Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Explanation of Nuclear binding energy curve
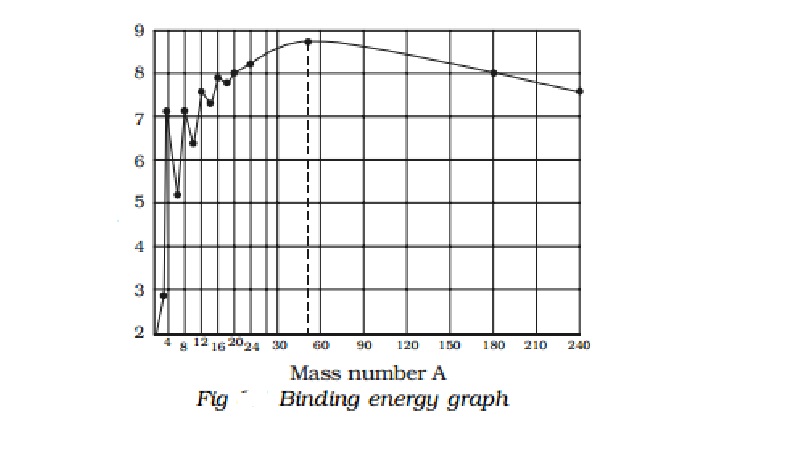
Nuclear Binding energy
When the protons and neutrons combine to form a
nucleus, the mass that disappears (mass defect, ∆m) is converted into an equivalent amount of energy (∆mc2). This energy is called the binding energy of the
nucleus.
Binding energy = [ZmP
+ Nmn - m] c2
= ∆m c2
The binding energy of a nucleus determines its
stability against disintegration. In other words, if the binding energy is
large, the nucleus is stable and vice versa.
The binding energy per nucleon is
BE/ A = Binding energy of the nucleus
/ Total number of nucleons
It is found that the binding energy per nucleon
varies from element to element. A graph is plotted with the mass number A of
the nucleus along the X−axis and
binding energy per nucleon along the Y-axis (Fig).
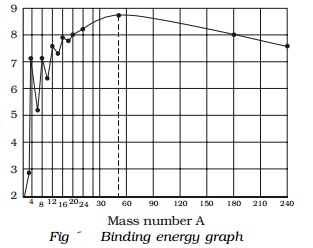
Explanation of binding energy curve
i.
The binding energy per nucleon increases
sharply with mass number A upto 20. It increases slowly after A = 20. For
A<20, there exists recurrence of peaks corresponding to those nuclei, whose
mass numbers are multiples of four and they contain not only equal but also
even number of protons and neutrons. Example: 2He4, 4Be8,
6C12, 8O16, and 10Ne20.
The curve becomes almost flat for mass number between 40 and 120. Beyond 120,
it decreases slowly as A increases.
ii.
The
binding energy per
nucleon reaches a
maximum of MeV at A=56,
corresponding to the iron nucleus (26Fe56). Hence, iron
nucleus is the most stable.
iii.
The average binding energy per nucleon is about
8.5 MeV for nuclei having mass number ranging between 40 and 120. These elements
are comparatively more stable and non radioactive.
iv.
For higher mass numbers the curve drops slowly
and the BE/A is about 7.6 MeV for uranium. Hence, they are unstable and
radioactive.
v.
The lesser amount of binding energy for lighter
and heavier nuclei explains nuclear fusion and fission respectively. A large
amount of energy will be liberated if lighter nuclei are fused to form heavier
one (fusion) or if heavier nuclei are split into lighter ones (fission).
Related Topics