Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Monochrome picture tube
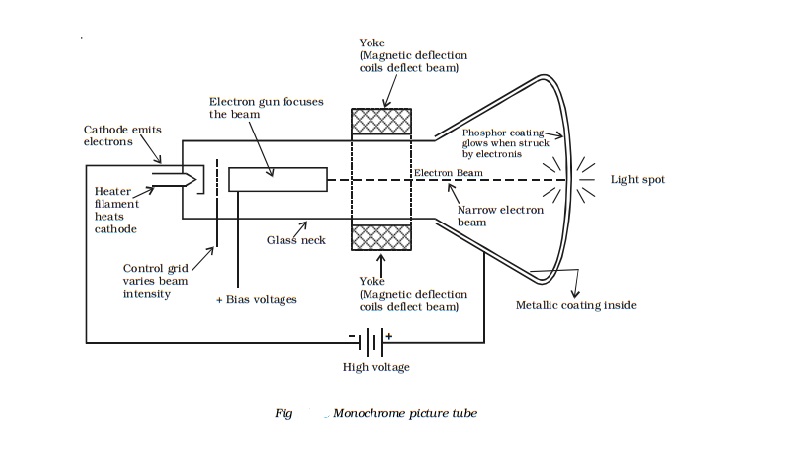
Monochrome picture tube
The picture tube is a special form of cathode
ray tube, the face plate of which serves as a screen of the television
receiver. The various parts of a monochrome picture tube are shown in Fig . The cathode ray tube (CRT) is housed in a bell-shaped glass enclosure. A
filament heats a cathode that emits electrons. The negatively charged electrons
are attracted and accelerated by positive-bias voltages on the elements in an
electron gun assembly. The electron gun also focuses the electrons into narrow
beam.
A control grid that is made negative with
respect to the cathode, controls the intensity of the electron beam and
brightness of the spot it makes. The beam is accelerated towards the screen by
a very high voltage applied to an internal metallic coating called aquadag. The
face or front of the picture tube is coated internally with a phosphor, that glows
and produces white light, when it is struck by the electron beam.
Around the neck of the picture tube is a structure of magnetic
coils called the deflecting yoke. The horizontal and vertical current linear
saw tooth waves generated by the sweep and synchronising circuits are applied
to the yoke coils. This produces the magnetic field inside the tube that
influence the position of the electron beam. When the electrons flow, a
magnetic field is produced around the conductor through which the current flows.
In a CRT, the electron beam is moved or deflected by the magnetic field
produced by the deflection coils in the yoke. Thus the electron beam is swept
across the face of the picture tube.
As the beam is being swept across the face of the tube to trace out
the scene, the intensity of the electron beam is varied by the luminance or Y
signal. The Y signal is applied to the cathode or in some cases to the control
grid. The control grid is an element in the electron gun, that is negatively
biased with respect to the cathode. By varying the grid voltage, the beam can
be made weaker or stronger, thereby varying the intensity of the light spot
produced by the beam, when it strikes the phosphor. Any shade of grey from
white to black can be reproduced.
Related Topics