Definition, Average and Instantaneous power, Unit of power, Solved Example Problems - Power | 11th Physics : UNIT 4 : Work, Energy and Power
Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 4 : Work, Energy and Power
Power
POWER
Definition of power
Power
is a measure of how fast or slow a work is done. Power is defined as the rate of work
done or energy delivered.
Average power
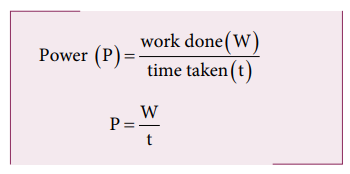
The average power (Pav)
is defined as the ratio of the total work done to the total time taken.

Instantaneous power
The
instantaneous power (Pinst) is defined as the power delivered at an
instant (as time interval approaches zero),
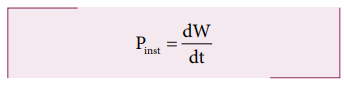
Unit of power
Power
is a scalar quantity. Its dimension is [ML2T-3]. The SI
unit of power is watt (W), named after the inventor of the steam engine James
Watt. One watt is defined as the
power when one joule of work is done in
one second, (1 W = 1 J s-1).
The
higher units are kilowatt(kW), megawatt(MW), and Gigawatt(GW).
1kW = 1000 W = 103
watt
1MW = 106 watt
1GW = 109 watt
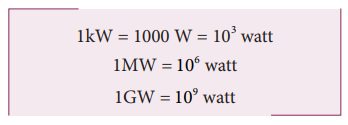
For
motors, engines and some automobiles an old unit of power still commercially in
use which is called as the horse-power (hp). We have a conversion for
horse-power (hp) into watt (W) which is,
1 hp = 746 W
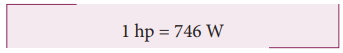
All
electrical goods come with a definite power rating in watt printed on them. A
100 watt bulb consumes 100 joule of electrical energy in one second. The energy
measured in joule in terms of power in watt and time in second is written as, 1
J =1 W s. When electrical appliances are put in use for long hours, they
consume a large amount of energy. Measuring the electrical energy in a small
unit watt. second (W s) leads to handling large numerical values. Hence,
electrical energy is measured in the unit called kilowatt hour (kWh).
1 electrical unit = 1
kWh = 1 x (103W) x (3600 s)
1 electrical unit =
3600×103 Ws
1 electrical unit =
3.6×106 J
1 kWh = 3.6×106
J

Electricity bills are generated in units of kWh for electrical energy consumption. 1 unit of electrical energy is 1 kWh. (Note: kWh is unit of energy and not of power.)
Relation
between power
and velocity
The
work done by a force ![]() for a displacement d
for a displacement d![]() is
is
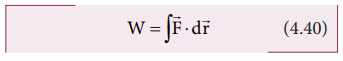
Left
hand side of the equation (4.40) can be written as
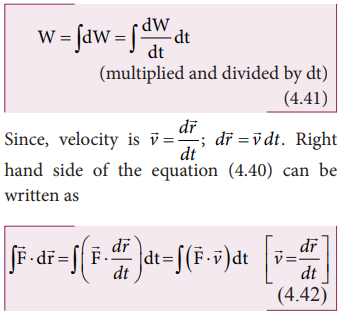
Substituting
equation (4.41) and equation (4.42) in equation (4.40), we get
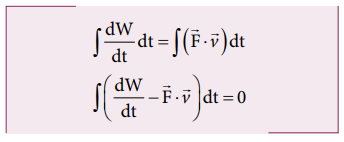
This
relation is true for any arbitrary value of dt. This implies that the term
within the bracket must be equal to zero, i.e.,
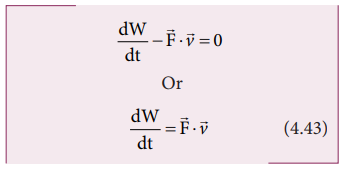
Solved Example Problems for Unit of power
Example 4.18
Calculate the energy consumed in electrical units when a 75 W fan is used for 8 hours daily for one month (30 days).
Solution
Power, P = 75 W
Time of usage, t = 8 hour × 30 days = 240 hours
Electrical energy consumed is the product of power and time of usage.
Electrical energy = power × time of usage = P × t

Solved Example Problems for Relation between power and velocity
Example 4.19
A vehicle of mass 1250 kg is driven with an acceleration 0.2 ms-2 along a straight level road against an external resistive force 500 N.Calculate the power delivered by the vehicle’s engine if the velocity of the vehicle is 30 m s-1 .
Solution
The vehicle’s engine has to do work against resistive force and make vechile to move with an acceleration. Therefore, power delivered by the vehicle engine is
Related Topics