Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Hydrocarbons
Directive influence of a functional group in monosubtituted benzene
Directive
influence of a functional group in monosubtituted benzene:
When
mono substituted benzene undergoes an electrophilic substitution reaction, the
rate of the reaction and the site of attack of the incomeing electrophile
depends on the functional group already attached to it. Some groups increase
the reactivity of benzene ring and are known as activating groups. While others
which decrease the reactivity are known as deactivating groups. We further
divide these groups into two categories depending on the way they influence the
orientation of attack by the incoming groups. Those which increases electron
density at ‘ortho’ and ‘para’ position are known as ortho-para directors while
those which increase electron density at ‘meta’ position is known as
meta-directors. Some examples of directive influence of functional groups in
mono-substituted benzene are explained below.
Ortho and para directing groups
All
the activating groups are ‘ortho-para’ directors. Example –OH, -NH2,
-NHR, -NHCOCH3, -OCH3-CH3 – C2H5
etc. Let us consider the directive influences of phenolic (-OH) group. Phenol is
the resonance hybrid of following structures.
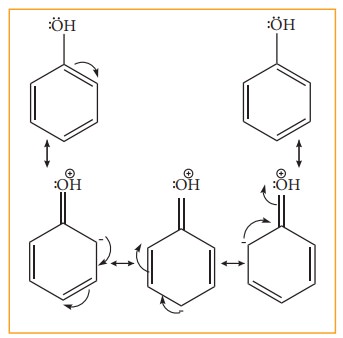
In
these resonance structures, the (-) charge residue is present on ortho and para
position of ring structure. It is quite evident that the lone pair of electron
on the atom which is attached to the ring involves in resonance and makes the
ring more electron rich than benzene. The electron density at ortho and
parapositions increases as compared to the meta position. Therefore phenolic
group activates the benzene ring for electrophilic attack at ‘ortho’ and ‘para
positions and hence –OH group is an ortho-para director and activator.
In
aryl halides, the strong –I effect of the halogens (electron withdrawing
tendency) decreases the electron density of benzene ring, thereby deactivating
for electrophilic attack. However the presence of lone pair on halogens
involved in the resonance with pi electrons of benzene ring, increases electron
density at ortho and para position. Hence the halogen group is an ortho-para
director and deactivator.
META DIRECTING GROUPS
Generally
all deactivating groups are meta-directors. For example –NO2, -CN,
-CHO, -COR, -COOH, -COOR, -SO3H etc. Let us consider the directive
influence of aldehyde (-CHO) group. Benz aldehyde is the resonance hybrid of
following structures.
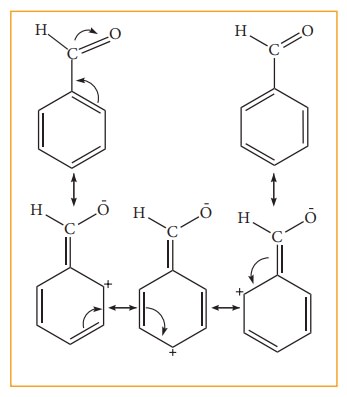
In
these resonance structures, the (+) charge residues is present on the ring
structure. It is quite evident that resonance delocalizes the positive charge
on the atoms of the ring, making the ring less electron rich than benzene. Here
overall density of benzene ring decreases due to –I effect of –CHO group there
by deactivating the benzene for electrophilic attack. However resonating
structure shows that electron density is more in meta position. Compared to o
& p-position. Hence –CHO group is a meta-director and deactivator.
Related Topics