mole of Mn+ as M(s).
The quantity of charge required to precipitate one mole of Mn+
= Charge of 'n' moles of electrons
= nF
In other words, the mass of substance deposited by one coulomb of charge
Electrochemical equivalent of Mn+ = Molarmass of M / n
(96500)
(or)
Z = Equivalent mass / 96500 .....(9.35)
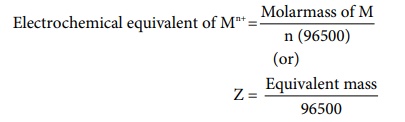
Second Law
When the same quantity of charge is passed through the solutions of
different electrolytes, the amount of substances liberated at the respective
electrodes are directly proportional to their electrochemical equivalents.
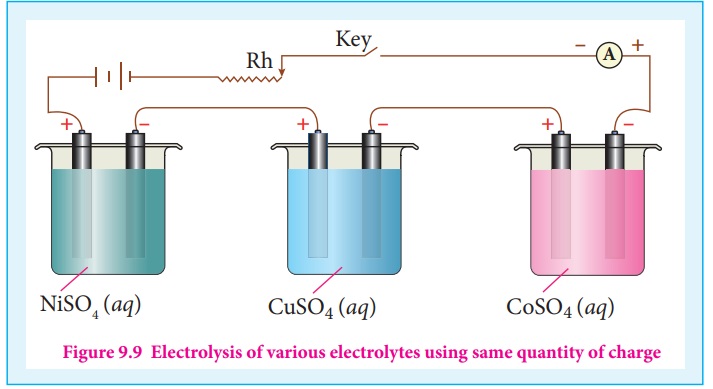
Let us consider three electrolytic cells connected in series to the same
DC electrical source as shown in the figure 9.9. Each cell is filled with a
different electrolytes namely NiSO4, CuSO4 and CoSO4,
respectively.
When Q coulomb charge is passed through the electrolytic cells the
masses of Nickel, copper and cobalt deposited at the respective electrodes be mNi
, mCu and mCo , respectively.
According to FaradayŌĆÖs second Law,
mNi ╬▒ ZNi,
mCu ╬▒ZCu and mCo ╬▒ ZCo
or
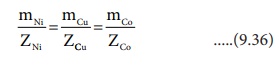
Example
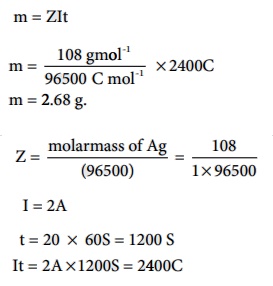
A solution of silver nitrate is electrolysed for 20 minutes with a
current of 2 amperes. Calculate the mass of silver deposited at the cathode.
Electrochemical reaction at cathode is Ag+ +e- ŌåÆ Ag
(reduction)
Evaluate yourself A solution of a salt of metal was
electrolysed for 15 minutes with a
current of 0.15 amperes. The mass of the metal deposited at the cathode is
0.783g. calculate the equivalent mass of the metal.
Related Topics