Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Properties of Alpha α, beta β and gamma γ rays
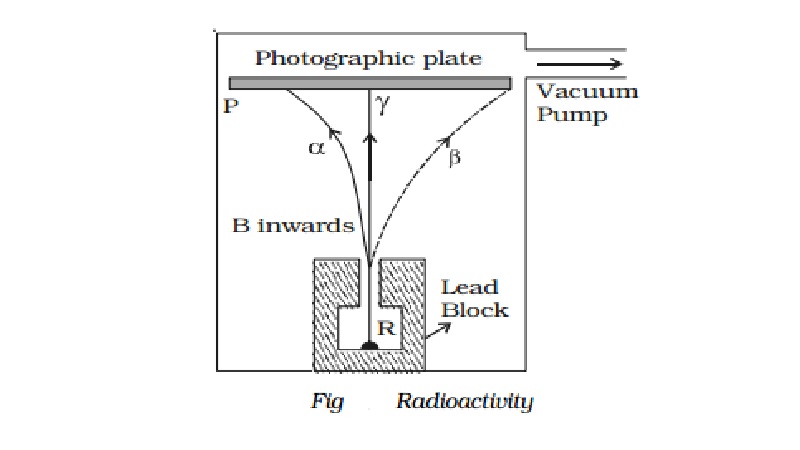
Alpha, beta and gamma rays
distinct types
of radiations, α, β and γ−rays can be easily found by the small amount of
radium (R) is placed at the bottom of a small hole drilled in a lead block,
which is kept in an evacuated chamber (Fig.).
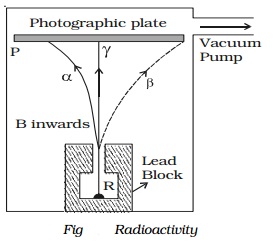
A photographic
plate is placed at a short distance
above the lead block. A strong magnetic field
is applied at right angles to
the plane of the
paper and acting
inwards.
Three distinct traces can be seen on the
photographic plate when it is developed. The trace towards left is due to
positively charged particles. They are named α-particles.The trace towards the right is due to negatively charged
particles. They are named β-particles.
The undeviated trace is due to neutral radiations which are called γ−rays. If an electric field is applied, the α-rays are deflected towards the negative plate, β−rays towards the positive plate and γ−rays are not deflected.
Properties of α-rays
1.
An α - particle is a helium nucleus consisting
of two protons and two neutrons. It carries two units of positive charge.
2.
They move along straight lines with high
velocities.
3.
They are deflected by electric and magnetic
fields.
4.
They produce intense ionisation in the gas
through which they pass. The ionising power is 100 times greater than that of
β-rays and 10,000 times greater than that of γ−rays.
5.
They affect photographic plates.
6.
They are scattered by heavy elements like gold.
They produce fluorescence when they fall on substances like zinc
sulphide or barium platinocyanide.
Properties of β - rays
1.
β-particles
carry one unit of negative charge and mass equal to that of electron.Therefore, they are nothing but electrons.
2.
The β-particles emitted from a source have velocities over the range of
0.3 c to 0.99 c, where c is the velocity of light.
3.
They are deflected by electric and magnetic
fields.
4.
The ionisation power is comparatively low
5.
They affect photographic plates.
6.
They penetrate through thin metal foils and
their penetrating power is greater than that of α−rays
7.
They produce fluorescence when they fall on
substances like barium platinocyanide.
Properties of γ - rays
1.
They are electromagnetic waves of very short
wavelength.
2.
They are not deflected by electric and magnetic
fields.
3.
They travel with the velocity of light.
4.
They produce very less ionisation.
5.
They affect photographic plates.
6.
They have a very high penetrating power,
greater than that of β-rays.
7.
They produce fluorescence.
8.
They are diffracted by crystals in the same way
like X−rays are
diffracted.
Related Topics