Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Magnetic induction at a point along the axial line due to a magnetic dipole (Bar magnet)
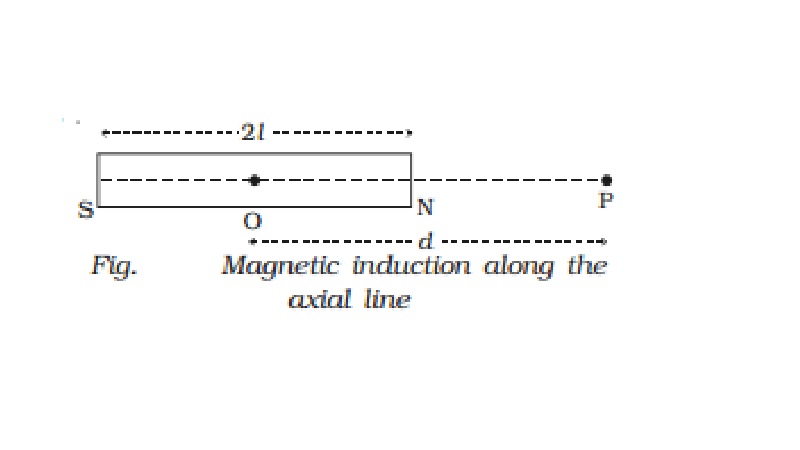
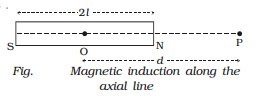
Magnetic induction at a point along the axial line due to a
magnetic dipole (Bar magnet)
NS
is the bar magnet of length 2l and of pole strength m. P is a point on the axial
line at a distance d from its mid point O (Fig.).
According
to inverse square law,
F
= ?0/ 4 π . m1m2/d2
∴ Magnetic induction (B1)
at P due to north pole of the magnet
B1
= ?0/4 π . m/NP2
along NP
=
?0/4 π . m/(d-l)2 along NP
Magnetic
induction (B2) at P due to south pole of the magnet,
B2
= ?0/4 π . m/(SP)2
along PS
B2=
?0/4 π . m/(d+l)2 along PS
Magnetic
induction at P due to the bar magnet,
B
= B1 ? B2
B
= ?0/4 π . 2Md/(d2-l2)2
where
M = 2ml (magnetic dipole moment).
For
a short bar magnet, l is very small
compared to d, hence l 2 is
neglected.
∴ B = ?0/4 π
. 2Md3
The
direction of B is along the axial line away from the north pole.
Coulomb?s inverse square law
Coulomb?s inverse square law
states that the force of attraction or
repulsion between the two magnetic poles
is directly proportional to the product of their pole strengths and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Related Topics