Chapter: Embedded Systems
Elements of Embedded Systems
ELEMENTS
OF EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Unit
Structure
Objectives
1. Introduction
2. Elements of Embedded Systems.
3. Case studies (examples)
Washing machine
Microwave owen
Automotive Embedded System (AES)
4. Review questions
5. References & further reading
OBJECTIVES
After learning this chapter you will be able to:
Define and describe the elements of an embedded
system
Understand how embedded system works with the
help of two case studies:
Washing
Machine
Microwave
Owen
1. INTRODUCTION
The previous chapter was an introduction to the
world of embedded systems and helped us define what is an embedded system.
This chapter introduces us to the elements of an
embedded system and explains how embedded system works with the help of two
case studies.
2. ELEMENTS
OF EMBEDDED SYSTEMS.
As defined earlier, an embedded system is a
combination of 3 things:
Hardware
Software
Mechanical Components
And it is supposed to do one specific task only.
Diagrammatically an embedded system can be
represented as follows:
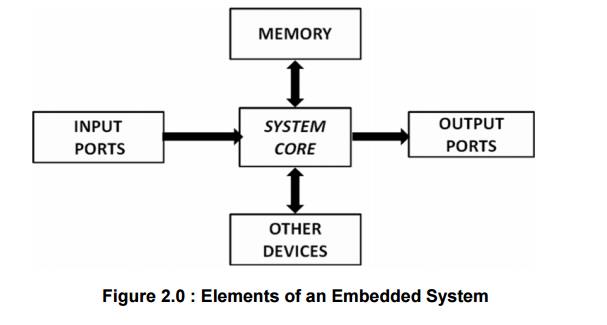
Embedded
systems are basically designed to regulate a physical variable (such Microwave
Oven) or to manipulate the state of some devices by sending some signals to the
actuators or devices connected to the output port system (such as temperature
in Air Conditioner), in response to the input signal provided by the end users
or sensors which are connected to the input ports.
Hence the
embedded systems can be viewed as a reactive system.
Examples
of common user interface input devices are keyboards, push button, switches,
etc.
The memory
of the system is responsible for holding the code (control algorithm and other
important configuration details).
An
embedded system without code (i.e. the control algorithm) implemented memory
has all the peripherals but is not capable of making decisions depending on the
situational as well as real world changes.
Memory for
implementing the code may be present on the processor or may be implemented as a
separate chip interfacing the processor In a controller based embedded system,
the controller may contain internal memory for storing code
Such controllers are called Micro-controllers
with on-chip ROM, eg. Atmel AT89C51.
3. CASE
STUDIES (EXAMPLES)
Here are some case studies on some commonly used
embedded systems that will help to better understand the concept.
3.1 Washing Machine
Let us see the important parts of the washing
machine; this will also help us understand the working of the washing machine:
Water
inlet control valve: Near the
water inlet point of the washing
there is water inlet control valve. When you load the clothes in washing
machine, this valve gets opened automatically and it closes automatically
depending on the total quantity of the water required. The water control valve
is actually the solenoid valve.
Water
pump: The water pump circulates water through the washing machine. It works in two
directions, re-circulating the water during wash cycle and draining the water
during the spin cycle.
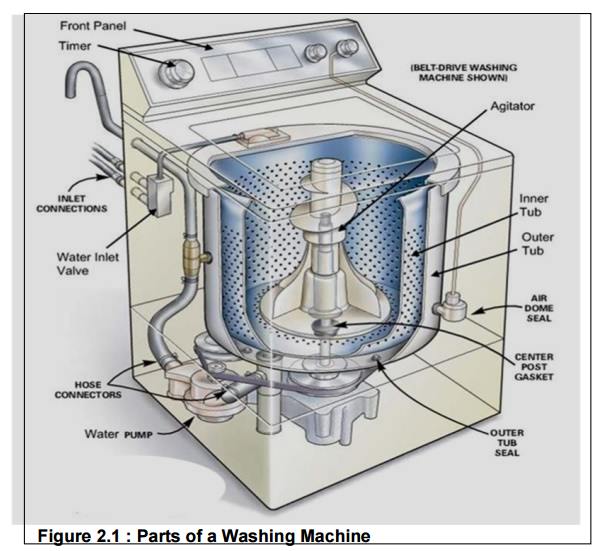
Tub: There are two types of tubs in the washing washing machine: inner and outer. The clothes are loaded in the inner tub,
where the clothes are washed, rinsed and dried. The inner tub has small holes
for draining the water. The external tub covers theinner tub and supports it
during various cycles of clothes washing.
Agitator or rotating disc: The agitator is located inside the tub of the washing machine. It is the
important part of the washing machine that actually performs the cleaning
operation of the clothes. During the wash cycle the agitator rotates
continuously and produces strong rotating currents within the water due to
which the clothes also rotate inside the tub. The rotation of the clothes
within water containing the detergent enables the removal of the dirt particles
from the fabric of the clothes. Thus the agitator produces most important
function of rubbing the clothes with each other as well as with water.
In some washing machines, instead of the long agitator,
there is a disc that contains blades on its upper side. The rotation of the
disc and the blades produce strong currents within the water and the rubbing of
clothes that helps in removing the dirt from clothes.
Motor of the washing machine: The motor is coupled to the agitator or the disc and produces it
rotator motion. These are multispeed motors, whose speed can be changed as per
the requirement. In the fully automatic washing machine the speed of the motor
i.e. the agitator changes automatically as per the load on the washing machine.
Timer: The timer helps setting the wash time for the
clothes manually. In the automatic
mode the time is set automatically depending upon the number of clothes inside
the washing machine.
Printed
circuit board (PCB): The PCB
comprises of the various electronic
components and circuits, which are programmed to perform in unique ways
depending on the load conditions (the condition and the amount of clothes
loaded in the washing machine). They are sort of artificial intelligence
devices that sense the various external conditions and take the decisions
accordingly. These are also called as fuzzy logic systems. Thus the PCB will
calculate the total weight of the clothes, and find out the quantity of water
and detergent required, and the total time required for washing the clothes.
Then they will decide the time required for washing and rinsing. The entire
processing is done on a kind of processor which may be a microprocessor or
microcontroller.
Drain pipe: The drain pipe enables removing the dirty water from the washing that has been used for the washing purpose.
3.2
Microwave Owen
Let us see the important parts of the microwave
oven; this will also help us understand the working of the washing machine:
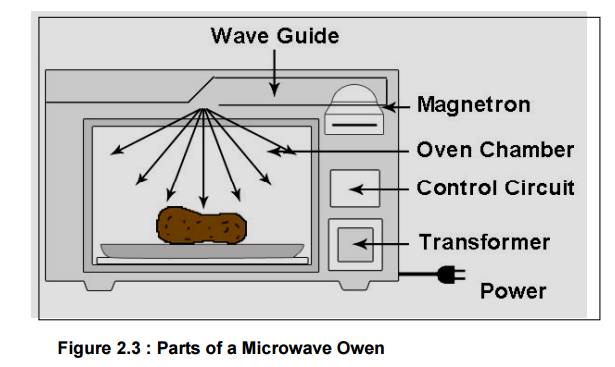
A microwave oven consists of:
A high voltage transformer, which passes energy
to the magnetron
A cavity magnetron,
A Control circuit with a microcontroller,
A waveguide, and
A cooking chamber
A Transformer transfers electrical energy
through a circuit by magnetic coupling without using motion between parts.
These are used for supplying power to the magnetron.
A Cavity
magnetron is a microwave antenna placed in a vacuum tube and oscillated in
an electromagnetic field in order to produce high GHz microwaves. Magnetrons
are used in microwave ovens and radar systems.
A control
circuit with a microcontroller is integrated on a circuit board. The
microcontroller controls the waveguide and the entire unit so the microwaves
are emitted at a constant rate.
A Waveguide
is any linear structure that guides electromagnetic waves for the purpose of
transmitting power or signals. Generally constructed of a hollow metal pipe.
Placing a waveguide into a vacuum causes radio waves to scatter.
A Cooking
Chamber is a microwave safe container the prevents microwaves from
escaping. The door has a microwave proof mesh with holes that are just small
enough that microwaves can't pass through but lightwaves can. The cooking
chamber itself is a Faraday cage enclosure which prevents the microwaves from
escaping into the environment. The oven door is usually a glass panel for easy
viewing, but has a layer of conductive mesh to maintain the shielding.
3.3 Automotive Embedded System (AES)
The Automotive industry is one of the major application
domains of embedded systems.
Automotive embedded systems are the one where
electronics take control over the mechanical system. Ex. Simple viper control.
The number of embedded controllers in a normal
vehicle varies somewhere between 20 to 40 and can easily be between 75 to 100
for more sophisticated vehicles.
One of the first and very popular use of
embedded system in automotive industry was microprocessor based fuel injection.
Some of the other uses of embedded controllers
in a vehicle are listed below:
Air Conditioner
Engine Control
Fan Control
Headlamp Control
Automatic break system control
Wiper control
Air bag control
Power Windows
AES are normally built around microcontrollers
or DSPs or a hybrid of the two and are generally known as Electronic Control
Units (ECUs).
Types
Of Electronic Control Units(ECU)
High-speed Electronic Control Units (HECUs):
HECUs are
deployed in critical control units requiring fast response.
They
Include fuel injection systems, antilock brake systems, engine control,
electronic throttle, steering controls, transmission control and central
control units.
Low Speed Electronic Control Units (LECUs):-
They are
deployed in applications where response time is not so critical.
They are
built around low cost microprocessors and microcontrollers and digital signal
processors.
Audio
controller, passenger and driver door locks, door glass control etc.
Automotive Communication Buses
Embedded system used inside an automobile
communicate with each other using serial buses. This reduces the wiring
required.
Following are the different types of serial
Interfaces used in automotive embedded applications:
Controller Area Network (CAN):-
CAN bus
was originally proposed by Robert Bosch.
It
supports medium speed and high speed data transfer
CAN is an
event driven protocol interface with support for error handling in data
transmission.
Local Interconnect Network (LIN):-
LIN bus is single master multiple slave communication interface with
support for data rates up to 20 Kbps and is used for sensor/actuator
interfacing
LIN bus
follows the master communication triggering to eliminate the bus arbitration
problem
LIN bus applications
are mirror controls , fan controls , seat positioning controls
Media-Oriented System Transport(MOST):-
MOST is
targeted for automotive audio/video equipment interfacing
A MOST bus
is a multimedia fiber optics point–to-point network implemented in a star ,
ring or daisy chained topology over optical fiber cables.
MOST bus
specifications define the physical as well as application layer , network layer
and media access control.
Related Topics