Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Urinary Disorders
Upper Urinary Tract Infection: Acute Pyelonephritis
UPPER
URINARY TRACT INFECTION:ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS
Pyelonephritis
is a bacterial infection of the renal pelvis, tubules, and interstitial tissue
of one or both kidneys. Upper UTIs are as-sociated with the antibody coating of
the bacteria in the urine. (This occurs in the renal medulla; when the bacteria
are excreted in the urine, the immunofluorescent test can detect the antibody
coating.) Bacteria reach the bladder by means of the urethra and ascend to the
kidney. Although the kidneys receive 20% to 25% of the cardiac output, bacteria
rarely reach the kidneys from the blood: fewer than 3% of cases are due to
hematogenous spread (Warren et al., 1999).
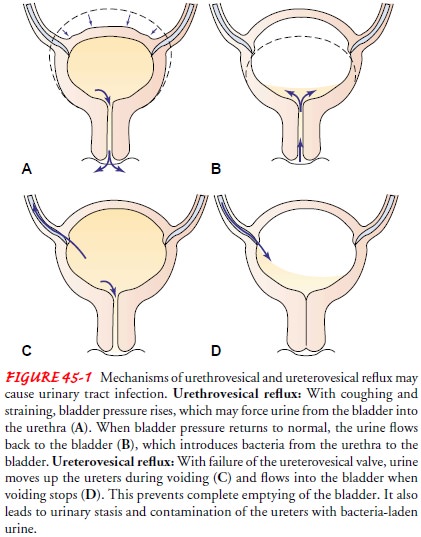
Pyelonephritis
is frequently secondary to ureterovesical reflux, in which an incompetent
ureterovesical valve allows the urine to back up (reflux) into the ureters (see
Fig. 45-1). Urinary tract ob-struction (which increases the susceptibility of
the kidneys to in-fection), bladder tumors, strictures, benign prostatic hyperplasia,
and urinary stones are some of the other causes. Pyelonephritis may be acute or
chronic.
Patients with acute pyelonephritis usually have enlarged kid-neys with interstitial infiltrations of inflammatory cells. Abscesses may be noted on the renal capsule and at the corticomedullary junction. Eventually, atrophy and destruction of tubules and the glomeruli may result. When pyelonephritis becomes chronic, the kidneys become scarred, contracted, and nonfunctioning.
Clinical Manifestations
The
patient with acute pyelonephritis appears acutely ill with chills and fever,
leukocytosis, bacteriuria and pyuria, flank pain, and CVA tenderness. In
addition, symptoms of lower urinary tract involvement, such as dysuria and
frequency, are common.
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings
An
ultrasound study or a CT scan may be performed to locate any obstruction in the
urinary tract. Relief of obstruction is essential to save the kidney from
destruction. An IVP is rarely indicated during acute pyelonephritis because
findings are normal in up to 75% of patients. Radionuclide imaging with gallium
citrate and indium-111 (In111)–labeled WBCs may be useful to identify sites of
infection that may not be visualized on CT scan or ultrasound. Urine culture
and sensitivity tests are performed to determine the causative organism so that
appropriate antimicrobial agents can be prescribed.
Medical Management
Patients
with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis are usually treated as outpatients if
they are not dehydrated, not experi-encing nausea or vomiting, and not showing
signs or symptoms of sepsis. In addition, they must be responsible and reliable
to ensure that all medications are taken as prescribed. Other pa-tients,
including all pregnant women, may be hospitalized for at least 2 or 3 days of
parenteral therapy. Oral agents may be substituted once the patient is afebrile
and showing clinical improvement.
PHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
For
outpatients, a 2-week course of antibiotics is recommended because renal
parenchymal disease is more difficult to eradicate than mucosal bladder
infections. Commonly prescribed agents include TMP-SMZ, ciprofloxacin,
gentamicin with or without ampicillin, or a third-generation cephalosporin
(Warren et al., 1999). These medications must be used with great caution if the
patient has renal or liver dysfunction.
A
possible problem in acute pyelonephritis treatment is a chronic or recurring
symptomless infection persisting for months or years. After the initial
antibiotic regimen, the patient may need antibiotic therapy for up to 6 weeks
if evidence of a relapse is seen. A follow-up urine culture is done 2 weeks
after completion of anti-biotic therapy to document clearing of the infection.
Related Topics