Differential Calculus | Mathematics - Angle between two curves | 12th Maths : UNIT 7 : Applications of Differential Calculus
Chapter: 12th Maths : UNIT 7 : Applications of Differential Calculus
Angle between two curves
Angle between two
curves
Definition 7.3
Angle between two curves, if they intersect, is defined as the
acute angle between the tangent lines to those two curves at the point of
intersection.
For the
given curves, at the point of intersection using the slopes of the tangents, we
can measure the acute angle between the two curves. Suppose y = m1
x + c1
and y = m2
x + c2
are two lines, then the acute angle ╬Ė
between these lines is given by,

where m1 and m2 are finite.
Remark
(i) If
the two curves are parallel at ( x1
, y1 )
, then m1 =
m2 .
(ii) If
the two curves are perpendicular at ( x1
, y1 )
and if m1 and m2 exists and finite then m1m2 = ŌłÆ1 .
Example 7.14
Find the
angle between y =
x2 and y = (x ŌłÆ 3)2.
Solution
Let us
now find the point of intersection of the two given curves. Equating x2 = (x ŌłÆ 3)2 we
get, x = 3/2. Therefore, the point of intersection is ( 3/2 ,9/4). Let ╬Ė be the
angle between the curves. The slopes of the curves are as follows :
For the
curve y = x2,

Example 7.15
Find the
angle between the curves y =
x2 and x = y2
at their points of intersection (0,0) and (1,1).
Solution
Let us
now find the slopes of the curves.
Let m1 be the slope of the curve y = x2,
then m = dy/dx = 2x .
Let m2 be the slope of the curve x = y2,
then m2 = dy/dx =1/2y .
Let ╬Ė1 and ╬Ė2 be the angles at (0,0) and (1,1) respectively.
At (0,
0) , we come across the indeterminate form of 0├Ś Ōł× in the denominator of tan╬Ė1
= 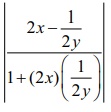 and so we follow the
limiting process.
and so we follow the
limiting process.
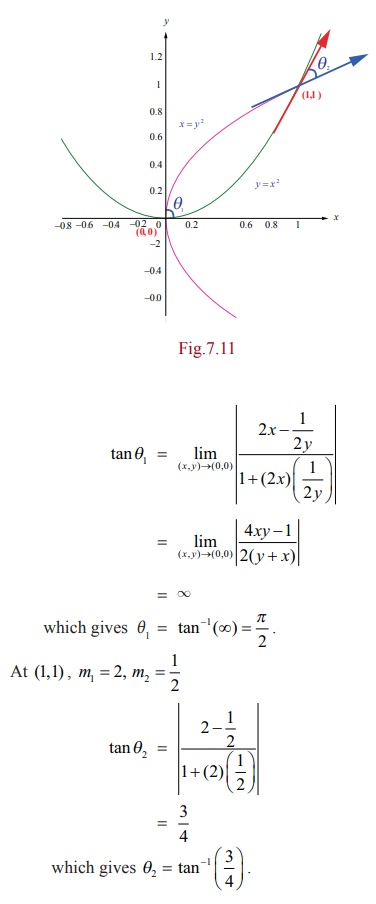
Example 7.16
Find the
angle of intersection of the curve y
= sin x with the positive x -axis.
Solution
When the
curve y = sin x intersects the positive x
-axis, y = 0 which gives, x = nŽĆ , n = 1, 2, 3,ŌĆ”. Now, dy/dx = cos x. The slope at x = nŽĆ
are cos(nŽĆ) = (ŌłÆ1)n. Hence, the required angle of intersection is
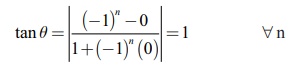
Example 7.17
If the
curves ax2 +
by2 =
1 and cx2 +
dy2 =
1 intersect each other orthogonally then, show that 1/a ŌĆō 1/b = 1/c ŌĆō 1/d .
Solution
Let the
two curves intersect at a point ( x0
, y0 ) . This leads to (a ŌłÆ c)x02 +
(b ŌłÆ d
) y02 =
0 .
Let us
now find the slope of the curves at the point of intersection ( x0 , y0 ) . The slopes of the curves are as follows :
For the
curve ax2 + by2 = 1, dy/ dx = ŌłÆ ax/by
For the
curve cx2 + dy2
= 1, dy/dx = ŌłÆ cx/dy
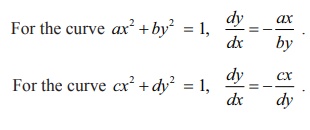
Now, if
two curves cut orthogonally, then the product of their slopes, at the point of
intersection (x0 ,
y0 ) , is
ŌłÆ1.
Hence, if the above two curves cut orthogonally at ( x0 ,
y0 ) then
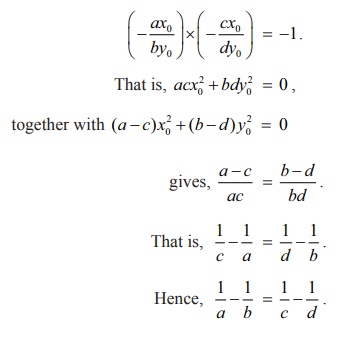
Remark
In the
above example, the converse is also true. That is assuming the condition 1/a ŌĆō 1/b = 1/c ŌĆō 1/d one can easily establish that the
curves cut orthogonally.
Example 7.18
Prove
that the ellipse x2 +
4y2 =
8 and the hyperbola x2 ŌłÆ
2y2 =
4 intersect orthogonally.
Solution
Let the
point of intersection of the two curves be (a
, b) . Hence,
a2 + 4b2 = 8 and a2 ŌłÆ 2b2 = 4 ... (4)
It is
enough to show that the product of the slopes of the two curves evaluated at (a , b)
is ŌłÆ1.
Differentiation
of x2 +
4 y2 =
8 with respect x , gives
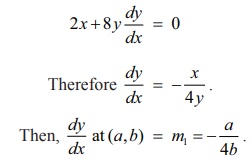
Differentiation
of x2 ŌłÆ 2y2 = 4
with respect to x, gives
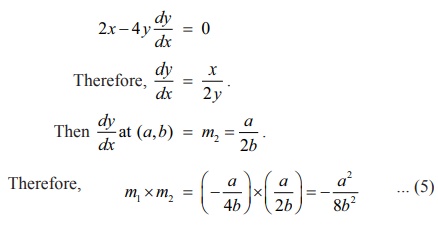
Applying
the ratio of proportions in (4), we get
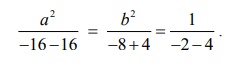
Therefore
a2/b2 = 32/4 = 8 . Substituting in (5), we get m1 ├Ś m2 = ŌłÆ1. Hence, the curves cut orthogonally.
Related Topics