Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Urinary Disorders
Urinary Diversions
Urinary Diversions
Urinary
diversion procedures are performed to divert urine from the bladder to a new
exit site, usually through a surgically created opening (stoma) in the skin.
These procedures are primarily per-formed when a bladder tumor necessitates
removal of the entire bladder (cystectomy). Urinary diversion has also been
used in managing pelvic malignancy, birth defects, strictures, trauma to
ureters and urethra, neurogenic bladder, chronic infection caus-ing severe
ureteral and renal damage, and intractable interstitial cystitis and as a last
resort in managing incontinence.
Controversy
exists about the best method of establishing per-manent diversion of the
urinary tract. New techniques are fre-quently introduced in an effort to
improve patient outcomes and quality of life. The age of the patient, condition
of the bladder, body build, degree of obesity, degree of ureteral dilation,
status of renal function, and the patient’s learning ability and willingness to
participate in postoperative care are all taken into consideration when
determining the appropriate surgical procedure. Creating a reliable continence
mechanism for a continent reservoir is a great challenge. The ability of
urinary diversions to be continent devices for both ease of emptying and better
quality of life has been the focus of research during recent years (Abol-Enein
& Ghoneim, 2001; Deliveliotis, Alargoff, Skolarikos et al., 2001; Kane,
2000; Yachia & Erlich, 2001; Zinman, 1999).
The
extent to which the patient accepts urinary diversion de-pends to a large
degree on the location or position of the stoma, whether the drainage device
(pouch or bag) establishes a water-tight seal to the skin, and the patient’s
ability to manage the pouch and drainage apparatus. Paying attention to these
consid-erations helps to promote a positive outcome (Kane, 2000).
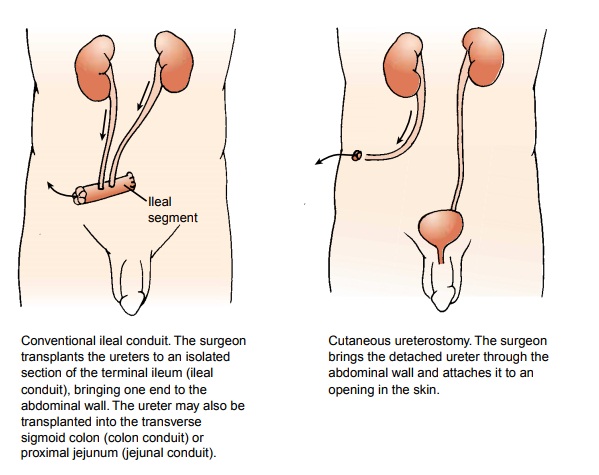
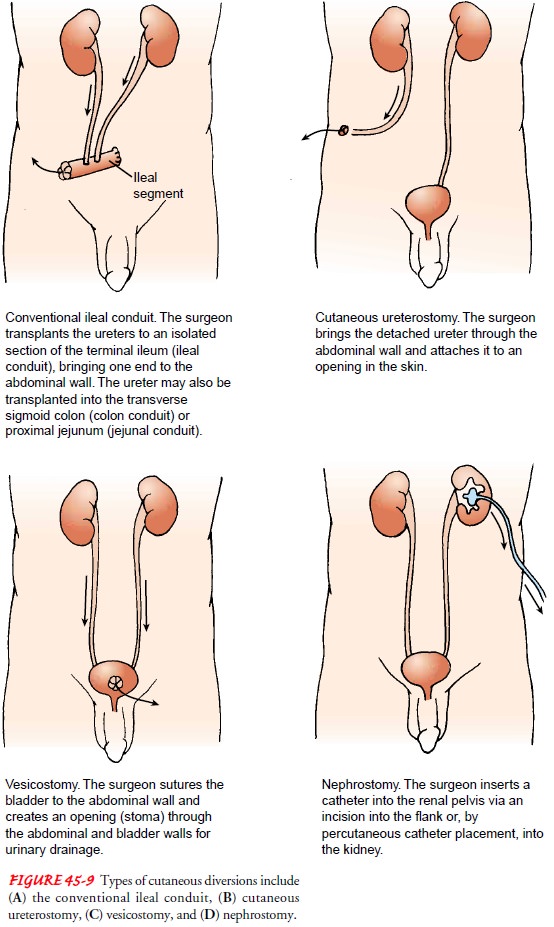
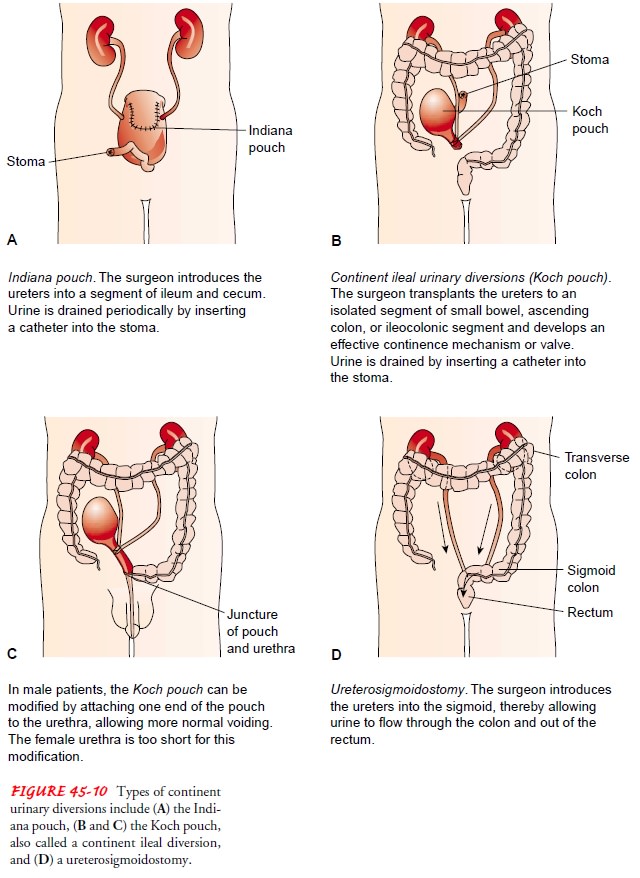
There
are two categories of urinary diversion: cutaneous uri-nary diversion, in which
urine drains through an opening created in the abdominal wall and skin (Fig.
45-9), and continent uri-nary diversion,
in which a portion of the intestine is used to cre-ate a new reservoir for
urine (Fig. 45-10).
Related Topics