Electro Chemistry | Chemistry - Choose the correct answer | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Electro Chemistry
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 9 : Electro Chemistry
Choose the correct answer
Chemistry : Electro Chemistry
EVALUATION
Choose the correct answer:
1. The number of electrons that have a total charge of 9650 coulombs is
a) 6.22 ├Ś1023
b) 6.022 ├Ś1024
c) 6.022 ├Ś1022
d) 6.022 ├Ś10ŌłÆ34
Solution:
1F = 96500 C = 1 mole of eŌłÆ = 6.023 ├Ś1023 eŌłÆ
Ōł┤ 9650 C = [ 6.22 ├Ś1023 / 96500 ] ├Ś 9650 = 6.022├Ś1022
= 6.022├Ś1022
Option (C)
2. Consider the following half cell reactions:
Mn2+ + 2eŌłÆ ŌåÆ Mn E┬║ = -1.18V
Mn2+ ŌåÆ Mn3+ + e- E┬║ = -1.51V
The E for the reaction 3Mn2+ ŌåÆ Mn+2Mn3+ , and the possibility of the forward reaction are respectively.
a) 2.69V and spontaneous
b) -2.69 and non spontaneous
c) 0.33V and Spontaneous
d) 4.18V and non spontaneous
Solution:
Mn2+ + 2eŌłÆ ŌåÆ Mn (E┬║red) = -1.18V
2[Mn2+ ŌåÆ Mn3+ + e- ](E┬║ox) = ŌłÆ1.51V
3Mn2+ ŌåÆ Mn + 2Mn3+ E┬║cell?
E┬║cell = ( E┬║ox )+ ( E┬║red )
= ŌłÆ1.51 ŌłÆ1.18 and non spontaneous
= ŌłÆ2.69V
Since Eo is ŌĆōve ŌłåG is +ve and the given forward cell reaction is non ŌĆō spontaneous.
(Option (b))
3. The button cell used in watches function as follows
Zn (s) + Ag2 O (s) + H2 O (l) Ōåö 2 Ag (s) + Zn2+ (aq) + 2OHŌłÆ (aq) the half cell potentials are Ag2 O (s) + H2O (l) + 2eŌłÆ ŌåÆ 2Ag (s) + 2 OHŌłÆ (aq) E = 0.34V The cell potential will be
a) 0.84V
b) 1.34V
c) 1.10V
d) 0.42V
Solution:
Anodic oxidation: (Reverse the given reaction)
( Eoox ) = 0.76V cathodic reduction
Ōł┤ Ecell = ( Eoox )+ ( Eredo )
= 0.76 + 0.34 = 1.1V
= 1.1V
(Option (c))
4. The molar conductivity of a 0.5 mol dm-3 solution of AgNO3 with electrolytic conductivity of 5.76 ├Ś10ŌłÆ3 S cmŌłÆ1 at 298 K is
a) 2.88 S cm2 mol-1
b) 11.52 S cm2 mol-1
c) 0.086 S cm2 mol-1
d) 28.8 S cm2 mol-1
Solution:
╬ø = ╬║/M ├Ś10ŌłÆ3 molŌłÆ1 m3
= [( 5.76 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ3 S cmŌłÆ1 ├Ś10ŌłÆ3 ) / (0. 5)] molŌłÆ1m3
= [(5.76 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ3 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ3 ├Ś106 ) / (0.5)] S cmŌłÆ1molŌłÆ1 cm3 .
= 11.52 S cm2 molŌłÆ1
(Option (b))
5.
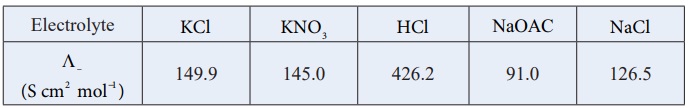
Calculate ╬ø┬║HOAC using appropriate molar conductances of the electrolytes listed above at infinite dilution in water at 25oC .
a) 517.2
b) 552.7
c) 390.7
d) 217.5
Solution:
( ╬ø┬║ )HoAC = ( ╬ø┬║)HCl + ( ╬ø┬║)NaOAC - ( ╬ø┬║)NaCl
= (426.2 + 91) ŌłÆ(126.5)
= 390.7
(Option (c))
6. Faradays constant is defined as
a) charge carried by 1 electron
b) charge carried by one mole of electrons
c) charge required to deposit one mole of substance
d) charge carried by 6.22 ├Ś1010 electrons.
Solution:
1F = 96500 C = charge of 1 mole of e- =
charge of 6.022 ├Ś1023 eŌłÆ
(Option (b))
7. How many faradays of electricity are required for the following reaction to occur MnO-4 ŌåÆ Mn2+
a) 5F
b) 3F
c) 1F
d) 7F
Solution:
7MnO-4 + 5eŌłÆ ŌåÆ Mn2+ + 4H2O
5 moles of electrons i.e., 5F charge is required.
(Option (a))
8. A current strength of 3.86 A was passed through molten Calcium oxide for 41minutes and 40 seconds. The mass of Calcium in grams deposited at the cathode is (atomic mass of Ca is 40g / mol and 1F = 96500C).
a) 4
b) 2
c) 8
d) 6
Solution:
m=ZIt
(41min 40sec = 2500 seconds)
Z = m/ (n ├Ś 96500) = 40 / (2 ├Ś 96500)
m = Zit
= ( 40 ├Ś 3.86 ├Ś 2500 ) / (2 ├Ś 96500)
= 2g
(Option (b))
9. During electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the time required to produce 0.1mole of chlorine gas using a current of 3A is
a) 55 minutes
b) 107.2 minutes
c) 220 minutes
d) 330 minutes
Solution:
m=ZIt
(mass of 1 mole of Cl2 gas = 71)
t = m/ ZI (Ōł┤mass of 0.1mole of Cl2 gas = 7.1 g molŌłÆ1 )
= 7.1 / [71/(2 ├Ś96500) ├Ś 3 ]
(2 Cl- ŌåÆ Cl2 +2e- )
= (2 ├Ś 96500 ├Ś 7.1) / (71├Ś 3)
= 6433.33sec
= 107.2 min
(Option (b))
10. The number of electrons delivered at the cathode during electrolysis by a current of 1A in 60 seconds is (charge of electron = 1.6 ├Ś10ŌłÆ19 C )
a) 6.22 ├Ś 1023
b) 6.022 ├Ś1020
c) 3.75 ├Ś1020
d) 7.48 ├Ś1023
Solution:
Q =It
= 1A├Ś60S
96500 C charge ŌēĪ 6.022 ├Ś1023 electrons
60 C charge ŌēĪ [ 6.022 ├Ś1023 / 96500 ] ├Ś 60
= 3.744 ├Ś1020 electrons
(Option (C))
11. Which of the following electrolytic solution has the least specific conductance
a) 2N
b) 0.002N
c) 0.02N
d) 0.2N
Solution:
In general, specific conductance of an electrolyte decreases with dilution. So, 0.002N solution has least specific conductance.
(Option (b))
12. While charging lead storage battery
a) PbSO4 on cathode is reduced to Pb
b) PbSO4 on anode is oxidised to PbO2
c) PbSO4 on anode is reduced to Pb
d) PbSO4 on cathode is oxidised to Pb
Solution:
Charging : anode : PbSO4 (s)+ 2eŌłÆ ŌåÆ Pb (s) + SO4-2 (aq)
Cathode : PbSO4 (s)+ 2H2 O (l) ŌåÆ PbO2 (s) + SO4-2 (aq)+2eŌłÆ
(Option (C))
13. Among the following cells
I) Leclanche cell
II) Nickel ŌĆō Cadmium cell
III) Lead storage battery
IV) Mercury cell
Primary cells are
a) I and IV
b) I and III
c) III and IV
d) II and III
Solution: Option (a)
14. Zinc can be coated on iron to produce galvanized iron but the reverse is not possible. It is because
a) Zinc is lighter than iron
b) Zinc has lower melting point than iron
c) Zinc has lower negative electrode potential than iron
d) Zinc has higher negative electrode potential than iron
Solution:
EoZn2+|Zn = ŌłÆ 0.76V and EoFe2+|Fe = ŌłÆ0.44V Zinc has higher negative electrode potential than iron, iron cannot be coated on zinc.
Option (d)
15. Assertion : pure iron when heated in dry air is converted with a layer of rust.
Reason : Rust has the composition Fe3 O4
a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c) assertion is true but reason is false
d) both assertion and reason are false.
Solution:
Both are false
i) Dry air has no reaction with iron
ii) Rust has the composition Fe2 O3 . x H2O
(Option (d))
16. In H2 -O2 fuel cell the reaction occurs at cathode is
a) O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + 4eŌłÆ ŌåÆ 4OHŌłÆ (aq)
b) H+ (aq) + OHŌłÆ (aq) ŌåÆ H2O (l)
c) 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) ŌåÆ 2H2O (g)
d) H+ + eŌłÆ ŌåÆ 1/2 H2
17. The equivalent conductance of M/36 solution of a weak monobasic acid is 6 mho cm2 equivalent ŌĆō1 and at infinite dilution is 400 mho cm2 equivalent ŌĆō1. The dissociation constant of this acid is
a) 1.25 ├Ś10ŌłÆ6
b) 6.25 ├Ś10ŌłÆ6
c) 1.25 ├Ś10ŌłÆ4
d) 6.25 ├Ś10ŌłÆ5
Solution:
╬▒ = ╬ø / ╬øo = 6/400
Ka =╬▒2C
= 6/400 ├Ś 6/400 ├Ś 1/36
= 6.25 ├Ś10ŌłÆ6
Option (b)
18. A conductivity cell has been calibrated with a 0.01M, 1:1 electrolytic solution (specific conductance ( ╬║ =1.25 ├Ś10ŌłÆ3 S cmŌłÆ1 ) in the cell and the measured resistance was 800 W at 25┬║ C . The cell constant is,
a) 10ŌłÆ1 c mŌłÆ1
b) 101 c mŌłÆ1
c) 1 c mŌłÆ1
d) 5.7 ├Ś10ŌłÆ12
Solution:
R = Žü. l/A
cell constant = R/Žü
= ╬║.R (1/ Žü =╬║ )
= 1.25 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ3 ╬®ŌłÆ1cmŌłÆ1 ├Ś 800 ╬®
= 1 cmŌłÆ1
Option (c)
19. Conductivity of a saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt AB (1:1 electrolyte) at 298K is 1 .85 ├Ś10ŌłÆ5 S mŌłÆ1 . Solubility product of the salt AB at 298K ( ╬ø┬║m )AB = 14 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ3 S m2 molŌłÆ1 .
a) 5.7 ├Ś10ŌłÆ12
b) 1.32 ├Ś10ŌłÆ12
c) 7.5 ├Ś10ŌłÆ12
d) 1.74 ├Ś10ŌłÆ12
Solution: Option (d)
20. In the electrochemical cell: Zn | ZnSO4 (0.01M) || CuSO4 (1.0M) | Cu , the emf of this Daniel cell is E1. When the concentration of is changed to 1.0M and that CuSO4 changed to 0.01M, the emf changes to E2. From the above, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2?
a) E1 < E2
b) E1 > E2
c) E2 Ōēź E1
d) E1 = E2
Solution:
Zn(s) ŌåÆ Zn2+ (aq) + 2e-
Cu2+ (aq)+2e- ŌåÆ Cu(s)
Zn(s) +Cu2+ (aq) ŌåÆ Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
Ecell =E┬║cell ŌĆō (0.0591/2) log ( [zn2+]/ [Cu2+] )
E1 =E┬║cell - 0.0591/2 log (10-2/1)
E1 =Eocell + 0.0591 ........(1)
E2 =E┬║cell - 0.0591/2 log (1/10-2)
E2 =Eocell - 0.0591 .........(2)
E1>E2
Option (b)
21. Consider the change in oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below:
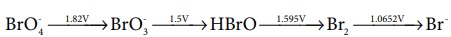
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is
a) Br2
b) BrOŌłÆ4
c) BrO3-
d) HBrO
Solution:
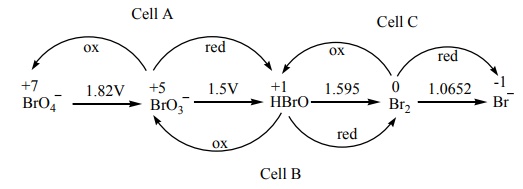
( Ecell )A =-1.82+1.5=-0.32V
( Ecell )B =-1.5+1.595=+0.095V
( Ecell )c =-1.595+1.0652=-0.529V
The species undergoing disproportionation is HBrO
(Option D)
22. For the cell reaction
2Fe3+ (aq) + 2lŌłÆ(aq) ŌåÆ 2Fe2+ (aq) + l2 (aq)
Eocell = 0.24V at 298K. The standard Gibbs energy (Ōłå, G┬║) of the cell reactions is :
a) -46.32 KJ molŌłÆ1
b) -23.16 KJ molŌłÆ1
c) 46.32 KJ molŌłÆ1
d) 23.16 KJ molŌłÆ1
Solution: Option (a)
23. A certain current liberated 0.504gm of hydrogen in 2 hours. How many grams of copper can be liberated by the same current flowing for the same time through copper sulphate solution
a) 31.75
b) 15.8
c) 7.5
d) 63.5
Solution: Option (b)
24. A gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1MY- and 1MZ- at 25oC . If the reduction potential of Z>Y>X, then
a) Y will oxidize X and not Z
b) Y will oxidize Z and not X
d) Y will oxidize both X and Z
d) Y will reduce both X and Z
Solution: Option (a)
25. Cell equation : A + 2B- ŌåÆ A2+ +2B;
A2+ + 2eŌłÆ ŌåÆ A ; E┬║ = + 0.34V and log10K = 15.6 at 300K for cell reactions find E for B+ + e ŌłÆ ŌåÆ B
a) 0.80
b) 1.26
c) -0.54
d) -10.94
Solution: Option (a)
PTA Question
Oneword:
1. Assertion : A small piece of
Zinc dissolved in dilute nitric acid but hydrogen gas not evolved.
Reason: HNO3 is an
oxidizing agent and this oxidizes hydrogen.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason is true. Reason is a correct explanation for
assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason is true. Reason is not correct explanation for the
assertion.
c) Assertion is correct but
Reason is wrong.
d)
Both assertion and Reason are wrong.
Answer: c)
2. Which of the following
statement is not correct with respect to electrolytic conductance?
a)
Conductivity increases with the decreases in Viscosity
b)
Conductivity increases with increase in temperature
c) Molar conductance of a
solution decreases with increase in dilution
d)
Conductance decrease with increase in temperature
Answer: c)
3. Which of the following is
Secondary cell?
a)
Laclanche cell
b) Lithium ion battery
c)
Mercury button cell
d)
both (a) and (c)
Answer: b)
4. The general representation of
a fuel cell is
a)
Fuel/Electrode/Electrolyte/Electrode/Oxidant
b)
Oxidatant/Electrode/Electrolyte/Electrode/Fuel
c)
Fuel/Electrode/Electrolyte/Electrode/Reductant
d)
Oxidant/Electrode/Electrolyte/Electrode/Reductant
Answer: a)
5. Laptops have
a)
Lead storage battery
b)
fuel cell
c)
Mercury button cell
d) Lithium ion-battery
Answer: d)
Related Topics