Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Hydrocarbons
Physical and Chemical properities of alkynes
Physical properties of alkynes
1. The first three members are gases, next eight are liquids and the higher alkynes are solids. They are all colour-less and odourless except acetylene which h as a garlic odour.
2. They are slightly soluble in water but dissolve readily in organic solvents like benzene, acetone and ethyl alcohol
Chemical properities of alkynes
Terminal Alkynes are acidic in nature. It un-dergoes polymerization and addition reaction.
1. Acidic nature of alkynes:
An alkyne shows acidic nature only if it contains terminal hydrogen. This can be explained by considering sp hybrid orbitals of carbon atom in alkynes. The percentage of S-character of sp hybrid orbital (50%) is more than sp2 hybrid orbital of alkene (33%) and sp3 hybrid orbital of alkane (25%). Because of this, Carbon becomes more electronegative facilitating donation of H+ ions to bases. So hydrogen attached to triply bonded carbon atoms is acidic.
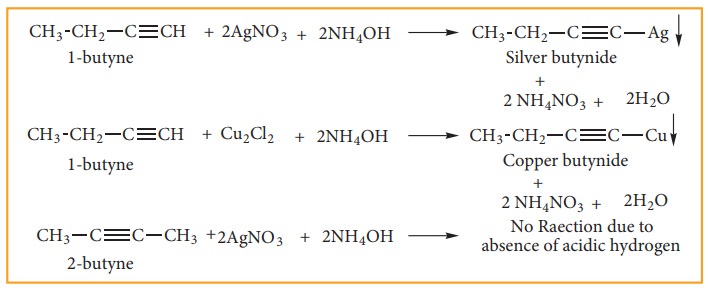
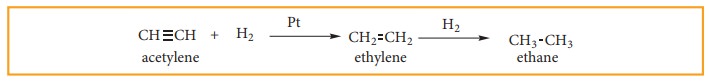
2. Addition reactions of alkynes
i) addition of hydrogen
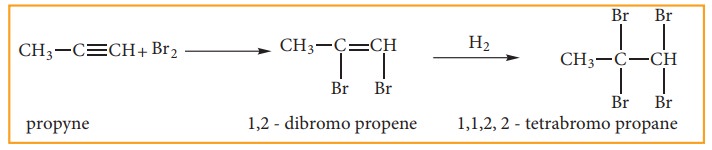
ii) Addition Of Halogens:
When Br2 in CCl4 (Reddishbrown) is added to an alkyne, the bromine solution is decolourised. This is the test for unsaturation.
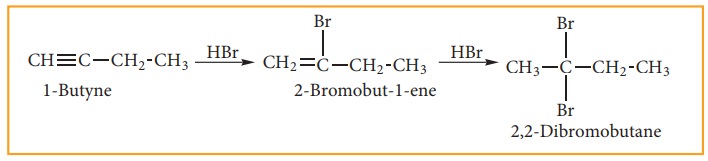
iii) Addition Of Hydrogen Halides:
Reaction of hydrogen halides to symmetrical alkynes is electrophilic addition reaction.
This reaction also follows Markovnikoff’s rule.
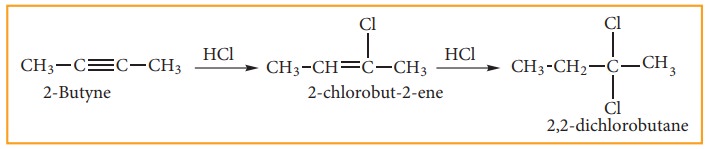
Addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkene follows Markownikoff’s rule.
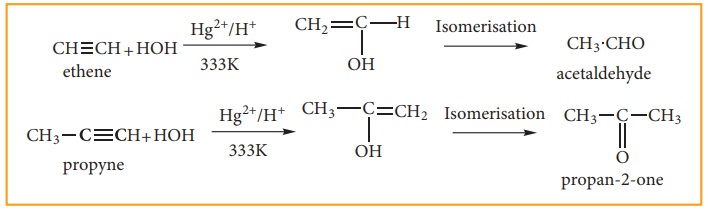
iv) Addition Of Water:
Alkynes undergo hydration on warming with mercuric sulphate and dilute H2SO4 at 333K to form carbonyl compounds.
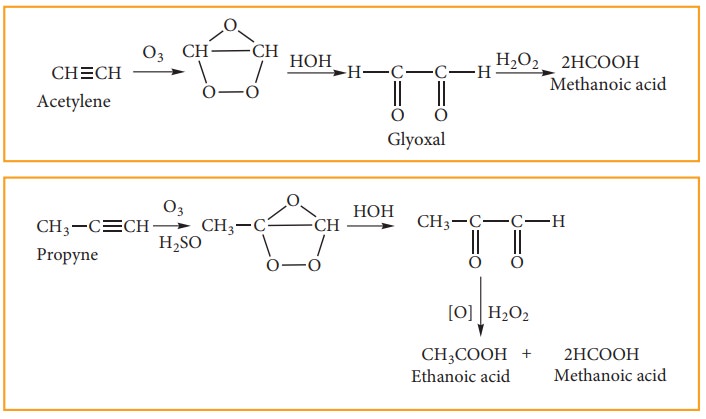
3. Ozonolysis:
Ozone adds to carbon-carbon triple bond of alkynes to form ozonides. The ozonides are hydrolyzed by water to form carbonyl compounds. The hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) formed in the reaction may oxidise the carbonyl compound to carboxylic acid.
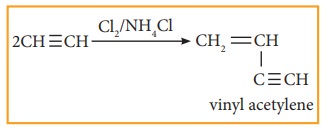
4. Polymerisation:
Alkyne undergoes two types of po-lymerisation reaction
(i) Linear Polymerisation:
Ethyne forms linear polymer, when passed into a solution of cuprous chloride and ammonium chloride.
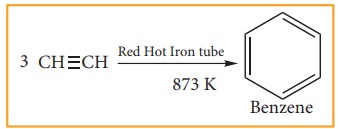
(ii) Cyclic Polymerisation:
Ethyne undergoes cyclic polymeriza-tion on passing through red hot iron tube. Three molecules of ethynepolymerises to benzene.
Related Topics