Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Multimeter
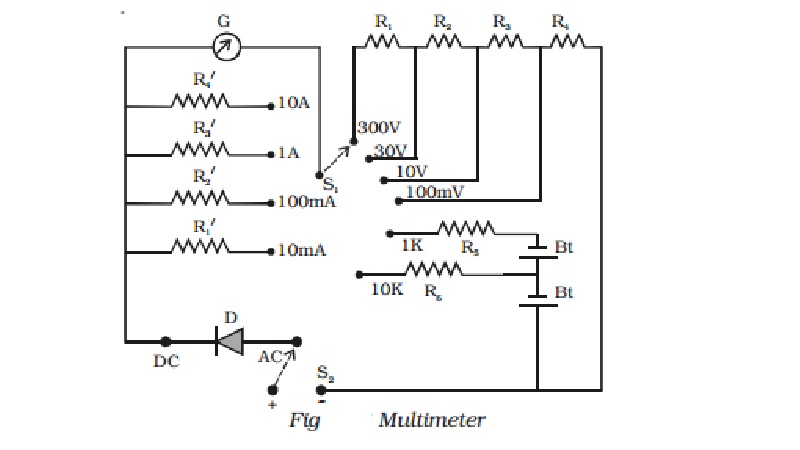
Multimeter
Multimeter is an electronic instrument, which is used
to measure voltage, current and resistance. This is called as AVO meter
(ampere, voltage, ohm). The internal circuit of the multimeter is shown in Fig.
It consists of a moving coil galvanometer. By incorporating suitable circuits
with the galvanometer, the measurement of voltage, current and resistance can
be done. Let us consider a galvanometer of resistance G (= 100 Ω), which gives a full scale deflection for 1 mA.
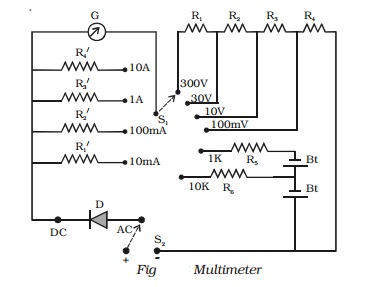
(a) as a voltmeter
The moving coil galvanometer is
converted into a voltmeter by connecting in series a high resistance of
suitable value. If a resistance of 900 Ω is connected in series with the galvanometer, the range of the
voltmeter becomes 10-3 × 1000 = 1 V. The same meter can be used to
measure voltage upto 10 V, if a resistance 9900 Ω is connected in series. Thus, in order to measure different
ranges, different high resistances are put in series with the galvanometer by a
switching arrangement.
(b) as an ammeter
The galvanometer is converted
into an ammeter by shunting it with suitable low resistances, one for each
range. For example, the galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter with range
0-1 A by shunting it with a resistance of 100/999 Ω or 0.1 Ω (approximately) and the range can be increased to 10 A by
shunting it with 100/9999 Ω (0.01 Ω approximately) and so on.
(c) as an ohm-meter
The galvanometer is converted into an ohm-meter by
connecting a battery and a suitable resistance in series (Fig). If a battery of
1 V is connected in series and the above galvanometer shows full scale
deflection, then the total resistance in the circuit (including that of the
galvanometer) be 1000 Ω.
Measurement of resistance
On the resistance scale 0 is marked against the
current of 1 mA. Now, if a unknown resistance is connected between the
terminals T1 and T2, the current passing through
the galvanometer decreases to 0.5
mA, then the unknown resistance is 1000 Ω. Hence, 1 k Ω is marked against 0.5 mA. If the
galvanometer current is 0.25 mA for another unknown resistance connected
between T1 and T2, then that resistance is 3000 Ω. Hence, 3 k Ω is marked against 0.25 mA.
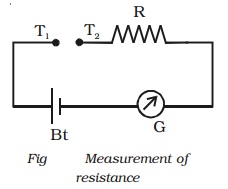
Usually an adjustable resistance
of small value is connected in series, so that the zero adjustment can be made,
even if the emf of the cell decreases slightly.
To measure a.c. voltage and current, a rectifier unit
is connected in series and by turning a switch to a.c., the instrument is used
to measure a.c. quantities. If the switch is turned to d.c., the rectifier unit
gets disconnected and the instrument is then used to measure d.c. current and
voltage.
Related Topics