Physics - Work, Energy and Power: Multiple choice questions with answers | 11th Physics : UNIT 4 : Work, Energy and Power
Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 4 : Work, Energy and Power
Work, Energy and Power: Multiple choice questions with answers
1.
A uniform force of (2iˆ+ ˆj) N acts on a particle of mass 1 kg. The particle displaces
from position (3 ˆj + ˆk ) m to (5iˆ+3ˆj)
m. The work done by the force on the particle is
(a)
9 J
(b)
6 J
(c) 10 J
(d)
12 J
2.
A ball of mass 1 kg and another of mass 2 kg are dropped from a tall building whose
height is 80 m. After, a fall of 40 m each towards Earth, their respective kinetic
energies will be in the ratio of
(a)
√2 : 1
(b)
1 : √2
(c)
2 : 1
(d) 1 : 2
3.
A body of mass 1 kg is thrown upwards with a velocity 20 m s−1. It
momentarily comes to rest after attaining a height of 18 m. How much energy is
lost due to air friction?. (Take g= 10ms-2 )
(a) 20 J
(b)
30 J
(c)
40 J
(d)
10 J
4.
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a
velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water of the jet. What is
the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water ?.
a) ½ mv2
b)
mv2
c)
½ mu2
d)
mu2
5.
A body of mass 4 m is lying in xy-plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into
three pieces. Two pieces each of mass m move perpendicular to each other with equal
speed v. The total kinetic energy generated
due to explosion is
(a)
mv2
(b) 3/2 mv2
(c)
2mv2
(d)
4mv2
6.
The potential energy of a system increases, if work is done
(a) by the system against a
conservative force
(b)
by the system against a non-conservative force
(c)
upon the system by a conservative force
(d)
upon the system by a non-conservative force
7.
What is the minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter a vertical
loop of radius R so that it can complete the loop?.
(a)
√(2gR)
(b)
√(3gR)
(c) √(5gR)
(d)
√(gR)
8.
The work done by the conservative force for a closed path is
(a)
always negative
(b) zero
(c)
always positive
(d)
not defined
9.
If the linear momentum of the object is increased by 0.1%, then the kinetic
energy is increased by
(a)
0.1 %
(b) 0.2%
(c)
0.4%
(d)
0.01%
10.
If the potential energy of the particle is α - β/2 x2, then force
experienced by the particle is
(a)
F=β/2 x2
(b)
F=βx
(c) F=-βx
(d)
F=-β/2 x2
11.
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electric energy. Assume that
the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its
blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output
will be proportional to
(a)
v
(b)
v2
(c) v3
(d)
v4
12.
Two equal masses m1 and m2 are moving along the same
straight line with velocities 5ms-1 and -9ms-1
respectively. If the collision is elastic, then calculate the velocities after
the collision of m1 and m2, respectively
(a)
-4ms-1 and 10 ms-1
(b)
10ms-1 and 0 ms-1
(c) -9ms-1 and 5 ms-1
(d)
5 ms-1 and 1 ms-1
13.
A particle is placed at the origin and a force F=kx is acting on it (where k is a positive
constant). If U(0)=0, the graph of U(x) versus x will be (where U is the
potential energy function)
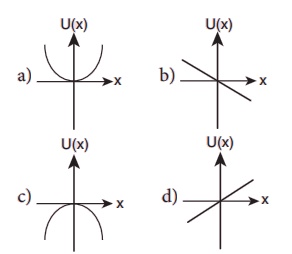
Ans: c
14.
A particle which is constrained to move along x-axis, is subjected to a force
in the same direction which varies with the distance x of the particle from the
origin as F(x) =-kx+ax3.
Here,
k and a are positive constants. For x
≥ 0, the functional form of the potential energy U(x) of the particle is

Ans: d
15.
A spring of force constant k is cut into two pieces such that one piece is
double the length of the other. Then, the long piece will have a force constant
of
(a)
2/3 k
(b) 3/2 k
(c)
3k
(d)
6k
Answers
1)
c 2) d 3) a 4) a 5) b
6)
a 7) c 8) b 9) b 10) c
11)
c 12) c 13) c 14) d 15) b
Related Topics