Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Satellite Communication: Merits and Demerits
Satellite Communication
Space technology has witnessed a phenomenal
growth, since the launch of man-made satellite Sputnik in 1957. One of the most
significant applications of space technology has been in the field of
communications. The people over world watch international events like Olympic
games via satellite. A number of countries are using satellites for military
communications, which include services to ships, air crafts and land mobile
terminals. Several direct TV broadcasting satellite systems are also being
used.
Satellite communication is basically a
microwave link repeater. A satellite receives energy from an earth station,
amplifies it and returns it to each at a frequency about 2 GHz away from the
uplink frequency (earth to satellite) . This prevents interference between the
uplink and the downlink (satellite to earth). Satellite so used is a
geostationary satellite which appears to be stationary at a given spot above
the equator. Actually, it moves with the same angular velocity as the earth
i.e. it completes one revolution per 24 hours and hence appears to be stationed
over one spot on the globe. Satellite orbiting the earth will be geostationary
when it is about 36,000 km away from the earth.
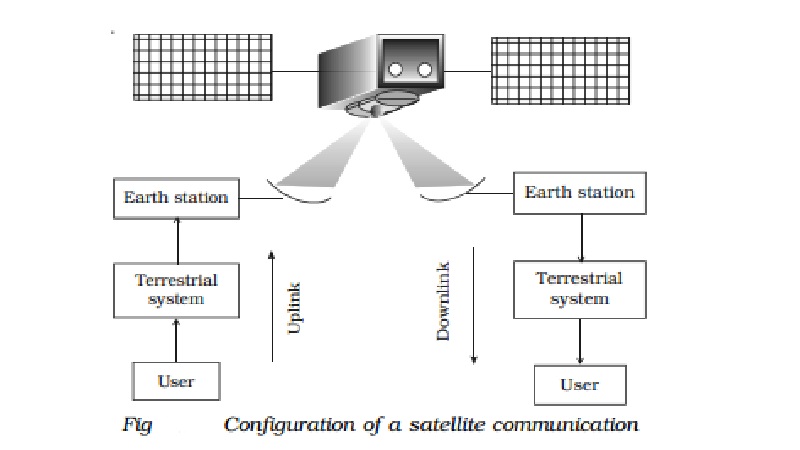
Fig 10.25 gives the general structure of a satellite communications
system. A satellite in space links many earth stations. The user is connected
to the earth station through terrestrial network.
This network may assume various configurations including a
telephone switch or a dedicated link to the earth station. Signal generated by
the user is processed and transmitted from the earth station to the satellite.
The satellite receives the modulated RF carrier at the pre-determined uplink
frequencies from all the earth stations in the network, amplifies these
frequencies and then re-transmits them back to earth at downlink frequencies.
The downlink frequencies are kept different from the uplink frequencies in
order to avoid interference. The modulated carrier received at receiving earth
station is processed to get back the original baseband signal. This signal is
then sent to the user through a terrestrial network.
As per WARC (World Administrative Radio
Conference) 1979 allocation, commercial communication satellites use 500 MHz
band-width near 6 GHz for uplink transmission and use 500 MHz bandwidth near 4
GHz for downlink transmission. In actual practice, uplink of 5.725
- 7.075 GHz is used while downlink of 3.4 - 4.8 GHz is used.
Merits
1.
Mobile communication can be easily established
by satellite communication.
2.
Satellite communication is economical compared
with terrestrial communication particularly where long distances are involved.
3.
Compared to the optical fiber communication,
satellite communication has the advantages that, quality of transmitted signal
and location of sending and receiving stations are independent of distance.
4.
For thin traffic remote areas like north east
regions in India, Ladakh etc., satellite communication is most economical.
5.
For search, rescue and navigation, satellite
communication is far superior and economical compared to other systems.
Demerits
1.
Between talks there is a time gap which becomes
quite annoying. This time delay also reduces the efficiency of satellite in
data transmission.
2.
An imperfect impedance match may cause echo,
received back after a delay. Echo suppressor has to be used.
3.
Repair of satellite is almost impossible, once
it has been launched.
Related Topics