Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Urinary Disorders
Infections of the Urinary Tract
Infections of the Urinary Tract
Urinary
tract infections (UTIs) are caused by pathogenic micro-organisms in the urinary
tract (the normal urinary tract is sterile above the urethra). UTIs are
generally classified as infections in-volving the upper or lower urinary tract
(Chart 45-1).
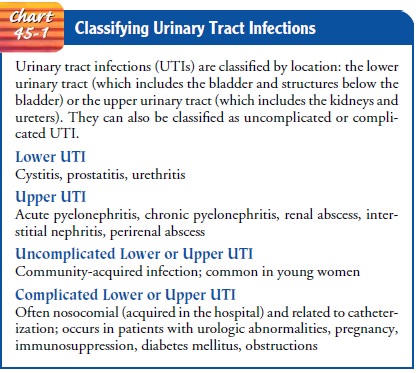
Lower
UTIs include bacterial cystitis
(inflammation of the uri-nary bladder), bacterial prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland), and bacterial urethritis (inflammation of the urethra).
There can be acute or chronic nonbacterial causes of inflammation in any of
these areas that can be misdiagnosed as bacterial in-fections. Upper UTIs are
much less common and include acute or chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis), interstitial nephritis (inflammation of
the kidney), and renal ab-scesses. Upper and lower UTIs are further classified
as uncom-plicated or complicated, depending on other patient-related conditions
(for example, whether the UTI is recurrent and the duration of the infection).
Most uncomplicated UTIs are community-acquired. Complicated UTIs usually occur
in people with urologic abnormalities or recent catheterization and are often
hospital-acquired. Bacteriuria and UTIs are more common in per-sons older than
65 years of age than in younger adults. Conser-vative estimates suggest that
20% to 25% of ambulatory women and 10% of men in this age group have
asymptomatic bacteriuria; the incidence rises to 50% in women over the age of
80 (Gomolin & McCue, 2000).
A UTI is one of the most common reasons patients seek health care. Most cases occur in women, with one of every five women in the United States developing a UTI sometime during her life-time. The urinary tract is the most common site of nosocomial infection, accounting for greater than 40% of the total number reported by hospitals and affecting about 600,000 patients each year.
In most of these
hospital-acquired UTIs, instrumentation of the urinary tract or catheterization
is the precipitating cause. More than 250,000 cases of acute pyelonephritis
occur in the United States each year, with 100,000 of these patients requiring
hospitalization. In general, 7 to 8 million UTIs are diagnosed in the United
States annually, representing an expenditure of about $1 billion in direct
heath care costs. This amount does not in-clude the indirect costs associated
with time lost from work and the negative impact on the individual’s lifestyle
(Foxman, 2002).
Related Topics