Chapter: Ophthalmology: Cornea
Exposure Keratitis
Exposure Keratitis
Definition
Keratitis resulting from drying of the cornea
in the case of lagophthalmos.
Epidemiology:
Exposure keratitis is a relatively frequent
clinical syndrome.For example, it may occur in association with facial
paralysis following a stroke.
Etiology:
Due tofacial
nerve palsy, there is insufficient closure of the eyelidsover the eyeball
(lagophthalmos), and the inferior third to half of the cornea remains exposed
and unprotected (exposure keratitis). Superficial punctate keratitis (see
above) initially develops in this region and can progress to cor-neal erosion
(see Fig. 18.5) or ulcer.
Other causes for exposure
keratitis without facial nerve palsy include:
❖ Uncompensated exophthalmos in Graves’
disease.
❖Insufficient eyelid closure following eyelid
surgery to correct ptosis.
❖Insufficient eye care in patients receiving
artificial respiration on the intensive care ward.
Symptoms:
Similar to superficial punctate keratitis (although
usually moresevere) but unilateral.
Diagnostic considerations:
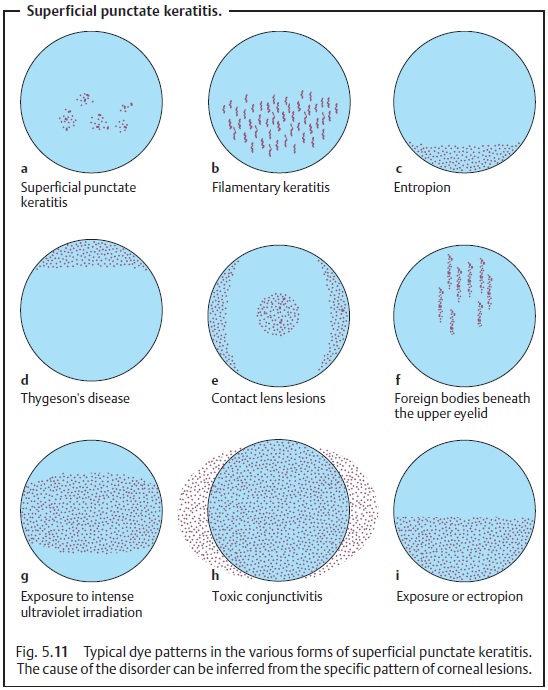
Application of fluorescein dye will reveal a
typical pattern of epithelial lesions (Fig. 5.11i).
Treatment:
Application of artificial tears is usually not
sufficient where eye-lid motor function is impaired. In such cases, high-viscosity gels, ointmentpackings (for antibiotic
protection), and a watch glass bandage are
required.The watch glass bandage must be applied so as to create a moist
airtight chamber that prevents further desiccation of the eye (see Fig. 2.9). In the pres-ence of persistent
facial nerve palsy that shows no signs of remission, lateraltarsorrhaphy is the treatment of choice. The same applies to
treatment ofexposure keratitis due to insufficient eyelid closure from other
causes (see Etiology).
Poor corneal care in exposure keratitis can
lead to superficial punctate keratitis, erosion, bacterial superinfection with
corneal ulcer, and finally to corneal perforation.
Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
This is one of the most frequent causes of
superficial keratitis. The syndrome itself is attributable to dry eyes due to
lack of tear fluid.
Related Topics