Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Mapping of magnetic field due to a bar magnet
Mapping of magnetic field due to
a bar magnet
A bar magnet is
placed on a plane sheet of a paper. A compass needle is placed near the north
pole of the magnet. The north and south poles of the compass are marked by
pencil dots. The compass needle is shifted and placed so that its south pole
touches the pencil dot marked for north pole. The process is repeated and a
series of dots are obtained. The dots are joined as a smooth curve. This curve
is a magnetic line of force. Even though few lines are drawn around a bar
magnet the magnetic lines exists in all space around the magnet.
(i) Magnet placed with its north
pole facing geographic north
A sheet of paper is fixed on a
drawing board. Using a compass needle, the magnetic meridian is drawn on it. A
bar magnet is placed on the magnetic meridian such that its north pole points towards
geographic north. Using a compass needle, magnetic lines of force are drawn
around the magnet. (Fig.)
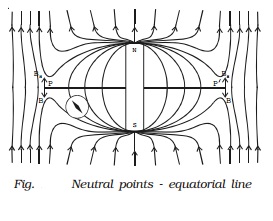
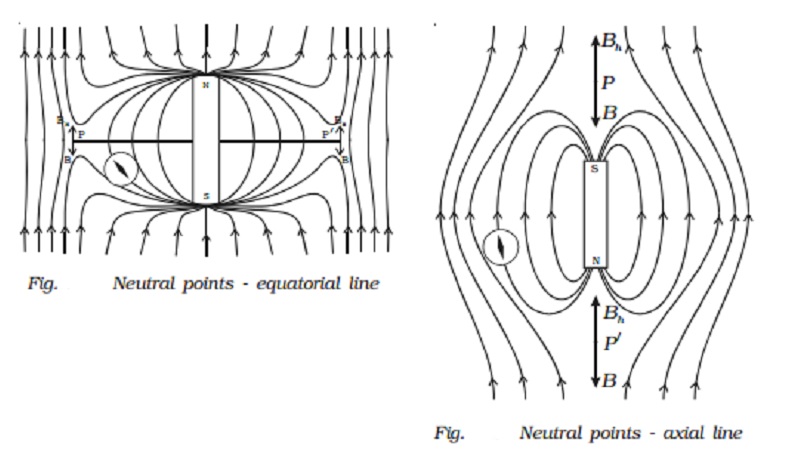
The magnetic lines of force is
due to the combined effect of the magnetic field due to the bar magnet and
Earth. It is found that when the compass is placed at points P and P ′ along
the equatorial line of the magnet, the compass shows no deflection. They are
called ?neutral points.? At these points the magnetic field due to the magnet
along its equatorial line (B) is exactly balanced by the horizontal component
of the Earth?s magnetic field. (Bh).
Hence, neutral points are defined as the points where the resultant magnetic field due to the magnet and Earth
is zero.
Hence,
at neutral points
B
= Bh
?o/ 4π . M/(d2+l2)3/2 = Bh
(ii) Magnet placed with its south
pole facing geographic north
A
sheet of paper is fixed on a drawing board. Using a compass needle, the
magnetic meridian is drawn on it. A bar magnet is placed on a magnetic meridian
such that its south pole facing geographic north. Using a compass needle, the
magnetic lines of force are drawn around the
magnet
as shown in Fig..
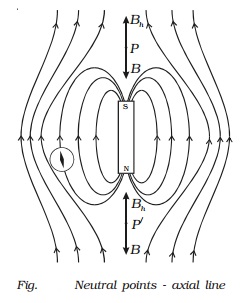
The
magnetic lines of force is due to the combined effect of the magnetic field due
to the bar magnet and Earth. It is found that when the compass is placed at
points P and P ′ along the axial line of the magnet, the compass shows no
deflection. They are called neutral points. At these points the magnetic field (B) due to the magnet
along its axial line is exactly balanced by the horizontal component of the
Earth?s magnetic field (Bh).
Hence
at neutral points, B = Bh
[
?0/ 4 π ] . [ ( 2Md )/ (d2 ? l2)2
] = Bh
Related Topics