Chapter: Case Study in Obstetrics and Gynaecology: General Obstetrics
Case Study Reports: Antenatal Care
ANTENATAL CARE
History
A
woman attends a routine antenatal appointment at 31 weeks’
gestation. She is 26 years old and this is her fourth
pregnancy. She has three children, all spontaneous vaginal
deliv- eries at term.
Her third child
is 18 months old and
the delivery was
complicated by a post-
partum haemorrhage (PPH)
requiring a 4 unit blood
transfusion. This pregnancy has been
uncomplicated to date,
with normal booking
blood tests, normal
11–14-week ultrasound and normal anomaly ultrasound scan.
She
feels generally tired and attributes this to caring for her three young children. She reports good fetal movements
(more than 10 per day).
Examination
Blood pressure is 126/73 mmHg.
Questions
·
What is the likely
diagnosis and what
are the implications for the pregnancy?
·
What further investigations would you wish to arrange?
·
How
will you manage this woman for the last trimester
of pregnancy?
ANSWER
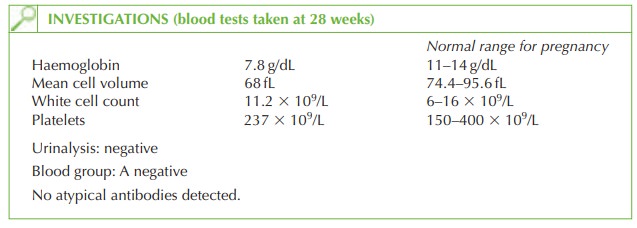
The
haemoglobin is significantly low even for pregnancy, and is associated with a low mean
cell volume. This is usually due to iron-deficiency anaemia. Iron deficiency anaemia usually
occurs when the woman enters pregnancy with depleted iron stores, although she may not at that stage have low
haemoglobin or any signs or symptoms
suggestive of anaemia.

At delivery, blood
loss is inevitable. This woman has
additional risk factors
of having her fourth delivery and having
a history of PPH. As she is already very
anaemic, she may decompensate easily if blood
loss occurs, increasing her likelihood of hypovolaemic shock and need for emergency blood transfusion.
Further investigations
Although the likely cause
of these indices
is iron deficiency, differential diagnoses include a mixed folate and iron deficiency, thalassaemia, chronic bleeding, or anaemia of chronic
disease (e.g. renal disease). A full history
should therefore be taken to exclude chronic
dis- eases and to elicit any family history
of thalassaemia.
Iron deficiency should be demonstrated with findings of low mean cell haemoglobin (MCH) and low serum ferritin. Ferritin below 12 μg/L confirms the diagnosis. Serum and red cell folate
should also be checked and the woman
should be screened
for haemoglobinopathies.
If
chronic disease is suspected, then
further investigations may
be indicated such
as renal and liver
function tests for
chronic disease, or gastrointestinal tract
endoscopy for causes of chronic bleeding.
Further management
Correction of anaemia
·
The
woman should be prescribed ferrous
sulphate 200 mg twice daily, increasing to three times if tolerated. If iron tablets
are not tolerated then alternatives include
iron suspension or parenteral (intramuscular) iron injections. These are
painful and do not increase the serum
haemoglobin more than the maximum expected from oral iron (1 g/dL per week).
·
In
extreme cases, where
it is not possible to increase the haemoglobin level
by iron supplementation, blood
transfusion should be considered.
·
An iron-rich diet should be encouraged.
Delivery
·
At
delivery, she should
be considered at high risk of PPH and have an intravenous cannula inserted
in labour, with full blood
count and group
and save.
·
Active management of the
third stage is essential (syntometrine, controlled cord
traction) and an oxytocin infusion
considered if bleeding
is excessive or the uterus
is suspected to be atonic.
·
Following delivery, the woman
should continue iron
supplementation until iron
stores (ferritin) are restored,
even if haemoglobin is normal.
Related Topics