Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 13 : Hydrocarbons
Chemical Properties of Benzene
Chemical
Properties:
1.
Benzene contains delocalized π-electrons which make the ring to act as an
electro rich centre. So electrophilic substitution reaction occurs in benzene.
2.
Benzene ring is stabilized by delocalized π electrons. Though it is highly
stable, it undergoes addition and oxidation reaction under specific conditions.
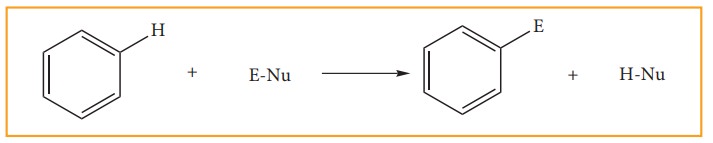
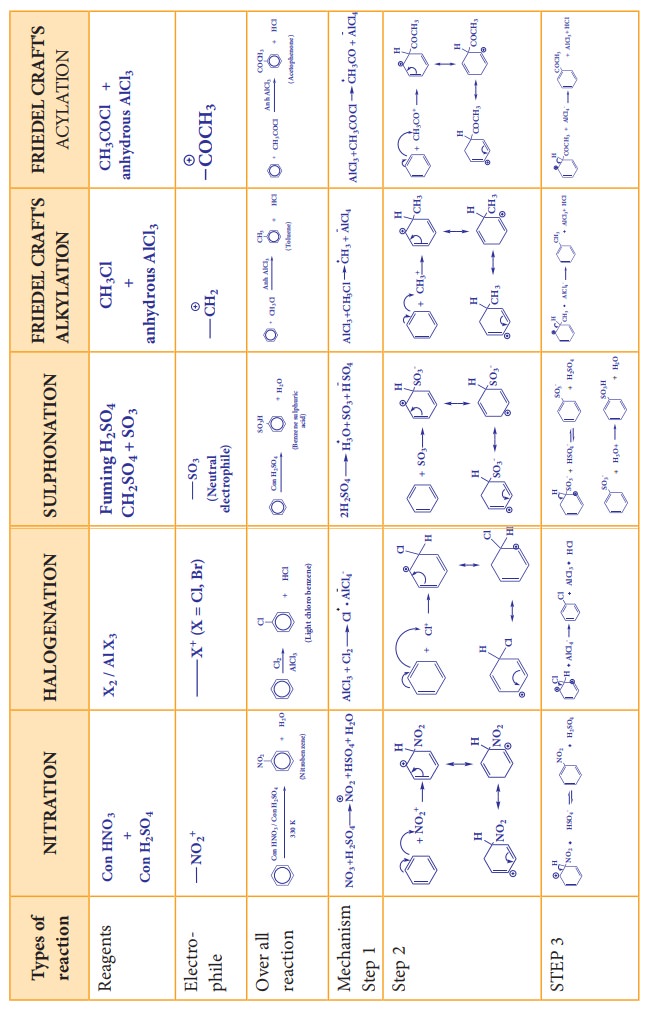
1. Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
(a) Nitration:
When
benzene is heated at 330K with a nitrating mixture (Con. HNO3 + Con.
H2SO4), nitro benzene is formed by replacing are hydrogen
atom by nitronium ion NO2+(electrophile)
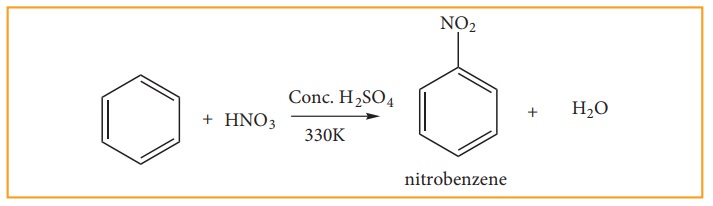
Concentrated
H2SO4 is added to produce nitronium ion NO2+
(b) Halogenation:
Benzene
reacts with halogens (X2=Cl2, Br2,) in the
presence of Lewis acid such as FeCl3, FeBr3 or AlCl3
and give corresponding halo benzene. In the absence of catalyst, Fluorine
reactsvigoursly with benzene even in the absence of catalyst. However iodine is
very inactive even in the presence of catalyst
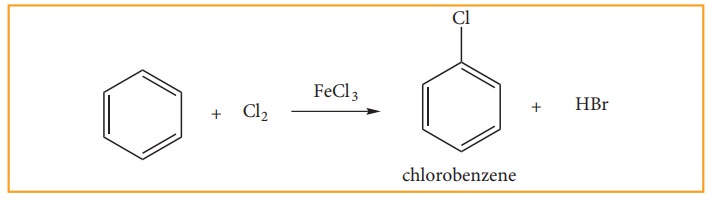
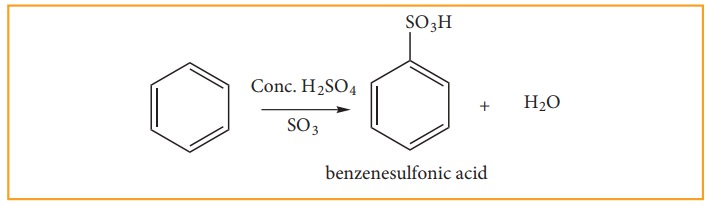
(c) Sulphonation:
Benzene
reacts with fuming sulphuric acid (Con H2SO4 + SO3)
and gives benzene sulphonic acid. The electrophile SO3 is a
molecule. Although it does not have positive charge, it is a strong
electrophile. This is because the octet of electron around the sulphur atom is
not reached. The reaction is reversible and desulphonation occurs readily in
aqueous medium.
(d) Friedel Craft’s Alkylation: (Methylation)
When
benzene is treated with analkyl halide in the presence of only AlCl3,
alkyl benzene is formed.

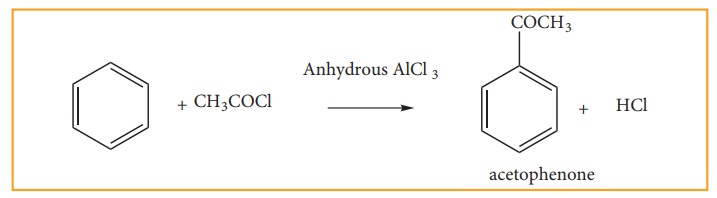
(e) Friedel Craft’s Acylation : Acetylation
When
benzene is treated withacetylchloride in the presence of AlCl3, acyl
benzene is formed
(f) Electrophilic Subitution Reactions: Mechanism
Benzene
undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction because it is an electron-rich
system due to delocalised π electron. So it a easily attacked by electrophilies
and gives substituted products.
Mechanism:
Step: 1
Formulation
of the electrophile

Step:2
The
electrophile attacks the aromatic ring to form a carbocation intermediate which
is stabilized by resonance.
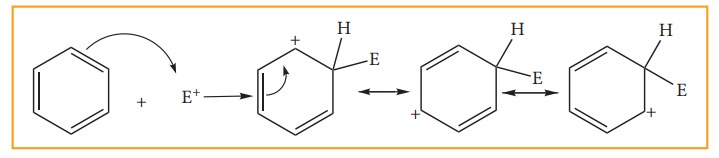
Step: 3
Loss
of proton gives the substitution product.

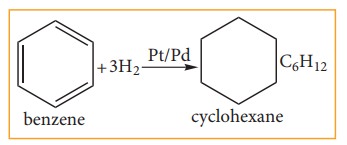
(ii) Addition Reaction:
a. Hydrogenation of benzene:
Benzene
reacts with hydrogen in the presence of Platinum or Palladium to yield
Cyclohexane. This is known as hydrogenation.
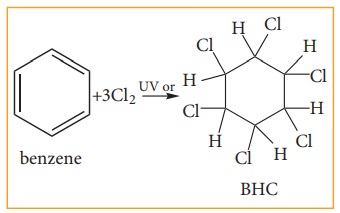
b. Chlorination of Benzene:
Benzene
reacts with three molecules of Cl2 in the presence of sun light or
UV light to yield Benzene Hexa Chloride (BHC) C6H6Cl6.
This is known as gammaxane or Lindane which is a powerful insecticide.
(iii) Oxidation:
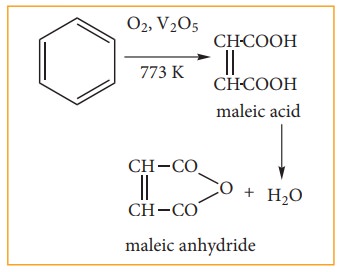
a. Vapour – phase oxidation:-
Although
benzene is very stable to strong oxidizing agents, it quickly undergoes vapour
phase oxidation by passing its vapour mixed with oxygen over V2O5
at 773k. The ring breaks to give maleic anhydride.
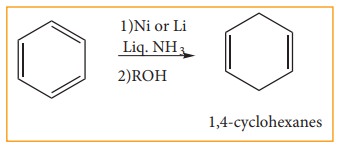
b. Birch reduction:
Benzene
can be reduced to 1, 4-cyclohexadiene by treatment with Na or Li in a mixture
of liquid ammonia and alcohol. It is the convenient method to prepare cyclic
dienes.
Related Topics