Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 6 : Gravitation
Solved Example Problems for Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth
EXAMPLE 6.7
1. Calculate the value of g in the following two cases:
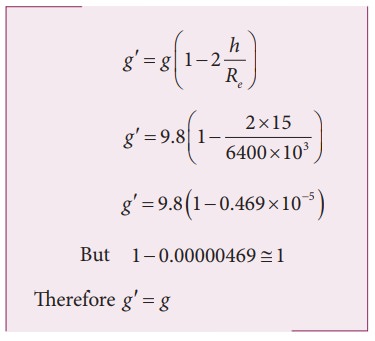
a) If a mango of mass ┬Į kg falls from a tree from a height of 15 meters, what is the acceleration due to gravity when it begins to fall?
Solution
b) Consider a satellite orbiting the Earth in a circular orbit of radius 1600 km above the surface of the Earth. What is the acceleration experienced by the satellite due to EarthŌĆÖs gravitational force?
Solution
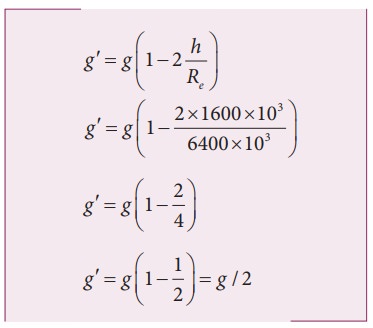
The above two examples show that the acceleration due to gravity is a constant near the surface of the Earth.
EXAMPLE 6.8
Find out the value of gŌĆ▓ in your school laboratory?
Solution
Calculate the latitude of the city or village where the school is located. The information is available in Google search. For example, the latitude of Chennai is approximately 13 degree.
g ŌĆ▓ = g ŌłÆŽē 2 R cos2 ╬╗
Here Žē2R = (2x3.14/86400)2 x (6400x103) = 3.4x10ŌłÆ2 mŌĆåsŌłÆ2.
It is to be noted that the value of ╬╗ should be in radian and not in degree. 13 degree is equivalent to 0.2268 rad.
gŌĆ▓ = 9.8 ŌłÆ ( 3.4 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ2 ) ├Ś ( cos 0.2268)2
g = 9.7677 mŌĆåsŌłÆ2
Related Topics