Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Hallwachs Experiment - photo electric effect
Photoelectric emission is the
phenomena by which a good number of substances, chiefly metals, emit electrons
under the influence of radiation such as γ rays, X-rays, ultraviolet and even visible
light. This effect was discovered by Heinrich Hertz in 1887 while working with
resonance electrical circuits. A year later, Hallwachs, Elster and Geitel
investigated the phenomenon with a simple experimental arrangement.
Hallwachs
Experiment
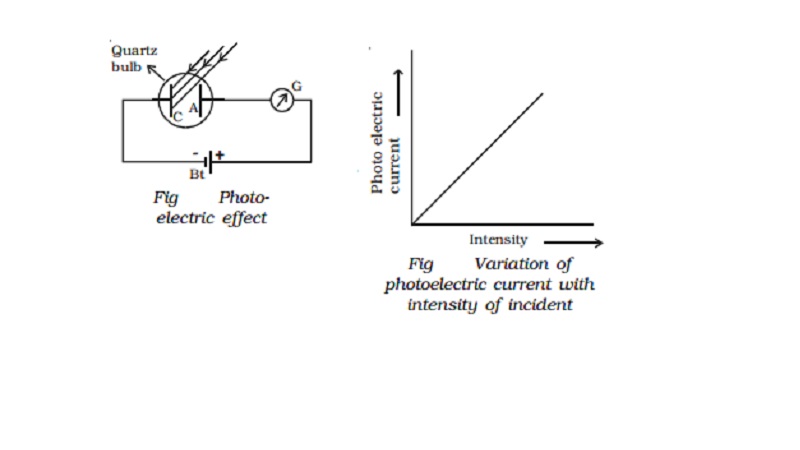
Hallwachs experimental set-up to study the
photo electric effect is shown in Fig It
consists of an evacuated quartz bulb with two zinc plates cathode C and anode
A. The plates are connected to a battery and a sensitive galvanometer. In the
absence of any
radiation incident on the
plates, there is no flow of current and hence there is no deflection in the
galvanometer.
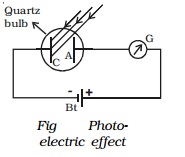
But, when an electro magnetic radiation like
ultraviolet radiation is allowed to fall on the plate C which is connected to
the negative terminal of the battery, a current begins to flow, indicated by
the deflection in the galvanometer (G). But, when ultraviolet radiation is made
to fall on A, there is no deflection in the galvanometer. These observations
reveal that the particles emitted by the plate C due to the photoelectric
effect are negatively charged. These particles were found to be electrons. The
observed current known as the photoelectric current is due to the flow of
electrons.
After the study of photoelectric effect by
Hallwachs, scientists J.J.Thomson, Lenard, Richardson, Compton did a series of
experiments to study the relationship between photoelectric current, intensity
of incident radiation, velocity and the kinetic energy of the photo electrons,
and their dependence on the wave length of incident radiation used.
Effect of intensity of incident radiation on
photo electric current
Keeping the
frequency of the Photo
electric incident radiation and
the potential difference between the cathode and the
anode at constant values, the intensity of incident radiation is varied. The
corresponding photoelectric current is
measured in the microammeter.
It
is found that the photo electric current increases
linearly with the intensity of incident radiation (Fig).
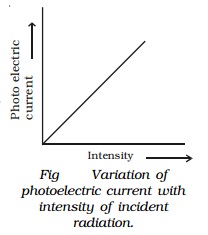
Since the photoelectric current is directly
proportional to the number of photoelectrons emitted per second, it implies
that the number of photoelectrons emitted per second is proportional to the
intensity of incident radiation.
Related Topics