Chapter: Case Study in Obstetrics and Gynaecology: General Gynaecology
Case Study Reports: Cervical Cancer
CERVICAL CANCER
History
A
28-year-old woman was referred to the colposcopy clinic because of intermenstrual and postcoital bleeding. On examination a macroscopically visible
lesion was present
and on colposcopy features of malignancy were
seen. Subsequent biopsy
showed invasive squa- mous carcinoma of the cervix.
The
woman was informed
of the diagnosis and as a result
went on to undergo an examin-
ation under anaesthetic, cystoscopy and
proctoscopy for staging. The mass was
found to be 3 cm in size and
there was no palpable extension into the uterus,
vagina or parametrial tissues. The cystoscopy and proctoscopy were both normal.
She
has had one child but had been hoping to have at least one more and is devastated by the diagnosis.
Question
What are the possible treatment options and
their potential complications?
ANSWER
Cervical cancer may be treated surgically or by radiotherapy. Staging is performed
clin- ically at examination under anaesthetic as described.
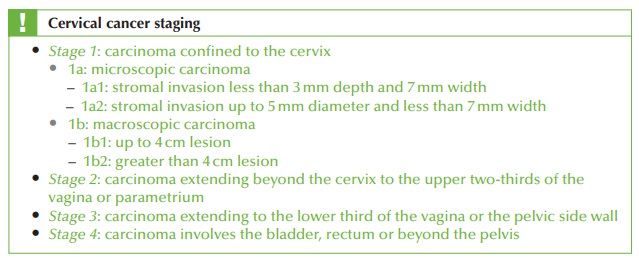
Radical hysterectomy
Up to stage 1b women may be treated
with radical hysterectomy (also known as Wertheim’s hysterectomy). This involves
removal of the uterus, cervix,
pelvic lymph nodes and parametrial tissue as well as the upper
third of the vagina. Complications involve bleeding and infection. Ureteric damage may
occur and blood
vessel injury is not uncom- mon. Postoperative complications include
infections of the chest, wound
or urinary tract as
well as venous
thromboembolism and later-onset lymphoedema from interruption of lymphatic drainage from the lower limbs.
The
advantage of this treatment is that it preserves ovarian
function, important for well-
being and prevention of osteoporosis. It also avoids the complications of radiotherapy outlined below.
Trachelectomy
This involves removal of the cervix,
lymph nodes and parametrial tissue with conserva- tion of the ovaries
and uterine body with insertion of a suture
(cerclage) at the base of the
uterus. It is used selectively for women with early stage
disease who wish to preserve
their fertility.
Radiotherapy
Disease beyond stage 1b, and postmenopausal women should be treated with radiotherapy
which is effective but is associated with long-term effects
of bowel stenosis,
cystitis and vaginal stenosis.
It also generally renders women menopausal due to radiation to the ovaries.
Related Topics
