Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Uses of ferromagnetic materials
Uses of ferromagnetic materials
(i) Permanent magnets
The ideal material for making
permanent magnets should possess high retentivity (residual magnetism) and high
coercivity so that the magnetisation lasts for a longer time. Examples of such
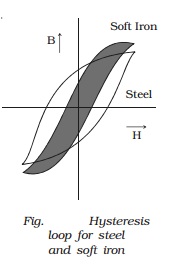
substances are steel and alnico (an alloy of Al, Ni and Co).
(ii) Electromagnets
Material used for making an
electro-magnet has to undergo cyclic changes. Therefore, the ideal material for
making an electromagnet has to be one which has the least hysteresis loss.
Moreover, the material should attain high values of magnetic induction B at low
values of magnetising field H. Soft iron is preferred for making electromagnets
as it has a thin hysteresis loop (Fig.) [small area, therefore less hysteresis
loss] and low retentivity. It attains high values of B at low values of
magnetising field H.
(iii) Core of the transformer
A material used for making
transformer core and choke is subjected to cyclic changes very rapidly. Also,
the material must have a large value of magnetic induction B. Therefore, soft
iron that has thin and tall hysteresis loop is preferred. Some alloys with low
hysteresis loss are: radio-metals, pern-alloy and mumetal.
(iv) Magnetic tapes and memory
store
Magnetisation of a magnet depends
not only on the magnetising field but also on the cycle of magnetisation it has
undergone. Thus, the value of magnetisation of the specimen is a record of the
cycles of magnetisation it has undergone. Therefore, such a system can act as a
device for storing memory.
Ferro magnetic materials are used
for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player and for building a memory store
in a modern computer. Examples : Ferrites (Fe, Fe2O, MnFe2O4
etc.).
Related Topics