Chapter: 12th Physics : Current Electricity
Electric Current: Solved Example Problems
EXAMPLE 2.1
Compute the current in the wire if a charge of 120 C is flowing through a copper wire in 1 minute.
Solution
The current (rate of flow of charge) in the wire is
I = Q/t = 120/60 = 2A
EXAMPLE 2.2
If an electric field of magnitude 570 N C-1, is applied in the copper wire, find the acceleration experienced by the electron.
Solution:
E = 570 N C-1, e = 1.6 ├Ś 10-19 C, m = 9.11 ├Ś 10-31 kg and a = ?
F = ma = eE
a = eE/m = 570├Ś1 .6├Ś10ŌłÆ19/9 .11├Ś10-31
= 912 ├Ś10ŌłÆ19 ├Ś1031 / 9 .11
= 1.001 ├Ś 1014 m s-2
EXAMPLE 2.3
A copper wire of cross-sectional area 0.5 mm2 carries a current of 0.2 A. If the free electron density of copper is 8.4 ├Ś 1028 m-3 then compute the drift velocity of free electrons.
Solution
The relation between drift velocity of electrons and current in a wire of cross-sectional area A is
vd = I/ ne A
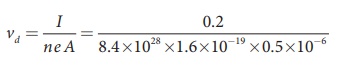
vd = 0.03 x 10-3 m s-1
EXAMPLE 2.4
Determine the number of electrons flowing per second through a conductor, when a current of 32 A flows through it.
Solution
I = 32 A , t = 1 s
Charge of an electron, e = 1.6 ├Ś 10-19 C
The number of electrons flowing per second, n =?
I = q/t = ne/t
n = It/e
n = 32├Ś1 / 1 .6├Ś10ŌłÆ19 C
n = 20 ├Ś 1019 = 2 ├Ś 1020 electrons
Related Topics