Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Physics sciense Higher secondary school College Notes
Intrinsic semiconductor
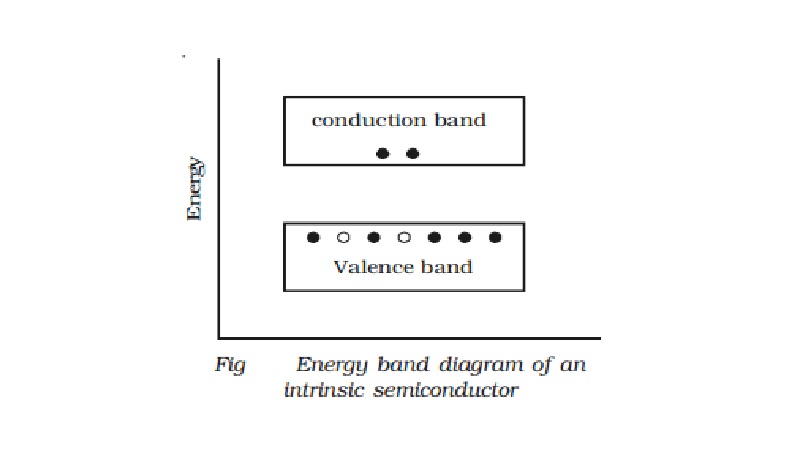
Intrinsic semiconductor
A semiconductor which is pure and
contains no impurity is known as an intrinsic semiconductor. In an intrinsic
semiconductor, the number of free electrons and holes are equal. Common
examples of intrinsic semiconductors are pure germanium and silicon.
The forbidden energy gap is so
small that even at ordinary room temperature, there are many electrons which
possess sufficient energy to cross the forbidden energy gap and enter into the
conduction band. Schematic band diagram of an intrinsic semiconductor at room
temperature is represented in Fig.
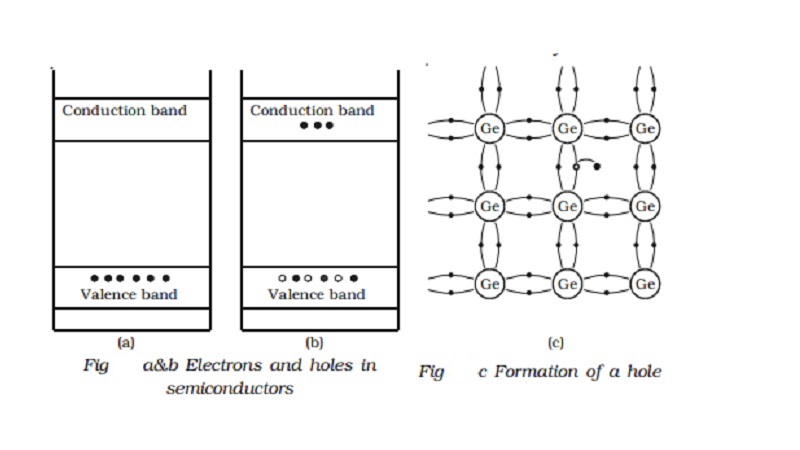
Doping a semiconductor
Electrons and holes can be
generated in a semiconductor crystal with heat energy or light energy. But in these
cases, the conductivity remains very low. The efficient and convenient method
of generating free electrons and holes is to add very small amount of selected
impurity inside the crystal. The impurity to be added is of the order of 100
ppm (parts per million). The process of addition of a very small amount of
impurity into an intrinsic semiconductor is called doping. The impurity atoms
are called dopants. The semiconductor containing impurity atoms is known as
impure or doped or extrinsic semiconductor.
1. The impurity atoms are added to
the semiconductor in its molten state.
2. The pure semiconductor is
bombarded by ions of impurity atoms.
3. When the semiconductor crystal
containing the impurity atoms is heated, the impurity atoms diffuse into the
hot crystal.
Usually, the doping material is
either pentavalent atoms (bismuth, antimony, phosphorous, arsenic which have
five valence electrons) or trivalent atoms (aluminium, gallium, indium, boron
which have three valence electrons). The pentavalent doping atom is known as
donor atom, since it donates one electron to the conduction band of pure
semiconductor. The trivalent atom is called an acceptor atom, because it
accepts one electron from the pure semiconductor atom.
Related Topics