Chapter: The Massage Connection ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY : Nervous System
Structure of the Neuron
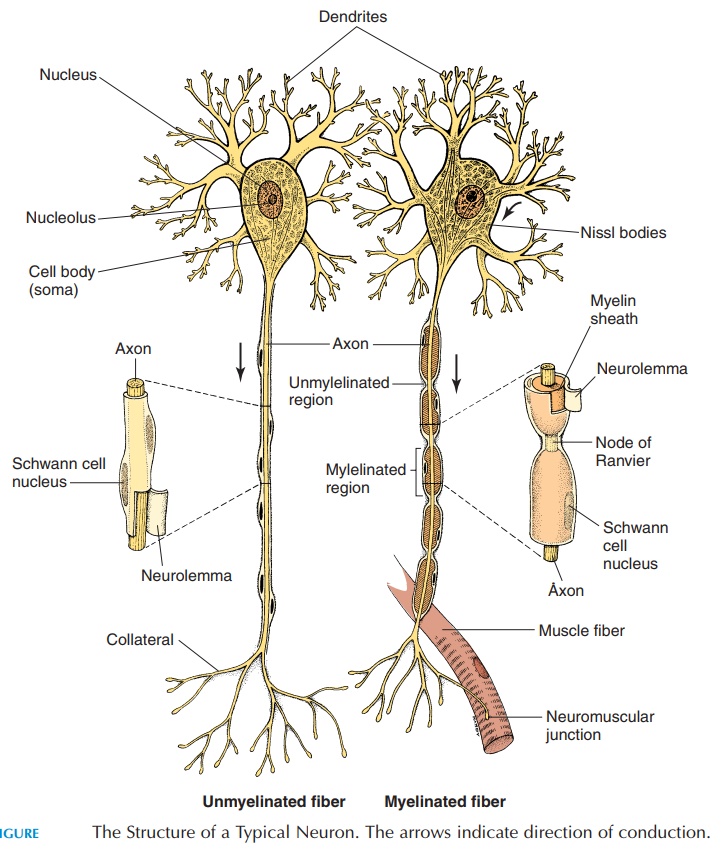
STRUCTURE OF THE NEURON
The structure of the neuron (see Figure 5.2), the func-tional unit of the nervous system, varies from site to site. Typically, a neuron has a cell body/soma, or perikaryon, with a nucleus and cytoplasm, alongwith the organelles normally found in a cell. The prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum is known as Nissl bodies. However, most neurons do not have acentriole and lose the ability to multiply.Nuclei are clusters of cell bodies of neurons in the CNS (excep-tion, basal ganglia). These clusters in the PNS are known as ganglia.
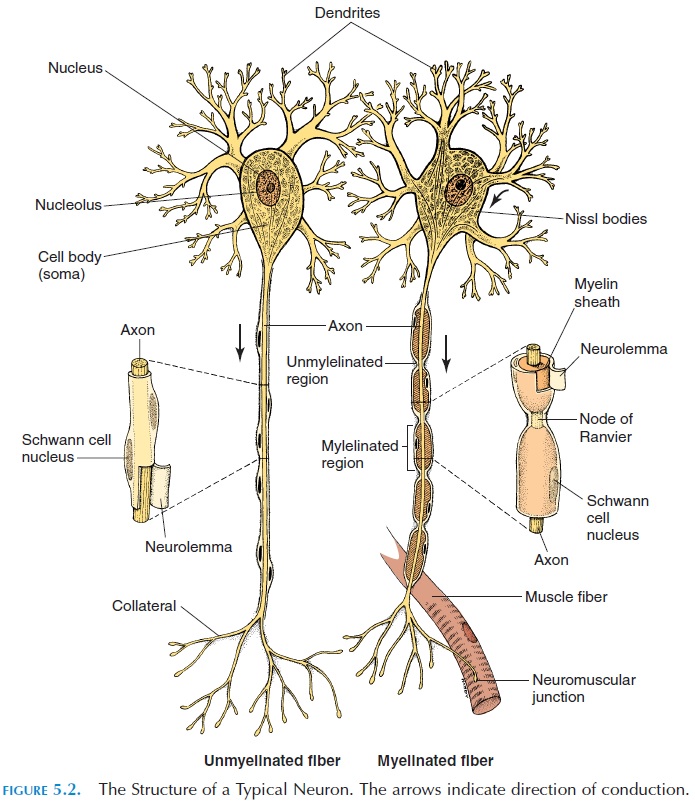
Many processes lead off from the soma. The axon is long and helps conduct impulses away from the cell body. The axon may have many branches, known as collaterals. The collaterals help the cell commu-nicate with more than one neuron. The dendrites are highly branched processes from the cell body that take impulses to the soma. The presence of numerous dendrites enables many neurons to have an effect on one cell.
Related Topics