Chapter: Ophthalmology: Cornea
Problems with Contact Lenses
Problems with Contact Lenses
Etiology:
These problems occur either withpoorly seated rigid contact lensesthat
rub on the surface of the cornea or from overwearing
soft contact lenses.
If contact lenses are worn for extended
periods of time despite symptoms, severe inflammation, corneal ulceration, and
vascularization of the corneal periphery may result.
Symptoms:
Patients find the contact lenses increasingly
uncomfortable andnotice worsening of their vision. These symptoms are
especially pronounced after removing the contact lenses as the lenses mask the
defect in the corneal epithelium.
Diagnostic considerations:
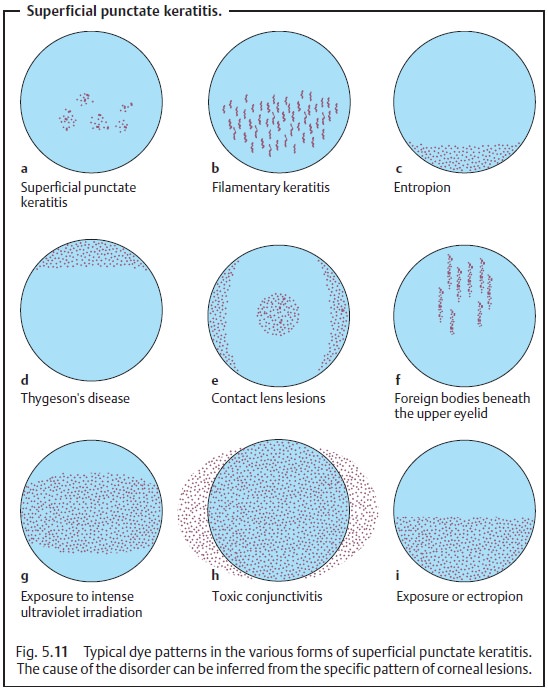
The ophthalmologist will detect typical
cornealchanges after applying fluorescein dye (Fig. 5.11e). Keratoconjunctivitis on the superior limbus with formation of
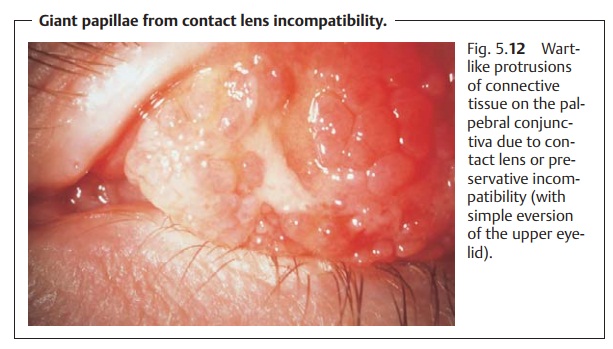
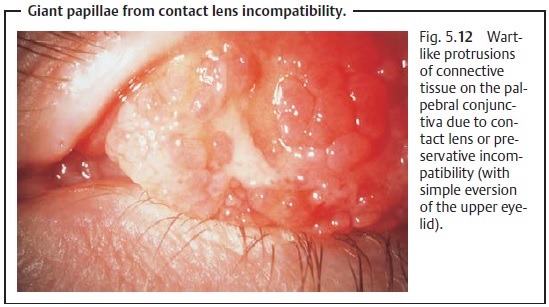
giant papillae, wart-like protrusions of connective tissue frequently observed
on the superior tarsus (Fig. 5.12),
are signs of contact lens or preservative incompatibility.
Treatment:
The patient should temporarily discontinue
wearing the contactlenses, and inflammatory changes should be controlled with
steroids until the irritation of the eye has abated.
Protracted therapy with topical steroids
should be monitored regularly by an ophthalmologist as superficial epithelial
defects heal poorly under steroid therapy. Protracted high-dosage steroid
therapy causes a secondary increase in intraocular pressure and cataract in
one-third of all patients.
The specific ophthalmologic findings will
determine whether the patient should be advised to permanently discontinue
wearing contact lenses or whether changing contact lenses and cleaning agents
will be sufficient.
Related Topics