Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Bainbridge mass spectrometer - Determination of isotopic masses of nuclei
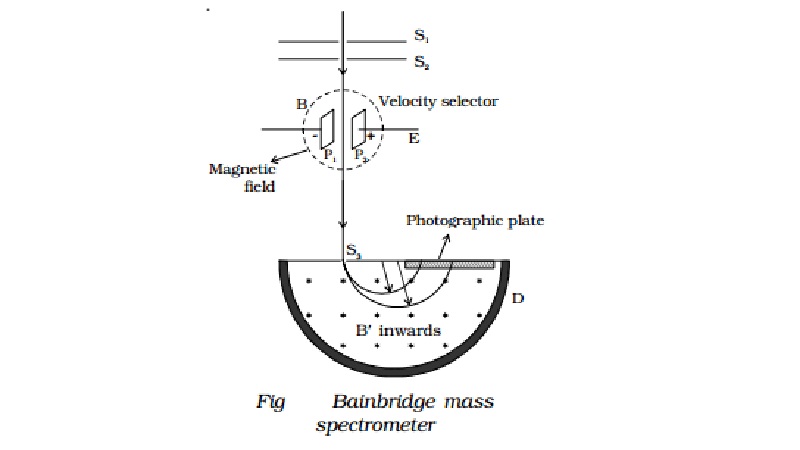
Bainbridge mass spectrometer -
Determination of isotopic masses of nuclei
Bainbridge mass spectro-meter is an instrument
used for the accurate determination of atomic masses. A schematic diagram of
this spectrometer is shown in Fig.
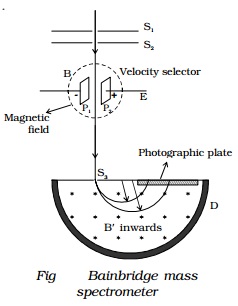
Atoms with one
or more electrons removed,
have a net positive charge and they become positive
ions. A beam of positive ions produced in a discharge tube is collimated into a
fine beam by two narrow slits S1 and S2. This fine beam enters into a velocity selector. The velocity selector allows
the ions of a particular velocity to come out of it, by the combined action of
an electric and a magnetic field. The velocity selector consists of two plane
parallel plates P1 and P2, which produces a uniform
electric field E and an electromagnet, to produce uniform magnetic field B
(represented by the dotted circle). These two fields are at right angles to
each other and to the direction of the beam.
The electric field and magnetic field are so
adjusted that the deflection produced by one field is nullified by the other, so
that the ions do not suffer any deflection within the velocity selector. Let E and B be the electric field intensity and magnetic induction
respectively and q be the charge of
the positive ion. The force exerted by the electric field is equal to qE and the
force exerted by the magnetic field is equal to Bqv where v is the
velocity of the positive ion.
qE = Bqv
v = E/B
Only those ions having this velocity v, pass out of the velocity selector and
then through the slit S3, to enter the evacuated
chamber D. These positive ions having the same velocity are
subjected to another strong uniform magnetic field of induction B′ at right angles to the plane of the paper
acting inwards. These ions are deflected along circular path of radius R and strike the photographic plate. The
force due to magnetic field B′qv
provides the centripetal force.
B′qv = mv2
R
B ′qR m = v
Substituting v = E/B
m = BB ′qR
E
Ions with different masses trace semi-circular
paths of different radii and produce dark lines on the plate. The distance
between the opening of the chamber and the position of the dark line gives the
diameter 2R from which radius R can be calculated.
Since q,
B, B′, E and R are known, the mass of the positive
ions and hence isotopic masses can be calculated.
Related Topics