Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 6 : Gravitation
Interesting Astronomical Facts
Interesting Astronomical Facts
1. Lunar eclipse and measurement of shadow of Earth
On January 31, 2018 there was a total lunar eclipse which was observed from various places including Tamil Nadu. It is possible to measure the radius of shadow of the Earth at the point where the Moon crosses. Figure 6.31 illustrates this.
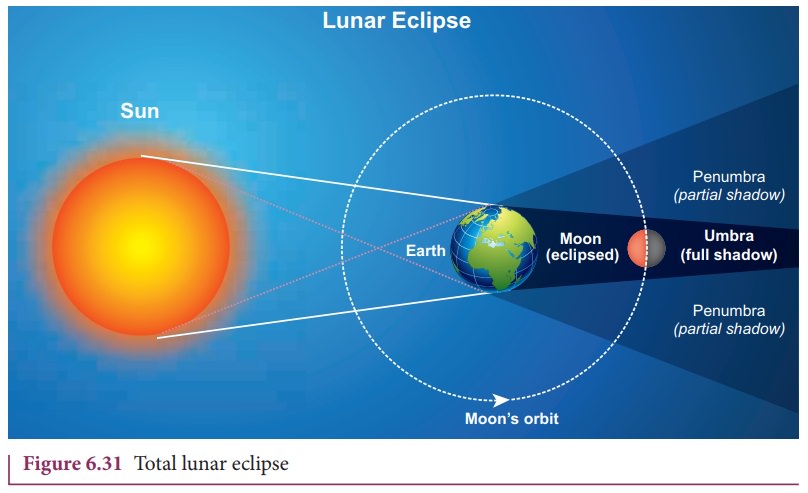
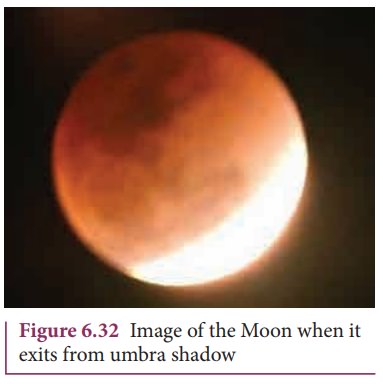
When the Moon is inside the umbra shadow, it appears red in color. As soon as the Moon exits from the umbra shadow, it appears in crescent shape. Figure 6.32 is the photograph taken by digital camera during MoonŌĆÖs exit from the umbra shadow.
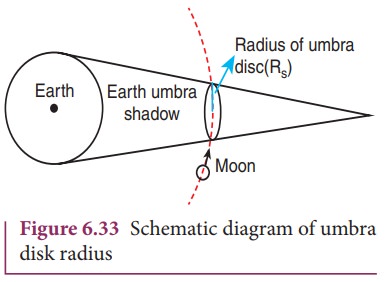
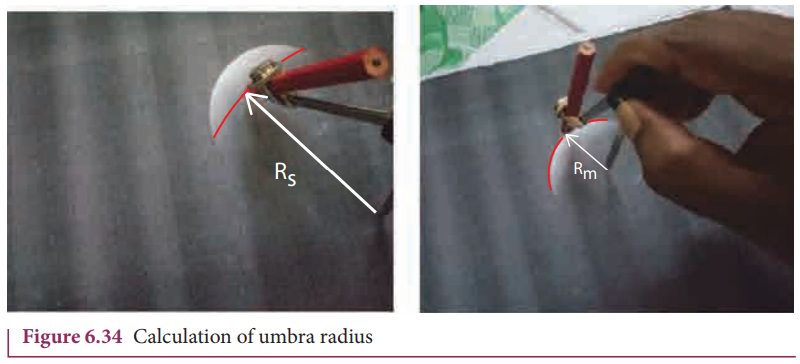
By finding the apparent radii of the EarthŌĆÖs umbra shadow and the Moon, the ratio of the these radii can be calculated. This is shown in Figures 6.33 and 6.34.
The apparent radius of EarthŌĆÖs umbra shadow = Rs = 13.2 cm
The apparent radius of the Moon = Rm= 5.15 cm
The ratio Rs/Rm Ōēł 2.56
The radius of the EarthŌĆÖs umbra shadow is Rs = 2.56 x Rm
The radius of Moon Rm = 1737 km
The radius of the EarthŌĆÖs umbra shadow is Rs = 2.56x1737km ~ŌēĪ4446 km.
The correct radius is 4610 km.
The percentage of error in the calculation = [ (4610 ŌĆō 4446) / 4610 ] x 100 = 3.5% .
The error will reduce if the pictures taken using a high quality telescope are used. It is to be noted that this calculation is done using very simple mathematics.
Early astronomers proved that Earth is spherical in shape by looking at the shape of the shadow cast by Earth on the Moon during lunar eclipse.
2. Why there are no lunar eclipse and solar eclipse every month?
If the orbits of the Moon and Earth lie on the same plane, during full Moon of every month, we can observe lunar eclipse.
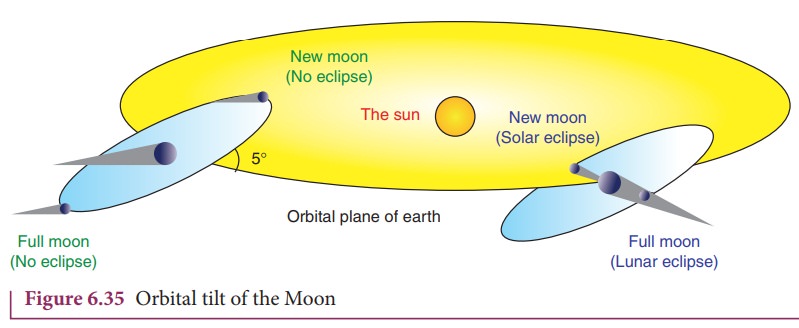
If this is so during new Moon we can observe solar eclipse. But MoonŌĆÖs orbit is tilted 5┬░ with respect to EarthŌĆÖs orbit. Due to this 5┬░ tilt, only during certain periods of the year, the Sun, Earth and Moon align in straight line leading to either lunar eclipse or solar eclipse depending on the alignment. This is shown in Figure 6.35
3. Why do we have seasons on Earth?
The common misconception is that ŌĆśEarth revolves around the Sun, so when the Earth is very far away, it is winter and when the Earth is nearer, it is summerŌĆÖ.
Actually, the seasons in the Earth arise due to the rotation of Earth around the Sun with 23.5┬░ tilt. This is shown in Figure 6.36
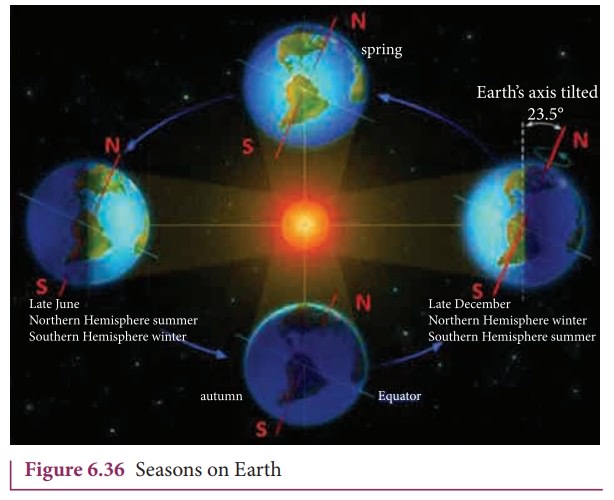
Due to this 23.5┬░ tilt, when the northern part of Earth is farther to the Sun, the southern part is nearer to the Sun. So when it is summer in the northern hemisphere, the southern hemisphere experience winter.
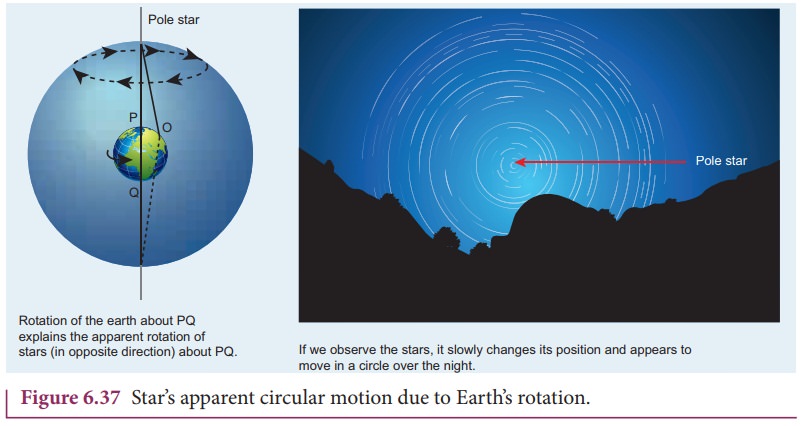
4. StarŌĆÖs apparent motion and spinning of the Earth
The EarthŌĆÖs spinning motion can be proved by observing starŌĆÖs position over a night. Due to EarthŌĆÖs spinning motion, the stars in sky appear to move in circular motion about the pole star as shown in Figure 6.37
Related Topics