Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Moment of a force
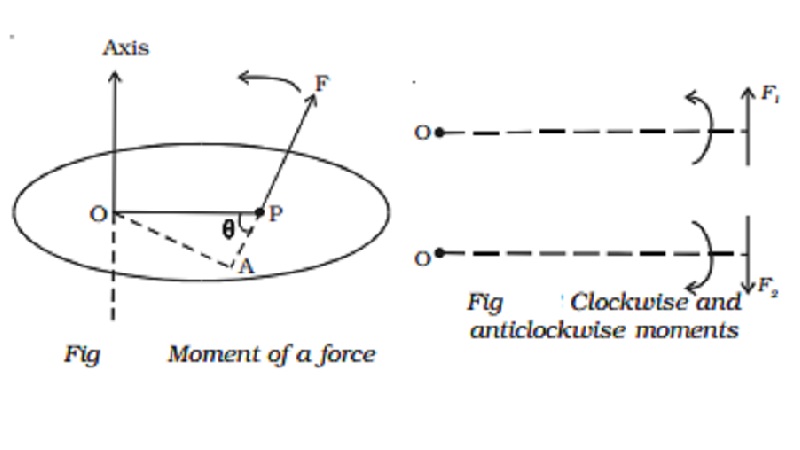
Moment of a force
A force can rotate a nut when
applied by a wrench or it can open a door while the door rotates on its hinges (i.e)
in addition to the tendency to move a body in the direction of the application
of a force, a force also tends to rotate the body about any axis which does not
intersect the line of action of the force and also not parallel to it. This
tendency of rotation is called turning effect of a force or moment of the force
about the given axis. The magnitude of
the moment of force F about a point is defined as the product of the magnitude of force and the perpendicular distance of
the point from the line of action of the force.
Let us consider a force F acting at the point P on
the body as shown in Fig.. Then, the moment of the force F about the point O =
Magnitude of the force ? perpendicular distance between the direction of the
force and the point about which moment is to be determined = F ? OA.
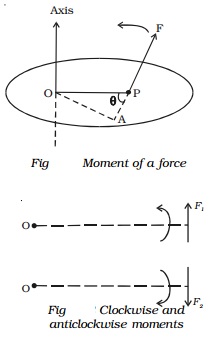
If the force acting on a body rotates the body in
anticlockwise direction with respect to O then the moment is called
anticlockwise moment. On the other hand, if the force rotates the body in
clockwise direction then the moment is said to be clockwise moment. The unit of
moment of the force is N m and its dimensional formula is M L2 T-2.
As a matter of convention,an anticlockwise moment is
taken as positive and a clockwise moment as negative. While adding moments, the
direction of each moment should be taken into account.
In terms of vector product, the moment of a force is
expressed as,
Vec m = Vec r ?
Vec
F
where Vec r
is the position vector with respect to O. The direction of Vec m is perpendicular to the plane containing Vec r and Vec F.
Related Topics