Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Hydrocarbons
General methods of preparation of alkenes
General methods of preparation of alkenes:
(1) Preparation of alkene by dehydra-tion of alcohol:
When an alcohol is heated at 430-440 K with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid, a molecule of water from alcohol is removed and an alkene is formed. This reaction is called elimination reaction.
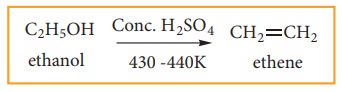
Ethene can also be prepared in laboratory by catalytic dehydration of alcohol.
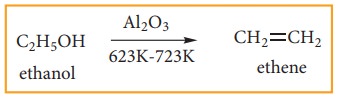
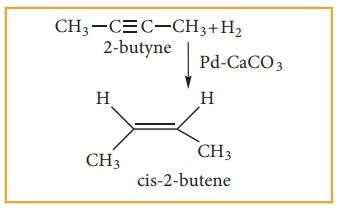
(2) Preparation of alkenes from alkynes:
Alkynes can be reduced to cis-alkenes using Lindlar’s catalyst (CaCO3 sup-ported in palladuium partially deactivated with sulphur (or) gasoline). This reaction is stero specific giving only the cis- alkene.
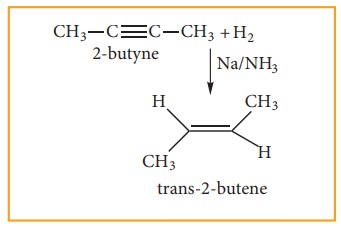
Alkynes can also be reduced to trans-alkenes using sodium in liquid ammonia. This reaction is stereospecific giving only the trans-alkene.
(3) Preparation of alkenes by dehydro-halogenaton of halo alkanes.
Halo alkanes react with alcoholic KOH and eliminate hydrohalide resulting in the formation of alkene.
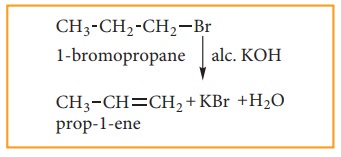
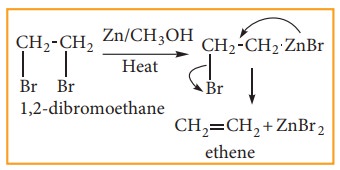
(4) Preparation of alkenes from vicinal dihalogen derivative of alkanes or vici-nal dihalides
The compound in which two halogen atoms are attached to adjacent carbon-atoms are called as vicinal dihalides. When vicinal dihalides are warmed with granulated zinc in methanol, they lose a molecule of ZnX2 to form an alkene.
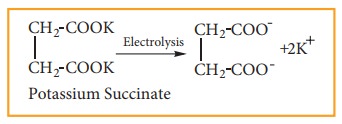
(5) Preparation of ethene by kolbe’s electrolytic method:
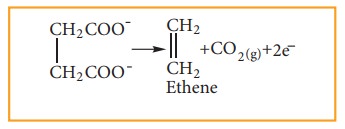
When an aqueous solution of potas-sium succinate is electrolyzed between two platinum electrodes, ethene is produced at the anode.
At anode
Related Topics