Gravitation | Physics - Short Questions and Answer | 11th Physics : UNIT 6 : Gravitation
Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 6 : Gravitation
Short Questions and Answer
Gravitation | Physics
Short Answer Questions
1. State KeplerŌĆÖs three laws.
Law of
orbits:
Each
planet moves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at one of the
foci.
Law of
area:
The
radial vector (line joining the Sun to a planet) sweeps equal areas in equal intervals
of time
Law of
period:
The
square of the time period of revolution of a planet around the Sun in its
Elliptical orbit is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of
The ellipse.
2. State NewtonŌĆÖs Universal law of gravitation.
Newton's law of gravitation states that a particle of mass M1 attracts any other particle of mass M2 in the universe with an attractive force. The strength of this force of attraction was found to be directly proportional to the product of their masses and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
3. Will the angular momentum of a planet be conserved? Justify your answer.
Yes,
Because 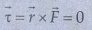
It
implies that angular momentum is a constant vector. The angular momentum of the
Earth about the Sun is constant throughout the motion.
4. Define the gravitational field. Give its unit.
The
gravitational force experienced by unit mass placed at that point.
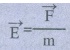
It is a
vector quantity.
5. What is meant by superposition of gravitational field?
Consider
ŌĆśn' particles of masses, m1 , m2 ...mn distributed
in space at positions r1,r2,r3 ....etc, with
respect to point P. The total gravitational field at a point P due to all the
masses is given by the vector sum of the gravitational field due to the
individual masses. This principle is known as superposition of gravitational
fields.
6. Define gravitational potential energy.
ŌŚÅ The
gravitational potential energy is defined as the work done to bring the mass m2
from infinity to a distance ŌĆśr' in the gravitational field of mass m1.
ŌŚÅ Its
unit is joule.
7. Is potential energy the property of a single object? Justify.
ŌŚÅ Potential
energy is a property of a system rather than of a single object due to its
physical position.
ŌŚÅ Because gravitational potential energy depends on relative position. So, a reference level at which to set the potential energy equal to zero.
8. Define gravitational potential.
The
gravitational potential at a distance r due to a mass ŌĆśm' is defined as the
amount of work required to bring unit mass from infinity to the distance r.
9. What is the difference between gravitational potential and gravitational potential energy?
Gravitational
potential: The amount of work done in bringing a body of unit mass from
infinity to that point without acceleration. V = -GM/R. unit J/kg
Gravitational
potential Energy:
ŌŚÅ The
energy stored in the body at that point.
ŌŚÅ If the
position of the body changes due to force acting on it, then change in its
potential energy is equal to the amount of work done on the body by the forces acting
on it.
U = ŌłÆGMm /
R unit (J)
10. What is meant by escape speed in the case of the Earth?
The
minimum speed required by an object to escape from Earth's gravitational field.
Ve = 11.2 kms-1
11. Why is the energy of a satellite (or any other planet) negative?
ŌŚÅ The
negative sign in the total energy implies that the satellite is bound to the
Earth and it cannot escape from the Earth.
ŌŚÅ As h
approaches Ōł×, the total energy tends to zero.
ŌŚÅ The
satellite is completely free from the influence of Earth's gravity and is not
bound to Earth at large distances.ŌĆā
12. What are geostationary and polar satellites?
Geostationary
satellites:
ŌŚÅ The
satellites revolving the Earth at the height of 36000 km above the equator, are
appear to be stationary when seen from Earth is called geo-stationary
satellites.
Polar
satellites:
ŌŚÅ The satellites which revolve from north to south of the Earth at the height of 500 to 800 km from the Earth surface are called Polar satellites.
13. Define weight
ŌŚÅ The
weight of an object is defined as the downward force whose magnitude W is equal
to that of upward force that must be applied to the object to hold it at rest
or at constant velocity relative to the earth.
ŌŚÅ The
magnitude of weight of an object is denoted as, W=N=mg.
14. Why is there no lunar eclipse and solar eclipse every month?
ŌŚÅ Moon's
orbit is tilted 5┬░ with respect to Earth's orbit.
ŌŚÅ Due to
this 5┬░ tilt only during, certain periods of the year, the Sun, Earth and Moon
align in straight line leading to either lunar eclipse or solar eclipse
depending on the alignment.
15. How will you prove that Earth itself is spinning?
ŌŚÅ The
Earth's spinning motion can be proved by observing star's position over a
night.
ŌŚÅ Due to
Earth's spinning motion, the stars in sky appear to move in circular motion
about the pole star.
Related Topics