Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Intermolecular or interatomic forces
Intermolecular or interatomic
forces
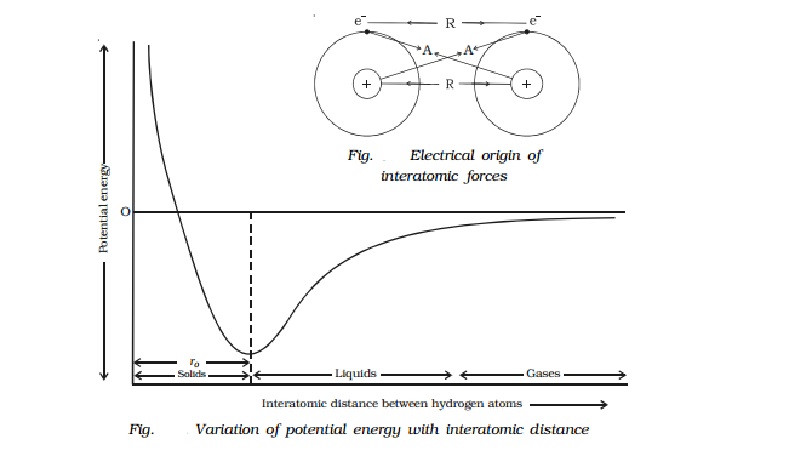
Consider two isolated hydrogen atoms moving towards each other as
shown in Fig..
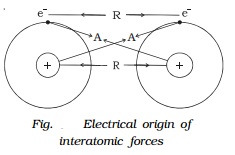
As they approach each other, the following interactions are
observed.
1.
Attractive force A between the nucleus of one
atom and electron of the other. This attractive force tends to decrease the
potential energy of the atomic system.
2.
Repulsive force R between the nucleus of one
atom and the nucleus of the other atom and electron of one atom with the
electron of the other atom. These repulsive forces always tend to increase the
energy of the atomic system.
There is a universal tendency of all systems to
acquire a state of minimum potential energy. This stage of minimum potential
energy corresponds to maximum stability.
If the net effect of the forces of attraction
and repulsion leads to decrease in the energy of the system, the two atoms come
closer to each other and form a covalent bond by sharing of electrons. On the
other hand, if the repulsive forces are more and there is increase in the
energy of the system, the atoms will repel each other and do not form a bond.
The variation of potential energy with interatomic distance between
the atoms is shown in Fig..
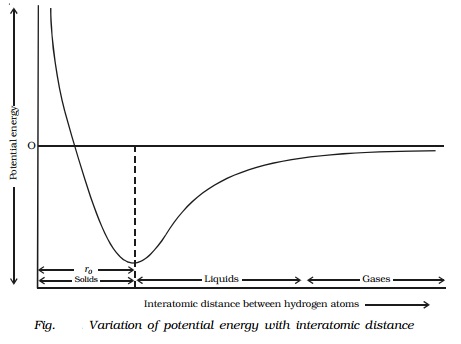
It is evident from the graph that as the atoms
come closer i.e. when the interatomic distance between them decreases, a stage
is reached when the potential energy of the system decreases. When the two
hydrogen atoms are sufficiently closer, sharing of electrons takes place
between them and the potential energy is minimum. This results in the formation
of covalent bond and the interatomic distance is ro.
In solids the interatomic distance is ro and in the case of liquids
it is greater than ro. For
gases, it is much greater than ro.
The forces acting between the atoms due to electrostatic
interaction between the charges of the atoms are called interatomic forces.
Thus, interatomic forces are electrical in nature. The interatomic forces are active
if the distance between the two atoms is of the order of atomic size ≈ 10-10 m. In the case of molecules, the range
of the force is of the order of 10-9
m.
Related Topics